Art-Trading, Connoisseurship and the Van Dyck Bonanza

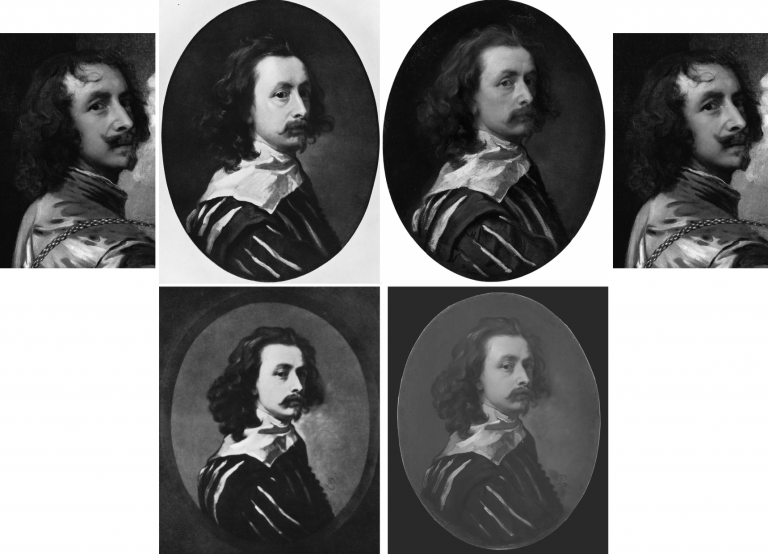
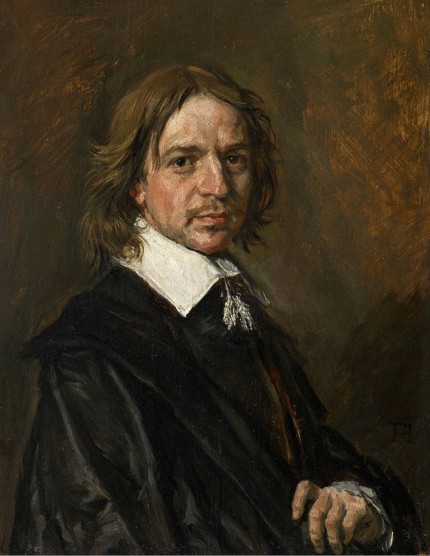
There are now two upgraded paintings in two museums that have been claimed as “The Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” and an upgraded third painting has been presented in a third museum as a lost, earlier Van Dyck self-portrait – see Fig. 1 below. This acceptance by three museums of three self-portraits in six years has coincided with a spate of exposed forgeries and restoration-led upgraded “discoveries”. The opaque means by which three problematic pictures found their separate ways into three museums as upgraded autograph Van Dycks are items of cultural/art-political concern.
This triple elevation has spotlighted levels of scholarship and transparency within the cross-linked spheres of connoisseurship, ownership, restoration, promotion and sales in the wake of the spectacular rise and demise of the now downgraded and disappeared $450m Leonardo School Salvator Mundi that had been bought for barely a thousand dollars and somehow netted nearly two thirds of a billion dollars through three sales in five years on an implausible provenance. The institutionally sensitive roles of upgraded old master paintings serving as conduits for financial exchanges and investment are attracting attention as never before. The Van Dyck bonanza has prompted public challenges on both the artistic status of the pictures being traded and the means and manner by which public and private monies pass hands.
THREE UPGRADED VAN DYCK SELF-PORTRAITS
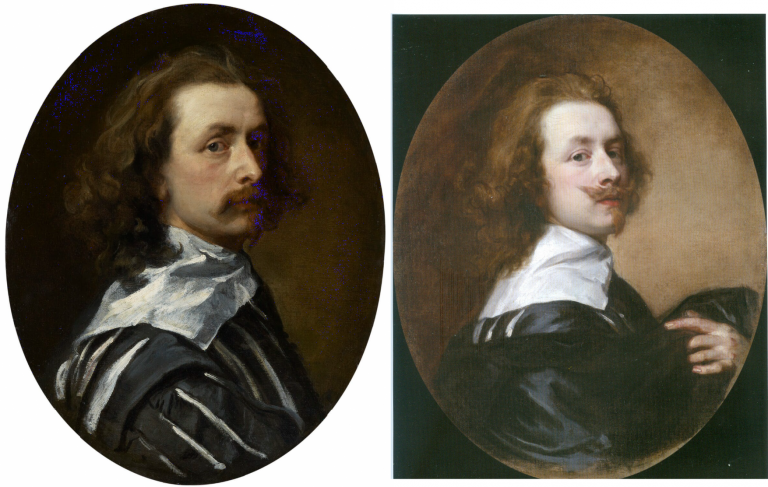
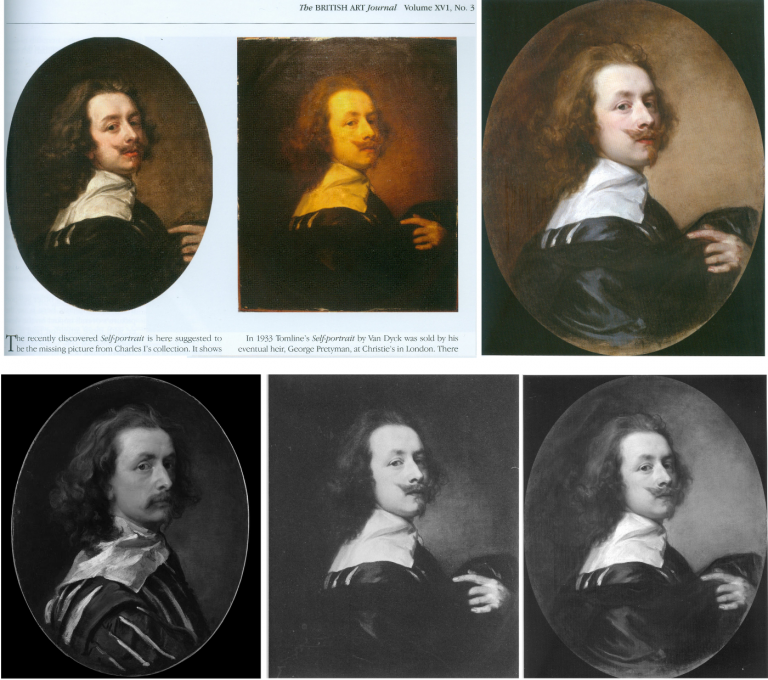
Above, Fig. 1: Left, the National Portrait Gallery’s “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”; centre, the new Bendor Grosvenor-accredited (and owned) “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”, as loaned to the Rubenshuis Museum, Antwerp; right, the Philip Mould/Grosvenor accredited, privately owned painting that has been loaned as an autograph Van Dyck self-portrait to the Minneapolis Institute of Arts, Minnesota.
All three of the above self-portraits changed hands recently as autograph Van Dyck self-portraits with the first two both now claimed to be the last Van Dyck self-portrait. All three have undergone modern or recent restorations. The two on the right were transformed within the last decade (and possibly by the same restorer). The picture on the left – an undeclared, covert upgrade – was bought by the National Portrait Gallery in 2014 for £10m.
Above, Fig. 2: Left, the “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” that was published in 1941 by Gustav Glück in The Burlington Magazine (“Reflections on Van Dyck’s early death”); right, the “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” that was sold to the National Portrait Gallery in 2014.
Above, Fig. 3: Left, the “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” as published by Glück in 1941; centre, the “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” as sold to the National Portrait Gallery in 2014; right the painting published by Glück in 1941 as a copy by Sir Peter Lely of the Glück claimed last Van Dyck self-portrait shown left, here.
Above, Fig. 4: Left, the painting published by Glück in 1941 as a copy by Sir Peter Lely of the then-claimed last Van Dyck self-portrait shown above left at Fig. 3; right, the painting published in 2011 as a copy by Sir Peter Lely of the then-claimed last Van Dyck self-portrait at Fig. 1, left, which was sold to the NPG in 2014.
MILLAR’S WARNINGS
The notoriously vexing challenge of identifying autograph Van Dycks was set out with frankness and high expertise by Sir Oliver Millar, a former Surveyor of the Queen’s Pictures, in his contribution to the 2004 catalogue raisonné Van Dyck – A Complete Catalogue of the Paintings, by Susan Barnes, Nora De Poorter, Oliver Millar and Horst Vey and published by the Paul Mellon Centre, London, the educational charity committed to supporting original research into the history of British art and architecture of all periods.
Covering Van Dyck’s last English period from 1632 to 1641, Millar listed 264 works and added an appendix of 37 works that comprise records of lost original paintings. Taken together they would average more than thirty-three paintings a year, including many double and very grand group portraits with brilliant elaborate costumes, accoutrements, settings, animals and part-landscapes but the work rate was even higher because of Van Dyck’s many and often long absences and periods of illness – he spent more than a year abroad in 1634-5 and suffered increasing pain in his painting hand. His employment of assistants caused some patrons to complain of work that was not autograph.
Millar assumed that Van Dyck had emulated the practices and “distribution of responsibilities as organised in Rubens’s studio” when setting up his own studio in London and he could hardly have spoken more bluntly of the artistic consequences of such production systems. A great deal of work “especially towards the end of his life”, he noted, “was assigned to Van Dyck’s assistants, and there was a heavy demand for repetitions, whether replicas, part replicas, variants or copies […] Sometimes Van Dyck would himself paint a new detail in a repetition otherwise painted entirely by an assistant”, whereas his “finest English portraits are painted…noticeably with a greater variety of touch.” A pronounced monotony of touch might itself, therefore, ring authorial alarms.
NEW EXPERTS ARE GROWING THE VAN DYCK MARKET
The art market correspondent, Colin Gleadell, restated the attribution problem in relation to current market expansionism, in the Telegraph (28 April 2018):
“Interestingly, Van Dyck has had more re-attributions than any other Old Master in recent times. Philip Mould, presenter of the BBC’s Fake or Fortune, traces this phenomenon to the publication of the first reliable catalogue raisonné in 2004, which allowed for detailed study of nearly 800 examples of the artist’s work.
“Of the catalogue’s four original scholars, only two are still alive, and a number of former museum directors have offered their views on attribution since. It’s differences in opinion that have allowed additional works to be added to the recognised Van Dyck corpus.
“Because Van Dyck was prolific and used studio assistants in his work, it can be tricky to unravel how much of a painting is solely by the master. Consequently, the number of works attributed to him, his studio and his many followers is plentiful. Around 300 have come up for auction in the last four years, with dozens subsequently upgraded with a full attribution.
“Taking some credit for the change in status was Mould’s researcher, Bendor Grosvenor, now a TV presenter in his own right and also a Van Dyck connoisseur, who has been quietly accumulating a small collection of discoveries of his own.
“But while Grosvenor prefers to keep his finds, his friend, Fergus Hall, is in the business of selling, his trained eye capable of recognising Van Dyck’s touch even through centuries of dirt, degraded varnish and additional paint. It is only after painstaking cleaning, though, that the full picture emerges…”
MAGICIANS ANNOINT SECOND-STRING WORKS
There exists an aggravating sub-phenomenon whereby venerable scholar/connoisseurs effectively acquire powers to elevate best available copies to autograph status. Some, like the late Sir Denis Mahon, have been known to elevate more than one such work to a single “vacancy”. (See “Art’s Toxic Assets and a Crisis of Connoisseurship”.) Occasional misattributions are inevitable (and correctable) in a field that necessarily rests on fine judgements, but wholesale upgrades risk diluting and adulterating oeuvres to the point of jeopardising market confidence. Risk is compounded when upgrades are products of prolonged restorations in which paint is subtracted and added to the surviving carcasses of pictures on singular, sometimes optimistic, readings of authorship.
BENDOR GROSVENOR’S ASSORTED CONTRIBUTIONS
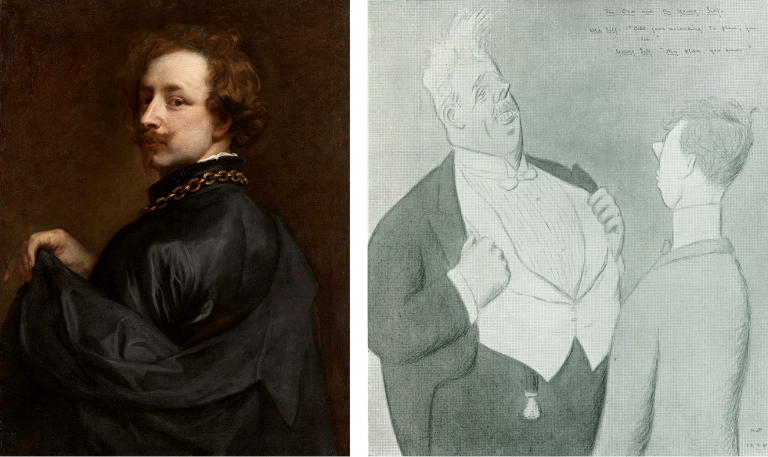
Above, Fig. 5: All six works above have been supported by Bendor Grosvenor.
The three recently and problematically upgraded Van Dyck self-portraits above left were all researched and espoused by Grosvenor. All three works on the right are manifest fakes. The Hals and the Gentileschi were initially accepted by Grosvenor and the “Raphael” attribution was made by him on television.
Respectively, the six are: left, the National Portrait Gallery’s “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”, as shown on the gallery’s 2015 celebratory book on the painting; second left, Grosvenor’s own and self-upgraded “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”, as loaned by him to the Rubenshuis Museum; third left, the privately owned, Grosvenor/Mould-attributed Van Dyck “Portrait of the Artist” that is now on loan to the Minneapolis Institute of Arts; third right, the now notorious “Frans Hals” (which Grosvenor, the Louvre Museum and a London dealer took to be authentic before Sotheby’s proved by technical analysis that it was a modern paints-riddled fake and fully refunded its buyer ); second right, the self-contained painted fragment of a figure that Grosvenor held to be part of a larger Raphael panel on his BBC4 Britain’s Lost Masterpieces programme (5 October 2016) with near-unequivocal support from the National Gallery’s then director, Sir Nicholas Penny. (The “Raphael” was subsequently rejected and deemed possibly 18th century by the National Gallery in August 2019 following lengthy examinations, but Grosvenor still insists that Raphael had painted this fragment of a “Madonna in a Cross-over Dress” even though it had been painted inside the edges of a piece of wood and therefore could never have been part of a full panel painting); right, the fake Orazio Gentileschi David and Goliath painted on a lapis lazuli slab and which had been exhibited as authentic at the National Gallery when loaned by an anonymous private collector who had bought it from the dealer who had sold on the fake Hals through Sotheby’s.
RESTORATION “SCIENCE” AND THE DETECTION OF AUTHENTICITY
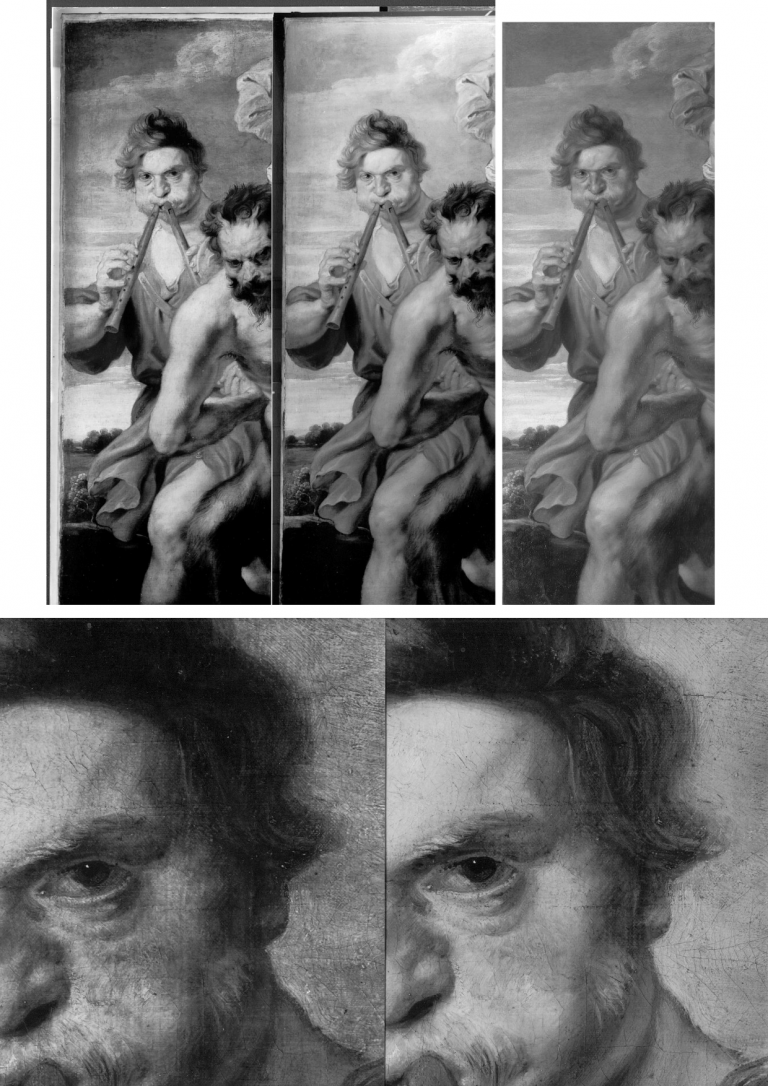
Even before Millar’s warnings, a non-art market exercise had confirmed the problem of identifying studio contributions in 1999 when, in the National Gallery’s Technical Bulletin, the restorer Larry Keith reported that a recent restoration of the Rubens studio work Drunken Silenus supported by Satyrs (Fig. 6 below) had “allowed the opportunity to consider the questions around its authorship and execution afresh in the context of a collaborative technical investigation with the scientific department”. Despite the gallery’s advanced scientific apparatuses and its staffs’ best efforts, it was recognised that “The very nature of the Rubens studio, with its streamlined production and group participation, meant that the painting techniques and materials were also largely uniform, which inevitably limits the ability of technical study to inform specific attributional problems.” In the absence of documentation and relying “heavily on traditional style-based Morellian connoisseurship” the gallery attributed the picture to Van Dyck on a traditional appraisal by eye.
Above, Fig. 6: Above, top left and centre, photographs of a part of the National Gallery’s Rubens studio work Drunken Silenus supported by Satyrs, showing the work before restoration (left), after restoration (centre) and (right) as digitally presented today; below, a detail of a face before and after restoration.
As seen above, the pre- and the post-restoration states are artistically different in their tonal values and relationships. We have examined the National Gallery’s dossiers on the painting and the gallery kindly supplied the two good, hard-copy directly comparative photographs above, top. Where Gleadell shared the sleeper hunters’ proclaimed view of restoration as a benign and “enabling” process, careful comparison of the above detail of a face and its relationship to the foil of a background/sky before and after a single restoration show the debilitating disruptions of values and relationships (relative values) that can occur during a single restoration. Given that what comes off first under restorers’ swabs is what went on last with the artist’s brush, and that highly successful painters like Rubens and Van Dyck often touched up and finished off works that had been largely executed by assistants, it is not hard to appreciate how such subtractions through cleaning followed by painted additions can aggravate difficulties of attribution.
MADE-OVER UPGRADES
The principal instrument in art market upgrades is a long, supposedly “diagnostic”, visually transforming restoration. With dramatically altered pictures, scholars can more easily be chivvied to endorse new and elevating ascriptions. Few restorations give rise to downgrades. Sleeper hunters invariably swear by the brilliance and moderation of their favourite restorers and impute scientific veracity to their methods. In naïve non-specialist circles like the BBC, there exists an unexamined conviction that because today’s technologies are more advanced than earlier ones, aesthetic judgements are now scientifically validated. For example, in short £540 weekend courses at the Royal Academy (with light refreshments, an evening reception and a certificate thrown in), Philip Mould’s former apprentice, Bendor Grosvenor, (who read modern – not art – history and now works as a BBC television arts programme maker, art history blogger, occasional journalist, auction house director, a self-declared ex-dealer collector and, most recently, a picture restorer – see below), promises that “The theory and history of connoisseurship will also be explored, along with the latest scientific techniques for assessing attribution”.
There are no such techniques – science cannot appraise authorship. No matter how technically sophisticated “non-invasive” images might be, they still need to be read for significance. While the “scientific” technical analysis of pictures’ material components can readily disqualify attributed old master works that have been liberally constructed with modern materials, there are no scientific means of assessing authorship, per se.
VISUAL APPRAISALS
Painters make pictures by eye to be viewed by eye and appraisals must also be made by eye, as the National Gallery recognised with its Rubens school picture. When Berenson praised the “seeing eye” and “active not passive eyes” he meant eyes employed “with all the faculties co-operating” but in so-saying he spoke a (self-confessed) part-truth: “As a consumer of the art product I have the right to do all that. As I am neither figure artist nor architect, nor musician, I have no certain right to speak of the producer. I am in the position of most critics, philosophers and scholars. We have enjoyed experiencing the creative process in the art of words only with the logical result that writers on art seldom have in mind any of the arts except the verbal ones.”
Faculties, however refined and words however eloquent, are not the whole story. Too often overlooked is the extent to which for art-practitioners (artists) the powers of the eye are drilled into being both constructive and critical through the marriage of looking and doing that comprises artistic practice. Strictly speaking, that sequence should read: thinking, looking; doing; appraising; looking… Those who see-through-doing are best placed to recognise what counts as undoing and redoing in art. Best-placed but holding no monopoly – Millar fully recognised that restoration alterations handicap appraisals: “…the treatment it may have undergone in the past may also make it impossible to be entirely confident about its quality”. In this regard and for good reasons auctioneers place high premiums on little- or never-restored pictures.
TWO PUBLICATIONS FOUR YEARS APART AND TWO OVERLAPPING CAMPAIGNS OF ATTRIBUTION
Above, Fig.7: Top, left, the 80 pp full colour catalogue FINDING VAN DYCK , pub. PHILIP MOULD LTD, June/July 2011; top right, the Winter 2015/16 British Art Journal, which carried Bendor Grosvenor’s article “A Self-portrait by Sir Anthony van Dyck (1599-1641) from the collection of Charles I”; above, left, the £10m National Portrait Gallery “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”; above, right, the Grosvenor-owned, Rubenshuis Museum exhibited, “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”.
SHARED EXCITEMENTS, RISKS, AND AVOIDANCE OF SIN
In 2011 Grosvenor, then an employee of the Philip Mould gallery, lauded the gallery’s (and later the National Portrait Gallery’s) “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” picture in the FINDING VAN DYCK catalogue shown above, top left:
“Our first exhibit, Cat. 1, is Van Dyck’s last self-portrait. It was acquired by this gallery in partnership with Dr Alfred Bader in December 2009 for £8.3m at Sotheby’s in London, a record for the artist at auction. Self-portraits tend to stand out among a painter’s oeuvre as some of their most compelling works, and as an instructive connoisseurial guide in what an unquestionably genuine and pre-eminent Van Dyck looks like, Cat. 1 takes some beating.” (Emphases added.)
As fulsome advocacy the entry itself takes some beating. The FINDING VAN DYCK exhibition celebrated recently claimed works of or after Van Dyck and it constituted the high-water mark of Van Dyck sleeper-hunting at Philip Mould Ltd which became Philip Mould and Co. from which Grosvenor would depart in 2014 with a (rumoured) £1m settlement. Grosvenor seemed unaware that the Cat. 1 picture, then unsold after eighteen months in the Mould gallery, was a recent upgrade made by stealth and without due scholarly interrogation – see below.
The catalogue bore the gnomic dedication “For Dr Alfred Bader CBE. A distinguished progenitor of adventure in old masters”. Bader, an industrialist, philanthropist as well as an “inveterate collector”, as he once put it, died in December 2018 but he had been a key player in the Mould gallery’s acquisition of the “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” and its subsequent sale to the NPG. Bader and Mould seemed not to – but should – have appreciated how recently the painting had been upgraded. The NPG might not have been aware when buying the £10m painting as Van Dyck’s Last Self-Portrait that it was one of three Van Dyck self-portraits then being processed by the Mould gallery, one of which would shortly be presented as being both the true Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait and one with a better provenance, to boot.
LOVE IS ALL YOU NEED
In the catalogue’s foreword, Mould held that “every time a work of art is bought for reasons of love it is a discovery of sorts, albeit of a personal regard or strong emotional connection that has been visually crystallised” and that by “getting to know the signature strokes and habits of a great master, the characteristics of age, restoration and degradation, the [professional sleeper-hunter’s] eye becomes attuned, and even though there may not be many others around who can see it as you do, it can appear little short of sinful not to express the excitement of it all.” A note of anxiety crept into the self-exultation: the exercise of discovering, proclaiming, and selling lost masterpieces “involves excavation, science, observation and research – as well as a fair degree of sometimes hair-raising financial risk”. The precise burdens of risk and divisions of ownership are rarely disclosed.
WHO FUNDS ATTRIBUTION UPGRADES?
Clarity on ownership is occasionally achieved in the courts. Recent London Court of Appeal proceedings revealed that the fake Frans Hals (Figs. 5 and 9) had been bought jointly by a London-based dealer, Mark Weiss Gallery in Paris, and an investment company, Fairlight Art Ventures, for €3m in 2010 from the prime suspect in a French criminal investigation into a huge group of suspected fake Old Masters. The painting was sold in 2011 by private treaty through Sotheby’s (on a 5% commission) to the Seattle collector Richard Hedreen, for $10.75m. Weiss and Fairlight were shown to have taken an equal share of the benefit. See “’The law has to fall on someone’: Seller of allegedly fake Frans Hals must pay Sotheby’s $5.3m for cancelled sale, judge insists”, The Art Newspaper, 29 November 2020.
After discovering the fraud, reimbursing the buyer, and establishing a technical analysis department, Sotheby’s pursued the dealer, who settled first, and the investment company in protracted legal actions which were only resolved last November. In 2013 the now disappeared and Louvre Museum de-attributed $450m Leonardo School Salvator Mundi was sold by a consortium of New York dealers through Sotheby’s in a private treaty sale. The immediate flipping of the picture from $80m into $127m to a Russian oligarch triggered still-running legal proceedings. The London Court of Appeal held that at the time of the Hals sale there was “no general accepted view of the authenticity” of a “newly discovered painting which had no proper provenance, had not been published and had never been in an exhibition”.
NO FAKE-BUSTER, THIS ATTRIBUTION-MAKER
On 21 March 2016 Grosvenor reported that the London art dealer Mark Weiss had bought and sold-on the fake Orazio Gentileschi that deceived the National Gallery (Figs. 5 & 9). He also provided a (now inactive) link to Weiss’s catalogue note on the Gentileschi and asked: “Is the Gentileschi genuine? I suspect it is, but again I’m not a Gentileschi expert, and nor am I much good with late 17th Century Italian art anyway. My conviction about the painting, such as it is, must be led in part by the fact that greater minds and eyes than mine (not least at the National Gallery) have declared the picture not only period, but genuine… My best guess at this stage, working mainly from photos, is that these pictures are not all fakes.” In truth photographs should have sufficed and would have saved time expense and error. Grosvenor later wrote: “For what it’s worth, I believe it is a forgery. But it took me a long time, and a flight to Berlin to see an undisputed original Gentileschi for comparison, to figure it out.”
Unlike Berenson, Grosvenor has evident difficulty reading photographic testimony: he spent decades believing that critics of the Sistine Capel ceiling restoration were “myopic” until a trip to Rome and sight of the chapel itself disabused him. But how so? What is left on the ceiling is still Michelangelo, and retains its magnificent – abeit less sculpturally enhanced – designs. Today, the restoration injuries can only be identified by recollection of how it once was or, less subjectively, through comparative photo-records of its pre- and post-cleaning states.
Richard Feigen, a New York Old Master art dealer and the author of Tales from the Art Crypt, called the recent fakes affair “one of the biggest scandals in my memory”, and one which should make institutions “very wary about things they are offered and the sources of those things”. Grosvenor reportedly expressed a sneaking admiration for the Moriarty of the Old Masters: “Whoever has been making them is an artist of extraordinary skill. Equally skilful is the ability to age these modern creations in such a way as to make them look centuries old. Sadly, we don’t yet know who this genius is.”
Above, Fig. 8: Patrick Chappatte’s 2017 take on the Salvator Mundi sale/attribution for the New York Times.
On 16 November 2017 Grosvenor responded immediately to the auction of the then attributed Leonardo Salvator Mundi on his Art History News website:
“…Christie’s just did something that re-writes the history of auctioneering. They took a big gamble with their brand, their strategy to sell the picture, and not to mention the reputations of their leadership team, and they pulled it off. They marketed the picture brilliantly – the best piece of art marketing I’ve ever seen… AHN congratulates them all… I was sure the picture would sell, but never imagined it would make this much… We must all now wonder where the picture is going to end up next… Will the sale prompt people to now look anew at Old Masters? Maybe. It will surely end for good now the tired clicheé [sic] that the Old Master market is dead.”
Feigen, who had been offered the “Cranach”, passed on it, and reportedly noted: “We’ve got to know the background and provenance of each object, and be more demanding for sources.”
PHOTO-TESTIMONY AND “ESSENTIAL JUXTAPOSITIONS”
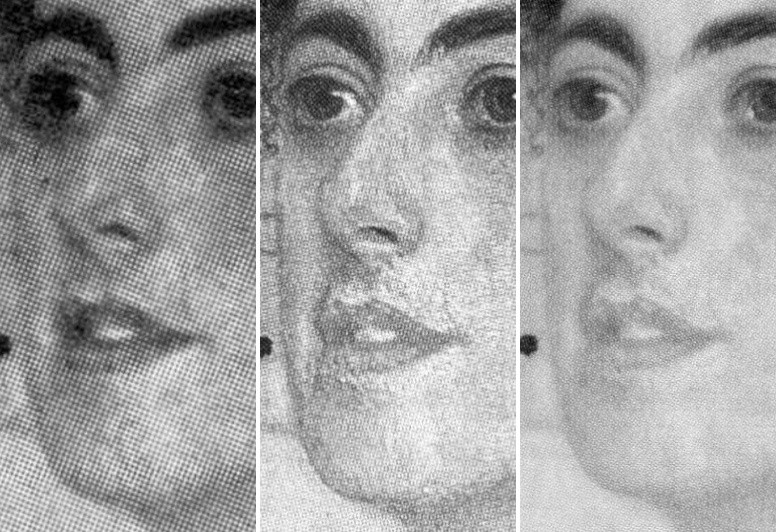
Above, Fig. 9: Here, left, we see the real Orazio Gentileschi David and Goliath (in the Galleria Spada, Rome) and, right, the loaned fake accepted as authentic by the National Gallery. Bottom right corner, the face of the fake Frans Hals portrait.
If, instead of whatever technical and art historical examinations were carried out, the National Gallery had run a few simple photo-comparison checks, as above at Fig. 9, it would have been apparent that the bona fide picture on the left had served as the model for the markedly inferior modern-looking version on the right. Had the fake Hals also been brought into comparison, as above, it would have disclosed a common authorial fondness – in two ostensibly historically disparate pictures – for arbitrary superimposed streaky white smears on the faces. In many respects, photo-comparisons are more helpful to appraisals than ones made from present and recollected pictures. First, there is a chronic logistical problem that Millar put well in 2004:
“…Although in tackling this particular problem it is more than ever essential to see the works in the original, it is difficult to compare works which are closely related but hundreds of miles apart, if not in different hemispheres. In spite of the legendary kindness of their owners these pictures often hang in inaccessible positions and never in ‘museum conditions’. Essential juxtapositions can hardly ever be made. The present state of the picture and the treatment it may have undergone in the past may also make it impossible to be entirely confident about its quality…”
Millar’s alertness to restoration-induced deformations may have been more evident in private than in public: in a letter held in a dossier at the Royal Collection he complained angrily of damage done to a Vermeer. As for his recognition of the need to effect ideal juxtapositions for comparative purposes, today’s sleeper-hunters might heed artists’ examples: when drawing or painting from nature they invariably align their sheet or canvas as closely as possible to their view of the subject, so that their eyes can either flick continuously upwards and downwards or sideways and thereby maintain a stream of direct visual comparisons between the subject and its evolving depiction. Such vital visual comparisons cannot be achieved with pictures in different locations and restorations can only be judged by before- and after treatment photo-comparisons because pre-restoration states disappear in restoration.
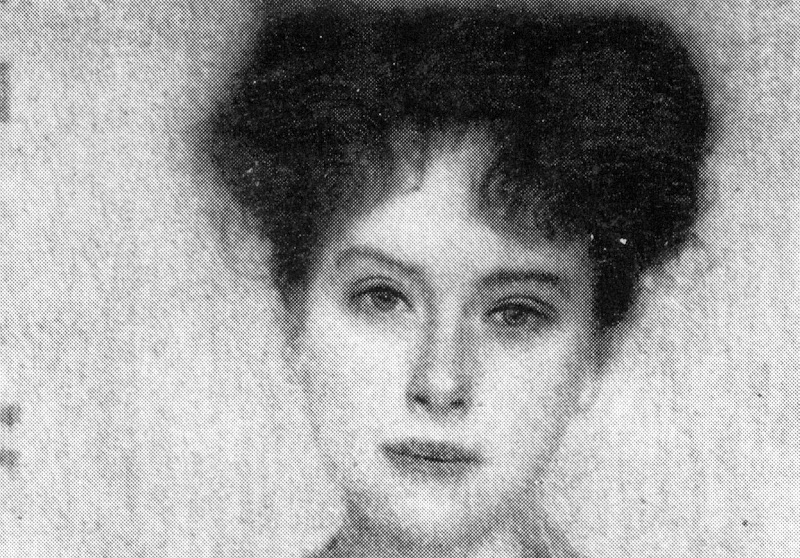
THE TWO PRETENDERS?
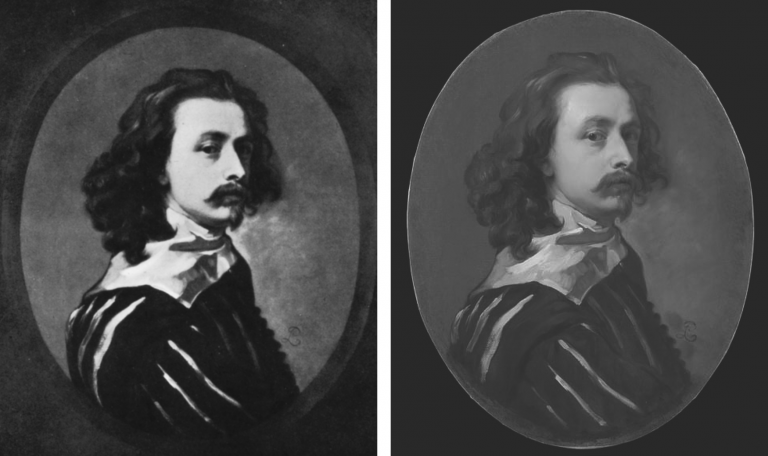
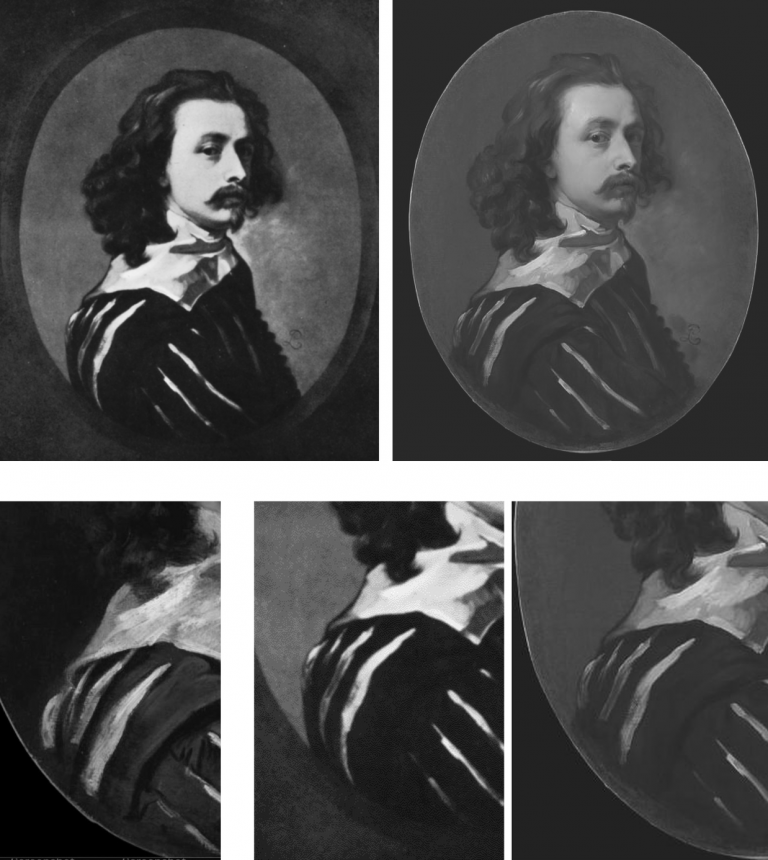
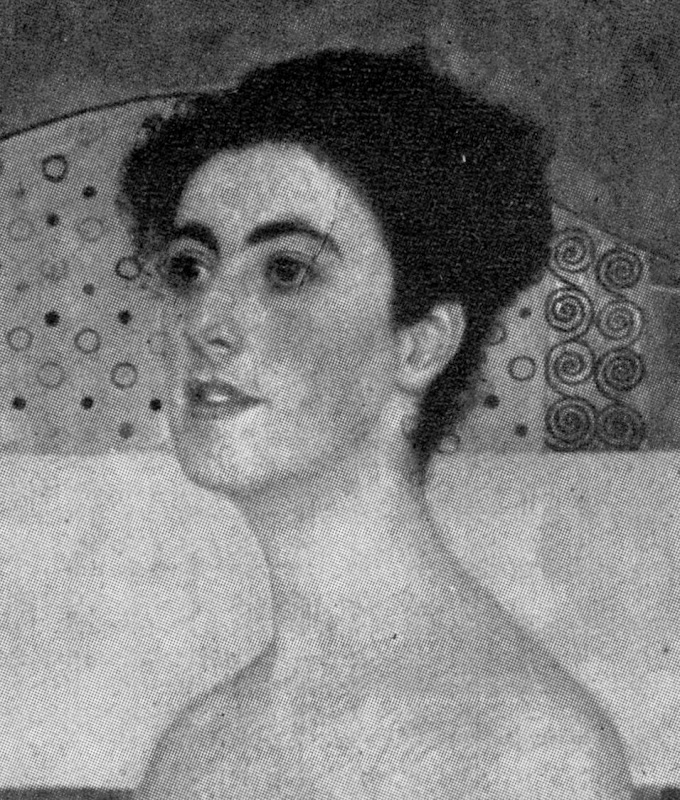
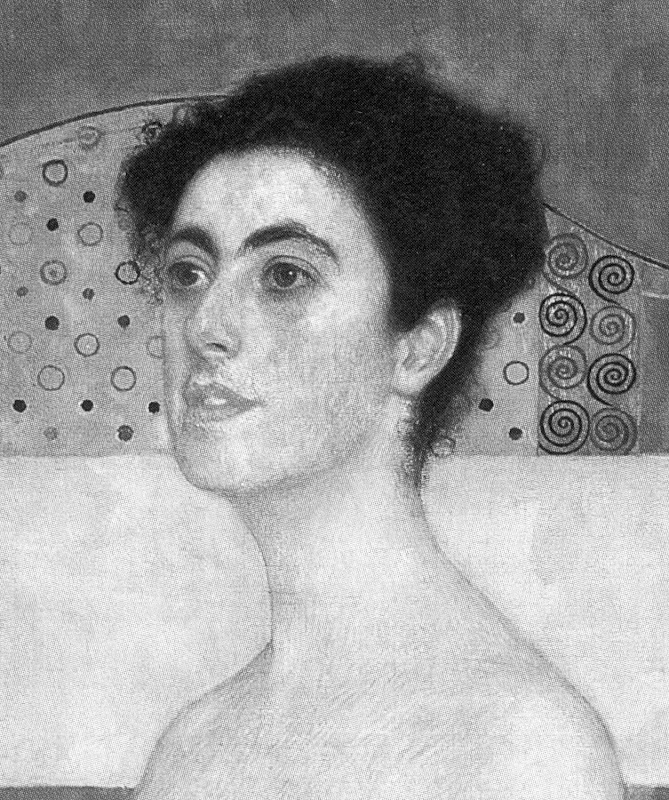
Above, Fig. 10: Left, the NPG “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”; right, the newly-restored, red-lipped and Grosvenor-accredited (and owned) “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”, as loaned to the Rubenshuis Museum, Antwerp.
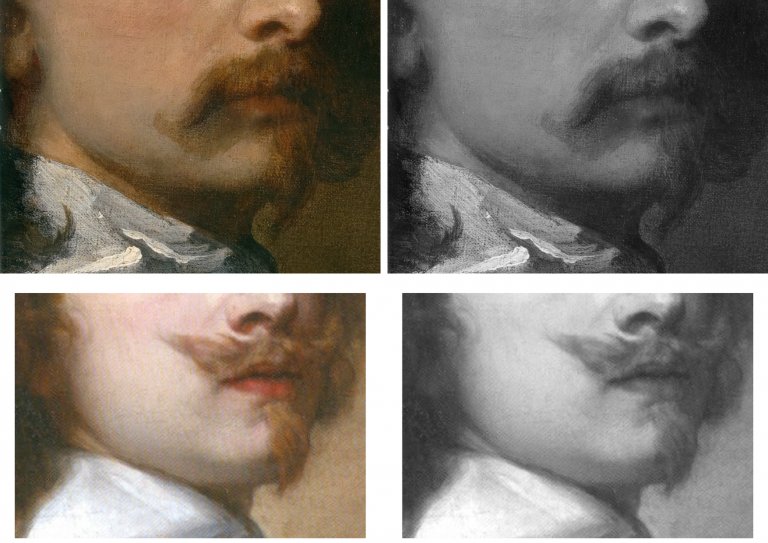
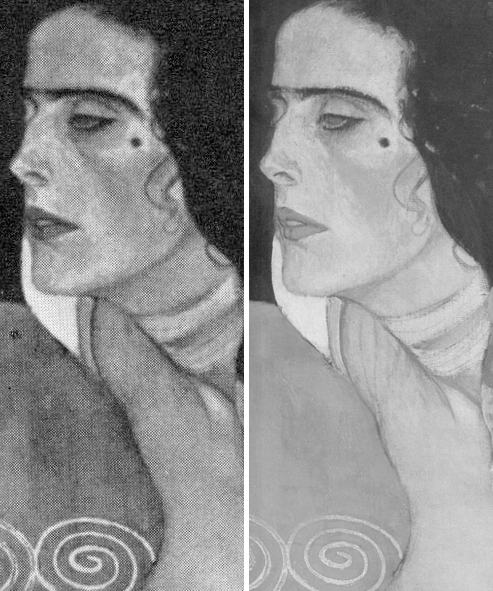
When Grosvenor was about to unleash his own “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” in 2015 (above right), the NPG’s formerly “unquestionably genuine, pre-eminent, Van Dyck” £10m world-record price “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” (above left) constituted an intrinsic threat: any closely attentive aesthetic appraisal and comparison of the now two rival supposed last self-portraits risked injury to the standing of one or the other. Although many other unresolved problems were attached to Grosvenor’s newly upgraded work (see below), it can sometimes seem that nothing ever counts against an on-the-market potential upgrade – as with the evident discounting of the NPG picture’s utterly out-of-character, out-of-period, anomalous droopy Mexican Bandit-style moustache seen above and below.
Above, Fig. 11: Top, detail of the National Portrait Gallery “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”; above, detail of the 2015 rosy-lipped Grosvenor-proposed “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”.
THE ANOMALOUS MOUSTACHE PROBLEM, PART I: GROSVENOR
Grosvenor has proposed that the NPG picture was a study for his own picture despite their numerous differences (see below). The most inexplicable difference is found in the two pictures’ moustaches, one of which is swept up, the other down. This divergence is presented with some ingenuity as a purposive species of social semaphore. Thus, within the NPG picture, which Grosvenor has reassigned to the role of a “study…[a] first attempt at the creation of a new type of self-portrait”, the moustache droops, where, in his own picture, the “moustache is raised, allowing not only for a more formal look perhaps appropriate to court appearance…” but also to illustrate the “difference between Van Dyck’s public and private faces…” Are we to understand, on the sole testimony of this (covertly upgraded) picture, that Van Dyck brushed his moustache down when going about his house and studio and brushed it up to attention whenever he thought he might be being observed?
While prompting incredulity, such a notion also defies artistic logic: given that works of art are made to a purpose within an artist’s practice, how can the same work be held a magnificent, self-sufficient masterpiece one minute and, in the next, to have been a study for another work of a different composition that would present a different aspect of the artist’s self-image to the world? In 2011 Grosvenor held that “the care and finesse of the brushwork in the face [of the NPG picture] is particularly assured” and that the whole was finished off with “more delicate and transparent glazes”. If Van Dyck really had been rehearsing the frigidly swanky public self-display found in Grosvenor’s painting, why would he have produced a highly resolved head which is not cocked back; where the artist does not look down his nose at the viewer; where he does not sport a cloak; where he does not hold a hand to his breast; or, even, where he does not wear a plausible collar that emerges from within his doublet?
THE ANOMALOUS MOUSTACHE PROBLEM, PART II: GLÜCK
Curiously, the problem of accounting for a rogue occurence within the oeuvre was not a new one. In 1941 Gustav Glück had addressed the same problem when he proposed yet another “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” version [*] to be Van Dyck’s last self-portrait (as at Figs. 2 and 3 above and 12 below). Describing his Self-portrait (which he had discovered a few years earlier “in a London private collection”) as a much more realistic and therefore interesting version than the Duke of Westminster’s sunflower self-portrait (then regarded as the last), Glück held it to constitute “authoritative evidence of the master’s appearance a short time before his death”, with features “still energetic and expressive, though lean and almost emaciated” – as at Fig. 12 below. The face looked, he felt, almost “spiritualised, and the melancholy character of the expression is enhanced by the ends of the moustaches being turned down instead of showing the upward twist they have in all of Van Dyck’s portraits”. No doubt yet other rationalisations could be made for this unique depiction.
[* We thus encounter two pairs of pictures, each comprised of a supposed Last Van Dyck Self-portrait and a supposed Lely copy of itself. In pressing his two discoveries, Glück acknowledged that “As is the case with most of Van Dyck’s works, several replicas and copies are known of this Self-portrait.” He recalls seeing the [later Mould/Bader/NPG] version and a head and collar copy (“near Matlock”) and a miniature. In 2011, Grosvenor, in contrast, simply accepted the then Mould/Bader picture as an indisputable autograph Van Dyck masterpiece on the authority of Sotheby’s (misleading) provenance and, perhaps, on the strength of it having recently been bought as such for the world record £8.3m by his employer and an investor.
Conspicuously, Grosvenor did not engage with Millar’s estimation of the picture – “The best surviving version of (probably) the last Self-portrait”. Instead, he gushes over the then-loaned privately-owned supposed Lely copy shown at Figs. 4, 12 and 13, as an “exceptionally good copy of a Van Dyck” which “must show that Lely had owned Cat. 1” – the then Mould/Bader picture. But why “must show?” when, as he further reports, the picture’s owners had “contacted us to say that they had a copy of our painting ascribed to Sir Peter Lely, but doubted by some to be by him…the monogram ‘PL’ was not of a type usually seen on Lely’s English portraits, and was thought to be false.” Grosvenor continued “We were immediately interested in researching Cat.4 further, for if it was indeed owned by Lely, it would help confirm that Lely owned Van Dyck’s last self-portrait, a theory much speculated on but unproven.”]
MOVEABLE FEASTS: THE NEW LAST VAN DYCK SELF-PORTRAIT
Above, Fig. 12: Top, left and top right, a detail of Van Dyck’s post-1633 Portrait of the Artist with a Sunflower; second left, the 1941 Glück-claimed “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”; third left, the National Portrait Gallery “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”. Above, left, a detail of the 1941 Glück-claimed Sir Peter Lely copy of the above claimed Van Dyck self-portrait; right, the Mould/Bader-claimed Sir Peter Lely copy of the NPG self-portrait (as published in the 2011 Mould gallery exhibition and catalogue as Cat.4).
In defence of his own Rubenshuis Museum-loaned “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” (above, Fig. 10, right), Grosvenor cheekily suggested “the dating of the National Portrait Gallery picture, currently thought to be c.1640 may need to be reconsidered, to perhaps between c.1637-39.” But why so – and on what stylistic basis is such chronological fine-tuning estimated? Not only had the NPG picture’s properties, appearance and relationship to other pictures not changed, only four years earlier Grosvenor had endorsed its late dating by “most scholars” to about 1640-1 – and on that late estimation he, like Glück (on another picture), had perceived a “faint air of melancholy” that added poignancy amidst the origins of the civil war about to erupt in London when the artist was “all the while plagued by the ill health that would shortly cause his death.”
It might seem that such recent perceptions notwithstanding, the NPG picture’s previous dating and estimation had to be jettisoned because Grosvenor was now seeking to attach his own painting to a “vacant” entry for a Van Dyck oval self-portrait, painted to the shoulders and with a hand to the breast, in an inventory of Charles I’s collection. If successfully attached, that entry would constitute a provenance jewel beyond price. But, most awkwardly, the original long-missing self-portrait had been recorded in the collection between 1637-39 and, therefore, Grosvenor’s newly upgraded candidate picture could not be said to have post-dated 1639. However, if so dated, and if the NPG picture were to be left in place at c.1640-1, the latter, with its pronounced differences from Grosvenor’s picture, would not only invite potentially damaging qualitative comparisons, it would retain the prized romantic cache on which it had been heavily promoted as Van Dyck’s last and most “modern” personal free-flowing etc., etc. depiction of himself.
Thus, and seemingly as if in protection of his own picture/investment, Grosvenor contended that the NPG picture, may no longer be considered the magnificent self-sufficient masterpiece that had commanded £1.7m on top of its world record £8.3m when sold to the NPG, and must now be moved back in time so as to do fresh duty as a study for his own picture – and therefore to predate his own picture which would become the new “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”, albeit at a somewhat earlier dating.
Although Millar had judged Grosvenor’s picture to be a copy of the lost picture that had been recorded in the Charles I collection, Grosvenor’s redating manoeuvre may have intimidated the NPG. Where it had held in its 2015 celebratory book Van Dyck – The Last Self-Portrait, that “Van Dyck’s self-portrait, now in the collection of the National Portrait Gallery… is probably the last and arguably the finest…” it now claims only that its picture is “one of three known self-portraits painted by van Dyck when he was in England, and it probably dates from the last years of his life”.
GROWING THE PROVENANCE
As seen, where Sotheby’s had claimed only that the [NPG] picture was “Possibly in the collection of Sir Peter Lely, d. 1680” and “possibly” in the 18th April 1682 sale of Lely’s estate, Grosvenor held in the 2011 FINDING VAN DYCK catalogue that his Cat. 4 (supposed) Sir Peter Lely copy of the NPG picture, “must therefore confirm that Lely owned [the then Mould/Bader picture and later NPG picture] and that it was sold from his [Lely’s estate] sale in 1682.” Again, why must it so confirm when the justification was especially feeble: “It is quite possible the self-portrait in Van Dyck’s possession at his death in 1641 was his last […] and that it passed into Lely’s possession at some point…Lely may have acquired it in a number of ways…Or, it may be that the painter and art dealer George Geldorp, for whom Lely worked when he first to came to London, was involved…” (Emphases added.)
In other words, Grosvenor had not added an atom of evidence that Lely had owned and copied the now NPG picture. He had not established when Lely first came to London or whether he had ever met Van Dyck: “Frustratingly, we do not know exactly when Lely first arrived in England, and [or?] the extent to which he knew of Van Dyck or knew of his estate. His early biographer Richard Graham, writing in 1695, said that Lely came over in 1641 (the year of Van Dyck’s death), whilst the art historian Arnoult Houbraken gives a date of 1643. It is perhaps most likely that the ambitious young Lely came to London in response to Van Dyck’s death thus ruling out any possible direct connection.” (Emphases added.) Nothing learned, no value added.
Not only had Grosvenor produced no evidence, he had disclosed in 2011 that the self-portrait in Van Dyck’s estate had not been rated highly by the artist’s contemporaries; and, that while the then Mould/Bader picture “now holds the world record for a work by Van Dyck” the painting in Van Dyck’s estate “had little value placed upon it” – to be precise, it was valued at 6s 8d, a fifteenth of a Van Dyck of Charles I in armour, and a sixtieth of Titian’s Perseus and Andromeda now in the Wallace Collection.
“IT IS, IF I SAY SO”
Lacking evidence that Lely had owned and copied the Bader/Mould self-portrait, Grosvenor, too, betrayed a note of anxiety in the 2011 catalogue: “The pictures after Van Dyck demonstrate that for the Van Dyck hunter the quantity and sometimes the quality of such copies can present potential danger.” In the absence of documentary evidence, Grosvenor played a bold card by appealing to the authority of his own eye: “…the first and most important skill you need to find a Van Dyck is simply the ability to spot a painting of the highest quality. If a painting is truly exceptional, the chances are it is by a truly exceptional artist.” Chance might be a fine thing, but its prospect is not a proof or a demonstration in the here and now.
THE SUPPOSED LELY COPIES OF THE SUPPOSED LAST VAN DYCK SELF-PORTRAITS
Above, Fig. 13: Top left, the attributed Sir Peter Lely copy, as published in 1941 by Glück; top right, the supposed Sir Peter Lely copy of the NPG self-portrait, as published in the 2011 Mould gallery exhibition catalogue. Above, details of costume from, respectively: the NPG self-portrait; the 1941 Glück-attributed Lely copy; the 2011 Mould/Grosvenor attributed Lely copy of the NPG picture.
Which of the two above versions is the more plausible Lely copy? Where is the Glück version today? Had it fallen by the wayside, much as had his 1934 espousal of what is now the Grosvenor/Rubenshuis last self-portrait (see below)? When did the Grosvenor/Mould-endorsed version of a supposed Lely copy first appear? Was it anywhere recorded before being taken to the Mould gallery? Do early photographs of it exist showing its reported appearance when enlarged onto a rectangular canvas? Did either of the canvases carry any historic material? Who owns it today?
It is said that when this unsettling mystery painting was brought to the Mould Gallery in 2010 shortly after the much-publicised acquisition of the £8.3m Sotheby’s self-portrait, it was “quite dirty and masked by a thick and substantially discoloured varnish.” The cleaning and researching were carried out by the Mould Gallery. Grosvenor claimed they had confirmed Lely’s authorship on the following grounds: [1] that after cleaning and restoration “there is no reason to doubt” it; [2] that “it is in fact by Lely”; and [3] that this is “a rare example of him copying another artist’s work”. The third claim weighed against it being a copy by Lely. The first statement was bluster – “there is no reason to doubt it”. The second contention was a non sequitur – Grosvenor asserted as fact something which had not been established.
SPOT THE DIFFERENCES
Grosvenor declined to address the discrepancies between the supposed Lely copy that had presented itself through an unidentified party to the Mould gallery from nowhere in 2010 or early 2011, and the supposed self-same Lely copy picture that had been published in December 1941 by Gustav Glück in The Burlington Magazine, “Reflections on Van Dyck’s early death” pp 172, 193, 195 and 199 (Fig. 12 above). There is a clear problem here: there are now two rival supposed versions of Van Dyck’s last self-portrait and each has its own supposed copy by Lely. Both pairs cannot be right. Where are the Glück ascribed pictures today? Have they been dismissed? Have they ever been compared with the two published Mould/Bader pictures?
A COVERT UPGRADE
In 2004, the now NPG picture had been described by Millar as:
“the best surviving version of (probably) the last Self-portrait, painted towards the end of Van Dyck’s years in London. The face is delicately modelled. The costume is handled very swiftly and in rough dry paint. There are some alterations made in the painting and it may be partly unfinished.”
In 2009 when included in the Tate’s “Van Dyck in Britain” exhibition, it was described in the catalogue on the (misleading) cited authority of Millar, as “thought to be Van Dyck’s last self-portrait”. Having died in 2007, Millar could not demur over the disappeared qualifier “after”.
On 9 December 2009, on the strength of that very recent Tate show and catalogue, Sotheby’s unequivocally presented what five years earlier had been no more than Millar’s “best surviving version” as an absolutely secure and precisely dated “Sir Anthony Van Dyck” – albeit on a provenance that began with two “Possiblys” – the first being “Possibly in the collection of Sir Peter Lely, d. 1680”. Sotheby’s declaimed:
“An outstanding self portrait by Sir Anthony van Dyck (1599-1641) – one of the most important Continental European artists to have worked in England – comes to auction with exemplary provenance[*] and an estimate of £2-3 million. The masterpiece, which is the artist’s last portrait of himself, was painted in London in 1641 in the final months of his life. It is one of only three self portraits that he painted in England and this, his last, captures him grandly attired in a black and white slashed silk doublet. The painting epitomises the elegant poise and relaxed informality that van Dyck brought to the art of portraiture in Britain and it undoubtedly ranks among the most important works by the artist ever to come to the auction market.” (Emphases added.)
[* On the accuracy of this estimation of the provenance, see Susan Grundy, below.]
THE “POSSIBLYS” AND “PROBABLYS” PLAGUE
A distinguishing characteristic of the upgrades stampede is the parading of superlatives and the drafting of fanciful provenances linked in daisy-chains of “possiblys” or “probablys”. This method was deployed to the most spectacular effect ever by Christie’s, New York, (albeit on the borrowed authority of the National Gallery which had earlier lifted it from a young art historian’s failed attempt to upgrade another and closely related Leonardo School Salvator Mundi) in their November 2017 sale provenance for the Louvre Museum-demoted $450m disappeared Leonardo School Salvator Mundi. It carried no fewer than three “possiblys” in the first item:
“(Possibly) Commissioned after 1500 by King Louis XII of France (1462-1515) and his wife, Anne of Brittany (1477-1514), following the conquest of Milan and Genoa, and possibly by descent to Henrietta Maria of France (1609-1669), by whom possibly brought to England in 1625 upon her marriage to King Charles I of England (1600-1649), Greenwich…”
In 1980, in Christie’s (London) sale of the now-National Gallery “Rubens” Samson and Delilah, the provenance began with three items prefaced: “Probably”; “Perhaps”; and “Perhaps”. The “Probably” – “Probably painted for Nicolaas Rockox” – was an own goal: if autograph, the work had to have been painted for Rockox because he was known to have commissioned Rubens to paint the subject. It was also known that two contemporary copies had been made from the subsequently lost Rockox Rubens original. They had survived. Both depart compositionally in the same manner from the National Gallery picture. In another Christie’s provenance item, the NG picture was said to be “perhaps” that recorded in an inventory of 1653 as a Samson (not a Samson and Delilah) by Rubens. There are two entries in that inventory, one to a Samson by Rubens, another to a Samson after Rubens…If those Samsons had been shorthand for Samson and Delilah, then the subject existed in two versions by 1653, one by Rubens and one after Rubens.
OVERTURNING AN INSTITUTIONAL APPLE CART
When, eventually, the Mould/Bader/Grosvenor campaign succeeded and the “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” was acquired by the NPG acquired in late 2014 many were happy: this was deemed a picture at the very top of the tree and Philip Mould’s apprentice, Grosvenor, had claimed no little credit for making it so (see below). However, some had seen matters differently: the means and manner of this particular upgrade attracted censure in a succession of expert warnings. In the May/June 2014 issue of the Jackdaw, its editor, David Lee, noted both disregarded expert opinion and a seeming over-eagerness to sell the picture – as seen below at Fig. 14:
On 23 January 2014 the Evening Standard’s art critic, Brian Sewell, had written of what was about to become the NPG picture:
“…Van Dyck looks wistful, apprehensive and uncertain; he has not flattered himself and his image is the more compelling for its melancholy, yet this careful self-analysis is set on a bust painted with almost vulgar bravura, a rumpled collar of white lawn over a black doublet slashed with white. Not since he painted himself in Italy in black and white has there been such impetuous painting — and not nearly with so loaded a brush.
“I sense dissonance between the face and the costume, as though two quite opposing aesthetics are at work. Does the head sit easily on the bust, the shoulder more brilliantly lit than the face? What exactly is the form of the wide collar and how is it related to the neck? Has the hair been extended over the collar to disguise this awkwardness? It is of a darker tone and subdued definition.
“One question leads to another. Is it possible that Van Dyck painted no more than his face and rather shorter hair, and left posterity an unfinished portrait, to be completed by another painter?”
FOLLOW THE MONEY
Sewell’s doubts had been elicited more colourfully by the MailOnline on 7 December 2013 (“Petra Ecclestone’s husband hopes fight to keep £12.5m Van Dyck in Britain will fail as he snaps it up for their £55m palace of bling in LA”):
“Mr Sewell said: ‘The painting must have been as important in 2009 as it is now. Why did we not buy it then? They [the NPG] didn’t try.[*] They said they put their heads together with Tate Britain to see whether they could do a joint purchase, but they didn’t say a word in public. There was no question of raising funds from the public. But now they’re perfectly happy to start a fundraising campaign at £12.5m. The logic of it completely escapes me…If the picture is as important as everyone’s saying it is, it should have been bought at £8.3m. Now that it hasn’t, they’re putting £4m in the pockets of Philip Mould.”
[* What was not disclosed at the time was that the National Heritage Lottery Fund and the National Heritage Memorial Fund had told the Tate and the National Portrait Gallery, in terms, that they would not get a grant towards the picture’s purchase because of the great drain on those funds for the 2012 Olympics. That unexpected arts funding shortfall had killed off any chance that might have been hoped to exist to make a quick-flip profit on the world record £8.3m Van Dyck by selling it on to the NPG.]
On 9 December 2013, Grosvenor responded in a blog post (on his Art History News site) to Sewell’s criticisms with a double slur: “This is, of course, only the latest salvo in Brian’s apparent campaign against the painting, which can only, I presume, benefit the overseas buyer… His remarks are a good example of that unattractive British habit of demeaning anyone who happens to be successful. Sewell sniffed at something Mr Stunt may or may not have said about his collection (which is already one of the best for 17th C English portraits), when as a lover of art he should applaud the fact that a successful British businessman under the age of 30 not only cares about ‘old’ British art, but also supports, very strongly, exhibitions, publications, loans and research.” (Had Stunt supported the Mould Gallery’s FINDING VAN DYCK exhibition and its 80 pp catalogue? On his support for other Mould/Grosvenor research, see below.) Sewell’s remarks had been given in response to this MailOnline quote from Stunt:
“All my Lelys are important. In Althorp, the Earl of Spencer has the Windsor Beauties, which is a very famous group of pictures by the artist. I’ve been trying to rival the Windsor Beauties. I have more, I think, than him, and I’m just five off the Royal Collection.”
That does not sound made-up. Sewell had responded: “Oh dear. I don’t know him but if he’s setting out to rival Althorp and Buckingham Palace, that’s hardly a meritorious way of collecting. It’s cigarette cards.” Snobby, perhaps, but not without force and humour. Of course, there is nothing wrong with successful businessmen buying art – if: a) they have the means and really are buying; and b) they buy judiciously and not as if from some competitive, vainglorious shopping list. Stunt’s taste for old masters was entirely worthy.
SOME SERIOUSLY AWKWARD CONNECTIONS
The NPG picture’s standing had been again and more radically challenged by Susan Grundy on its authorship, condition, and circumstances. She has shown that both Sotheby’s and the Mould gallery’s citations of the scholarly literature had implied high scholarly support for a Van Dyck ascription that was simply not present. As mentioned, Gustav Glück had seen the now NPG self-portrait picture in 1941 but, then, he had judged it a copy – as had Eric Larsen in 1980 and 1988, and, as seen above, Oliver Millar in 2004. There had been no major scholarly support for the picture as an autograph Van Dyck.
On 26 April 2020 the Mail-on-Sunday reported Grundy’s further startling investigations: “Is the £10m Anthony Van Dyck ‘selfie’ that Kate Middleton helped save for the nation a cheap copy?”
Specifically, Grundy had said: “Philip Mould, the dealer who brokered the sale at such a handsome price, is one of Britain’s most recognisable art experts. He makes regular appearances on the Antiques Roadshow [he also fronts, with Fiona Bruce, the BBC’s Fake or Fortune] and is known as something of an authority on Van Dyck. But this story also involves the unlikely figure of Petra Ecclestone’s ex-husband James Stunt, who once described himself as a billionaire art collector, but is today known as a shambolic, foul-mouthed bankrupt. The Mail-on-Sunday has previously revealed that Stunt lent a number of fake paintings to Prince Charles’s charity at Dumfries House in Scotland where, embarrassingly, they were put on public display. And that attempts had then been made by intermediaries to use the fakes as collateral for millions of pounds worth of loans. The paintings have now been taken down from public view, although Stunt still maintains they are originals. But the businessman’s reputation was intact back in 2013 when, while still married to Formula 1 heiress Petra, he was looking to add to a vast and rapidly expanding collection of masterpieces and agreed to buy the Van Dyck from Mould’s client, Canadian industrialist Alfred Bader.”
In Grundy’s account “agreed to buy” is both the operative and a problematic term. “Client”, too, is problematic: confusion over the 2009 £8.3m purchase at Sotheby’s abounds. It was rumoured that Mould had bought with money loaned by Bader; some expressed surprise that Stunt should have bought it at all at £12.5m, because his purchases rarely exceeded six figures. Many reports referred to a joint Mould/Bader sale to Stunt but those were ambiguously phrased, and it is nowhere confirmed that Stunt had paid £12.5m, taken title of the picture and was about to remove it to the U.S. The Heritage Fund claimed the picture “was sold to a private collector who wished to take it abroad” but the Art Fund disclosed that the picture was bought by the NPG not from Stunt – or Mould – but from “Alfred Bader Fine Arts”, which, if correct, would necessarily mean that that picture had not been sold to Stunt and, therefore, that public monies had been given to block a supposed but phantom pending removal of the picture from the country.
WHEN WAS THE GROSVENOR “LAST VAN DYCK SELF-PORTRAIT MARK II” BOUGHT?
Establishing the point at which Grosvenor acquired his own supposedly superior and historically more significant “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” is of interest re both his claimed value-adding role in the promotion of the NPG picture and his subsequent cheerleading role for the public fundraising campaign to secure the picture’s entry into the NPG in 2014. In 2015 Grosvenor disclosed that a restoration of his own picture (Figs. 7 and 10) had taken place “over the last few years”. See below. He also declared that it was only when “all the overpaint and dirt” had been removed, that the very “possibility of a full attribution to Van Dyck [had become] worth pursuing further”.
The “I-had-no-idea-at-first” dealers’ trope was also encountered with the now-famous consortium of New York dealers who had never suspected that their manifest Leonardo School Salvator Mundi might be an autograph Leonardo prototype painting until a certain pentimento on a thumb emerged during restoration. Grosvenor, too, reports a pentimento-on-the-thumb that he, similarly, holds to confirm autograph Van Dyck status on his own picture. However, hands are notoriously difficult to draw even when making a copy – and, as Jacques Franck has demonstrated here, if such thumb pentimenti are to be taken as proofs of autograph states, the Salai copy of Leonardo’s St. John the Baptist would now be considered a second autograph Leonardo St. John the Baptist.
Intriguingly, Grosvenor disclosed that the (eventual) NPG self-portrait had been joined during its near five-year long residence in the Mould gallery by other Van Dyck finds. Of one such, the privately owned picture now on loan to the Minneapolis Institute (Figs. 1, 15 and 19), Grosvenor disclosed on 5 March 2015: “What a pleasure it was to work with Philip Mould in his gallery with it [the now Minneapolis picture] – sometimes we would treat ourselves and hang it next to the later Van Dyck self-portrait we also had in the gallery (the one which was bought by the National Portrait Gallery last year).” But what of the Grosvenor-owned picture which was loaned to the Rubenshuis Museum on 8 March 2016? Had that picture, too, been hung next to the hard-to-shift self-portrait that would enter the NPG in 2014?
A HANDY SOURCE OF POTENTIAL VAN DYCK SELF-PORTRAIT UPGRADES
For those wondering how quite so many Van Dyck self-portraits could turn up in one place in such short time there is a simple explanation: Grosvenor and Mould, like many of us, are avid students of the 2004 catalogue raisonné.
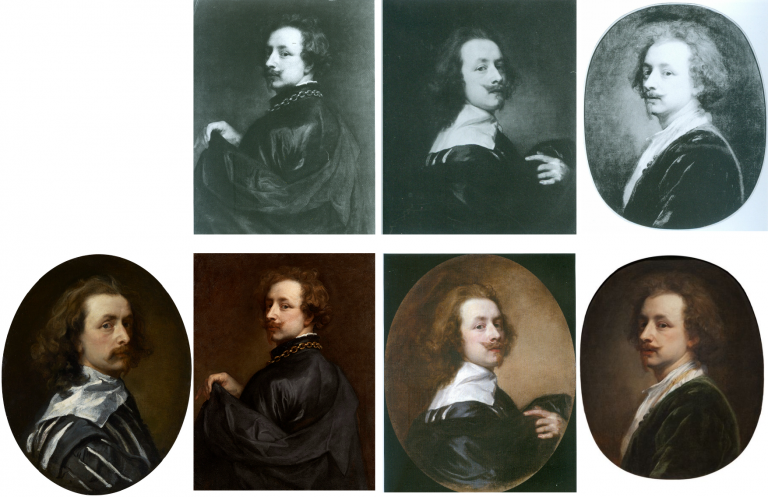
Above, Fig.15: Top row, three “self-portraits” as published in an appendix of copies by Oliver Millar in his contribution to the 2004 Van Dyck catalogue. Bottom row: the three recently upgraded former Millar self-portrait copies, as they presently appear, and the not-for-sale Indianapolis picture.
In this one small section of that invaluable and indispensable account of Van Dyck’s English period, Millar had unwittingly compiled a sort of sleeper-hunters’ treasure chest. Grosvenor has now upgraded the first two of Millar’s three Van Dyck self-portrait copies – and acquired one – both having been privately owned. Only Millar’s third self-portrait copy (above, top right) which cannot turn a penny because it is already in a museum – The Clowes Fund Collection, Indianapolis Museum of Art – remains on the upgrades shelf.
Thus, in the bottom row at Fig. 15 we see: left, the NPG picture judged by Millar to be “The best surviving version of (probably) the last Self-portrait, painted towards the end of Van Dyck’s years in London”; second left, the privately owned, Grosvenor/Mould upgraded self-portrait, now loaned to the Minneapolis Institute; second right, the Grosvenor-owned, restored and new “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” that Millar judged a copy of an unknown work recorded in the collection of Charles I; right, the Indianapolis picture with a fine gold chain – for excellent close-up photos, see here – that Millar judged the best-surviving version of an informal Van Dyck self-portrait of c.1634. It might be noted that in this informal attire and unhaughty demeanour, the artist’s moustache had not drooped or turned down.
VAN DYCK’S NOW TWO “LAST SELF-PORTRAITS”
Above, Fig. 16: Left, the National Portrait Gallery’s “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”; right, the Grosvenor/Rubenshuis Museum “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”.
So, to return to Grosvenor’s second and Rubenshuis loaned “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”, there are, as he acknowledges in his 2015-6 British Art Journal account, many outstanding problems of provenance: 1) “We cannot currently draw a direct documentary link from the painting today back to the royal collection”; 2) “there is no record of a payment by Charles I for the picture”; 3) the picture “was first certainly recorded in 1854 when accepted by Gustav Glück” [- sic Glück was born in 1871*]; 4) had the picture been the one owned by Charles I, it would most likely bear the royal monogram (the letters “CR” capped by a crown) on the back of the canvas – but it does not – see Fig. 18 below; and, 5), that the “somewhat loose, rapid handling of the Self-portrait is unlike the high degree of finish and detail that Van Dyck normally produced for Charles I”.
The last admission might seem particularly damaging given Grosvenor’s claim that the (in part) highly wrought NPG picture had been executed as a dress rehearsal for his own picture. Indeed, the NPG’s 2015 book had made a somewhat fanciful virtue of its picture’s stylistically incongruous execution: “The broad, rapid, virtuoso handling of the costume contrasts with the exquisitely fine painting in the face. The relative lack of finish in the costume draws attention to the act of painting that has produced this portrait, perhaps even suggesting that the artist is still in the process of creating it, while we, as viewers, watch him. It may be that Van Dyck was working in a more experimental way in this part of the painting, or it may simply be that it was left unfinished.” (Emphasis added.)
Which, then, might have been the case? The NPG, understandably, was at a loss because: “Nothing is known of the circumstances in which this portrait was produced: whether it was a gift for, or a commission from, a friend, relative or patron, or whether the artist had painted it for himself…” The work is therefore, an orphaned “one-off” or unicum – that intrinsically problematic art historical creature of which Professor James Beck warned his students at Columbia University always to beware. (He also cautioned students to address “what we know about this artist before what has been said or written”.)
[* Grosvenor effectively self-corrects the above slip in his BAJ footnote no. 27, when he cites the earlier and intended Gustav – Gustav Waagen – and his 1854 three-volume Treasures of Art in Great Britain [**]. Although Grosvenor gives the page number, he does not disclose how Waagen had referred to the painting. Had he said something flattering or simply cited an inventory? Grosvenor notes that Gustav Glück had later identified the picture as that in the collection of Charles I and that he had done so not on the grounds of stylistic analysis but of a contingent availability:
“As no other self-portrait answering to the same description is known, there can be no doubt that the picture…once belonged to the royal friend and warm supporter of Van Dyck.” Glück was playing the above-mentioned Denis Mahon Manoeuvre – conferring autograph status on the best available picture. In this case, Glück conferred it to the only possible surviving candidate. With his own (Rubenshuis) self-portrait picture, Grosvenor seems to follow the Gluck/Mahon practice even though he has also identified a second version of the picture that is of similar size and composition. Without addressing the possibility that both versions might have been copies of a lost autograph prototype, as Millar had concluded at the end of a long and distinguished career, Grosvenor holds the newly discovered version (below, Fig. 17, top left) to be a later copy of his own picture, and thereby elevates his own picture from Millar’s copy of a lost original to the original Van Dyck painting.]
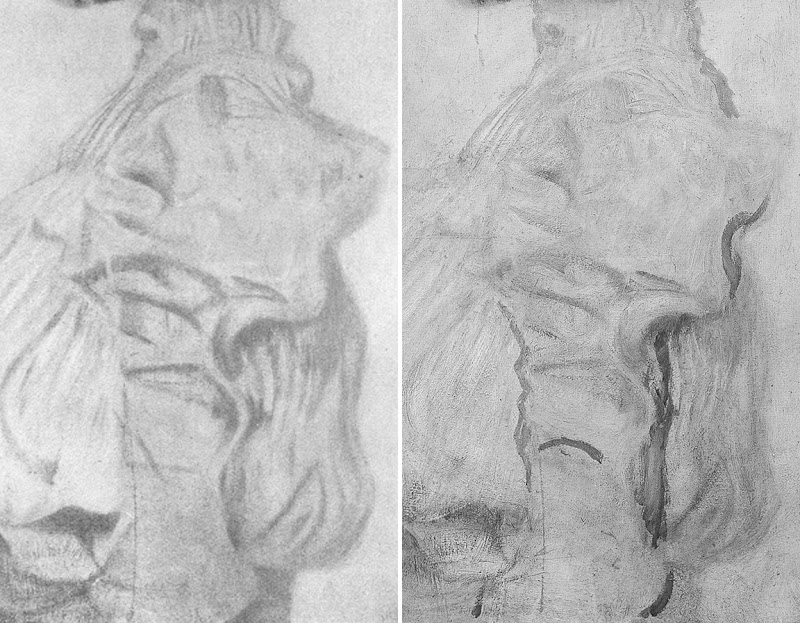
Above, Fig. 17: Top row, left a copy of a Van Dyck self-portrait attributed by Bendor Grosvenor to Charles Jervas (1675-1739); the Grosvenor attributed Van Dyck self-portrait before its two-year long restoration; the Grosvenor attributed Van Dyck self-portrait after its restoration. Bottom row: left, the NPG “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”; centre, the Grosvenor, Rubenshuis “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” before restoration; centre and right, the Grosvenor, Rubenshuis “Last Van Dyck Self-portrait”, as before and after restoration.
In the above-cited Mahon case, it took fifty years for the now accepted original version (at the Prado) to emerge and show Mahon’s claimed “autograph original” to have been a copy – which should have been recognised all along because it, just as with the National Gallery “Rubens” Samson and Delilah, was known from an etched copy to be a compositionally truncated version of a lost original. Where Millar resisted temptation to play the Glück/Mahon/Grosvenor gambit and judged what is now Grosvenor’s picture (above, Fig. 17, top right) to be no more than an early copy of a missing painting, Grosvenor has followed Glück’s earlier “opportunist” elevation (of what is now his own painting) even though it had not gained critical acceptance on Glück’s ascription and had been sold in 1969 for $350 as “after Van Dyck” and for $3,120 in 2006 as “after Van Dyck” (- when possibly bought by Grosvenor). As Millar appreciated, being the only available candidate is not a sufficient qualification for a painting to be accepted as autograph.]
[** As for Waagen’s cited but not quoted observation of Grosvenor’s picture, it too might best be treated with caution. When Nicholas Penny upgraded the Duke of Northumberland’s “Madonna of the Pinks” to Raphael in the February 1992 (Burlington Magazine – “Raphael’s Madonna dei garofnai rediscovered”), he quoted Waagen’s fulsome comment: “on occasion of my visit to England in 1854 I had the privilege of spending a day at Alnwick castle as his Grace’s guest…It is well known that the charming composition is by Raphael and of all the numerous specimens of the picture that I have seen, none appears to me so well entitled to be attributed to his hand as this.” High praise, certainly, but there were three overlooked dangers. First, gushing hyperbole in ascriptions might seem a required social obligation for guests of Dukes – Bernard Berenson and his wife were thrown out of a Scottish Duke’s lair late on a stormy evening when the scholar advised that his Grace’s “Leonardo” was no such thing. Second, Waagen had spoken twice on the Northumberland picture and both of his comments should have been addressed together. Waagen’s helpful-to-Penny’s-cause, praise appeared in the fourth and supplementary 1857 volume to his three-volume 1854 Treasures of Art in Great Britain. In the 1854 Vol. III, p. 253, Waagen, who had yet to enjoy the Duke’s hospitality, had dismissed the Northumberland picture (that would, like the NPG Last Self-portrait be Saved the for The Nation at £22m as the National Gallery’s Raphael “Madonna of the Pinks“): “the small picture in the Camuccini collection at Rome which I do not consider to be original. The tone of the flesh has something insipid and heavy. The treatment makes me suspect a Netherlandish hand.” Third, Waagen’s later fulsome revised comments were written in the knowledge that the whole Camuccini collection was to come to Alnwick Castle, having been bought by the Duke in 1856 (- as James Beck disclosed in his posthumously published 2007 book From Duccio to Raphael: Connoisseurship in Crisis, three chapters of which anatomised the untenability of the National Gallery picture’s Raphael ascription). Had Waagen stuck in 1857 to his earlier scholarly/critical guns, a Duke would likely have been mightily displeased, and Italy’s already lucrative “old masters” export industry would have been thrown into question if not crisis. However, of the two Waagen accounts that of the slightly younger, more disinterested c.1854 self better withstood the test of time: as with the Glück-ascribed now Grosvenor last self-portrait, the Duke’s picture duly came to be seen as a version of a lost Raphael autograph prototype painting – as Penny himself described it, as one of “numerous versions” with none being “generally acknowledged as an original work by Raphael”. It was only on Penny’s 1992 advocacy resting on the authority of the slightly older Waagen’s 1857 obsequious effusion that the scholar’s own earlier, sounder appraisal was eclipsed. When Penny stayed at Alnwick Castle – the second greatest castle in Britain – in the early nineteen-nineties (“The author is grateful to the Duke of Northumberland, the Duchess of Northumberland and Lady Victoria Cuthbert for their hospitality and encouragement”) the potential “oven-ready” upgrade in the form of the ex-Camuccini picture remained lurking-in-residence in its elaborate 19th century frame bearing the proud ascription “Raphael”, patiently awaiting a new scholarly response.]
THE MISSING MONOGRAM ON A GROSVENOR UPGRADE
Above, Fig. 18: Left, the back of the Pushkin Museum’s Salvator Mundi by Giampietrino which carries the Charles I monogram, at which period the picture had been attributed to Leonardo; centre, the Charles I monogram found on the back of the Van Dyck painting of Mary Villiers; right, Van Dyck’s Mary Villiers portrait
The presence of a monogram confirming ownership by Charles I adds very considerable value. In 2002 the Mould gallery discovered one (above, centre) on a Van Dyck portrait of Mary Villiers (above, right) that had been bought for £437,587. On discovery of the monogram (made, as with Grosvenor’s picture, during the traumatic act of stripping off and replacing a backing canvas) the Mould picture’s asking price leapt almost fourfold to £1.6m. It follows that Grosvenor’s Rubenshuis Van Dyck will likely be worth a quarter of what it might otherwise have beeen, had it been in Charles I’s collection and duly stamped with the royal monogram.
OUT OF THE FRYING PAN…
Lacking evidence that his picture had been in Charles I’s collection, Grosvenor addressed the absent record of a payment with an initial surmise that the picture had been presented by Van Dyck as a gift to the King. He then added: “Of course, the presumption that the self-portrait was originally presented to Charles I may be incorrect, and if it was part of the collection of Henrietta Maria instead (whose collection was looked after by Daniel Soreau of whom we know little), we would not expect to find a cypher [monogram] on the back.” (Emphases added.)
A neat swerve, but an expectation of an absence of evidence that rests on an unsupported supposition cannot be rolled together and taken to constitute evidence of any kind. If the picture lacks a monogram it lacks a monogram and that tells against it having been in the collection. If it lacks both a monogram and a record of payment, there is certainly no ground for concluding that it must therefore have been gifted by Van Dyck to the King’s wife, because that blatantly begs the question. Grosvenor reports that after the king’s execution the Van Dyck self-portrait that had been in the collection had been bought by the artist’s former assistant and copyist, Remigius van Leemput – and he says so on the cited authority of Oliver Millar, who judged the now-Grosvenor picture…to be a copy of that lost, formerly Charles I Van Dyck self-portrait.
The escape clause possibility of the picture having been owned by Henrietta Maria was suggested to Grosvenor by Margaret Dalivalle who had attempted to underpin the claimed double royal pedigree of the (now-disappeared and Louvre Museum-downgraded) $450m Leonardo school Salvator Mundi with a speculative suggestion that the painting might have been brought to England from the French royal collection by Henrietta Maria. It was also being claimed that the (then New York) Leonardo-attributed Salvator Mundi was the Leonardo Salvator Mundi that had been recorded in the Charles I collection. No evidence supported that claim and in 2018 another picture – the one that really had been attributed to Leonardo when in the collection of Charles I and the one which really does bear the royal monogram (above left, Fig. 18) had emerged in the Pushkin Museum, Moscow. However, that Salvator Mundi is of a different composition and, besides, it had been downgraded to Leonardo’s assistant Giampietrino. Thus, the painting that had been in Charles I’s collection as a Leonardo was not a Leonardo, regardless of whether or not it had been brought from the French royal collection, which it hadn’t: after years of trawling archives, Dalivalle admitted that she had found no evidence that Henrietta Maria had brought the painting from France and had abandoned her search.
A SERIALLY BEGGED QUESTION
In the absence of material or documentary evidence on his Last Van Dyck self-portrait, Grosvenor again appeals in circular fashion to the authority of his own judgement-by-eye on the picture’s artistic merits, which judgement he again confounds with hard evidence: “There is however, other evidence to suggest that this painting did indeed hang at Whitehall, in addition to the fact of its overall quality, and the fact that it certainly appears to be an original work by Van Dyck.” Having conflated his own impressions and judgements with facts, Grosvenor proceeds to add that Van Dyck, “is unlikely to have presented his patron with a second version or a studio replica” when he has not established that the (formerly $350) picture which he owns had been presented to Charles at all. (All emphases added.) Once again, “evidence” that “suggests” that something had happened of which there is no evidence, is not evidence, it is simply wishful thinking. Grosvenor’s painting could not have whispered in the Mould gallery (- had it ever been presented there) that it had once hung somewhere else in London.
If proof were ever to emerge that Van Dyck had gifted an unrecorded portrait of himself to the king’s wife, it would immediately beget another sleeper-hunting opportunity: Where is the Van Dyck self-portrait that was listed in the king’s collection and that would be expected to bear the royal monogram? Were such a monogrammed Van Dyck self-portrait to turn up tomorrow, we would then have two self-portraits gifted by Van Dyck to the royal couple (one to each), just as we now have two claimed last Van Dyck self-portraits in the NPG and Rubenshuis pictures.
BOUNCING THE NPG?
Whatever the exact relationship in this recent Mould and Bader “adventure in old masters”, two things are clear. First, an initial attempt to sell the £8.3m picture to the NPG failed. When the Philip Mould enterprise found no buyer for the picture between 2009 and 2013, the £8.3m purchase at Sotheby’s must indeed have seemed a hair-raising liability. Second, that although James Stunt’s much-reported purchase of the painting for £12.5m never materialised, his repeated and noisily declared intention to remove the painting from Britain greatly assisted the picture’s eventual sale to the NPG.
On the picture’s true or fair value between 2009 and 2014, there is no evidence that the already world record £8.3m Van Dyck had been sold for £12.5m to Stunt, a well-known collector of six-figure Lely paintings. Waldemar Januszczak mused in the Sunday Times: “Why Stunt has chosen to go for the Van Dyck now, when it has been hanging in Mould’s gallery for three years I do not know.”
HYPING A TOP-PRICE WORK
Putting Stunt’s involvement to one side, it might also be asked how the NPG’s £10m purchase of a picture that had been stealthily offered as a safely autograph work (on no scholar’s published account) in 2009 and on a £2-3 million estimate at Sotheby’s, came to be taken as a matter of Very Great National Concern. On 8 December 2013, Richard Brooks rebuked the NPG for dilatoriness over the purchase (Sunday Times “£3m bungle over Van Dyck selfie”): “…the gallery had the chance to buy it four years ago for at least £3m less than it will now have to pay”. If Brooks had meant that had the gallery bid directly at Sotheby’s 9 December 2009 auction it could have got the picture for the £8.3m paid by Mould/Bader, Grosvenor has countered: “we were delighted to acquire it in partnership with Alfred Bader for £8.3m. In fact, we had been prepared to bid much higher, and were slightly surprised when the hammer came down.”
Brooks continued: “In fact it [the NPG] missed the opportunity to buy the painting not once but twice…The gallery had in fact been tipped off by the auctioneer, Sotheby’s, that the painting was coming up for sale four months earlier, in August 2009, when one of its staff went to see Sandy Nairne, the director of the Gallery. ‘It was a heads-up for them to see if they could buy,’ said Sotheby’s last week. Nairne decided not to bid. Last week Nairne confirmed that the approach had been made but said he had worried about the ‘uncertainty’ of buying at auction. It was also thought that the earl [of Jersey] did not seem interested in selling privately to the gallery.” This last was likely the case – Grundy established that the earl had put his own family pile on the market at c.£10m, so he was not likely in financial self-sacrifice mode.
Having bought the picture for £8.3 million at auction, Brooks continued, “Mould and Bader offered the gallery another chance to buy it, this time from them. Initially they asked for £10 million but this was subsequently dropped to £9.5 million…” Those successive reductions might have been public-spirited generosity towards a national institution, but they could also have been hard-nosed commercial realism: the picture was proving impossible to shift. Four other parties, including two non-UK museums, were said to have driven the auction price to £8.3m but having dropped out at that price they were unlikely to re-enter at £10m, £9.5m or £12.5m – as indeed had resoundingly proved to be the case by 2013 when the work remained unsold. All in all, Brooks seemed rather cross that the NPG was not playing ball with a gallery that had failed to shift a picture bought three years earlier at a world record price with the assistance of an industrialist/collector.
HOW SOLID WAS STUNT’S OFFER TO BUY AT £12.5m?
Januszczak appreciated that: “the timing [of Stunt’s late-buying and declared intention to remove from the country] has forced the NPG and the government into action” – which action he and Grosvenor supported. As for Stunt’s declared intention to remove the picture from the country, had he bought it earlier for less and immediately applied for an export licence, there would, Grosvenor has claimed, have been no opposition and the picture would certainly “have left the country”. Instead of quietly buying it for £9.5m and removing it unopposed from the country, Stunt waited until the end of 2013 to declare an intention to buy the picture at the then full Mould/Bader £12.5m asking price and, simultaneously, to remove it from the country. For sure, that last declaration prompted the picture’s supporters to seek and obtain a three-month government export ban in November 2013. Stunt then amplified his Threat-to-Remove by saying that although he well understood the move to block his purchase from Mould, he still hoped he would be able to “take it to his home in Los Angeles and enjoy it.” Thus, without costing Stunt a penny, his noisy public stance greatly facilitated the Mould/Bader sale to the NPG when no other buyer was in sight.
A MAN OF SEVERAL HATS
Above, Fig. 19: Left, the newly attributed Van Dyck self-portrait on loan to the Minneapolis Institute of Arts (as discussed below); right, a 1925 Max Beerbohm cartoon in his “The Old and the Young Self” series. (Caption: Mr Arnold Bennett – Old Self: “All gone according to plan, you see.” Young Self: “My plan, you know.”)
Grosvenor’s role as a Mould employee becomes a greater matter of interest given his possibly overlapping role as a private, stand-alone collector/connoisseur. On 14 November 2013 he posted a blog saying that the picture had been sold to an overseas buyer [Stunt] and added: “For the art dealing day-jobber in me, this has to be seen as a Good Thing. We [at Philip Mould] bought the picture (in the thick of the global downturn) because we believed in it, and had the aim of adding value and selling it on. And I believe we have done that… However, for the Van Dyck fan, it obviously pains me that the picture might leave the UK. And it doubly pains me that I might in some small way be responsible for that!”
How so? In addition to his value-adding obligations as a Mould gallery employee, Grosvenor had attended a Government Export Licence Review “as a representative of the picture’s buyer [Stunt]”. It is not clear whether Grosvenor had spoken in support of, or against, Stunt’s declared intentions to remove the picture, at the Review – or whether, whichever line he adopted on that occasion, Stunt had known of it. It is possible that Grosvenor confined his remarks to underlining the seriousness of Stunt’s threat to remove the picture from the country but on 14 November 2013 he hinted that he had opposed the Mould gallery client’s declared intentions:
“A month or so ago we attended the UK government’s Export Licence Reviewing Committee – as representatives of the picture’s buyer – at the Arts Council’s new office… [and the picture] was temporarily blocked for export by the committee on all three ‘Waverley’ criteria (which is unusual). I felt a strange pride in Sir Anthony for pulling that off.” For “Sir Anthony”, we can only read “Dr Grosvenor” and further assume that Stunt was happy to have his by then doubly expressed determination to remove the picture from the country thwarted by a Mould gallery employee. Grosvenor asked: “Will a UK institution [now] be able to raise the funds to stop the sale?” With his gallery salesman’s hat on, he helpfully volunteered: “The price is £12.5m (about 1/3 of a Koons Orange Dog).”
Eleven days later (25 November 2013) Grosvenor reported: “I went to the launch this morning of the National Portrait Gallery’s campaign to save Van Dyck’s last self-portrait for the nation. The picture has been sold to an overseas buyer, and the NPG has 8 months to try and raise £12.5m to keep the painting in the UK. It’s the largest such campaign ever mounted by the NPG… Regular readers will know that I work for the company which has sold the picture, so I’m in something of a predicament. But of course, the Van Dyck fan in me (he’s my favourite artist) wants to see the picture remain on public display in the UK. A large part of whether the campaign to save the picture succeeds will come down to how the public reacts…” (All emphases added.) On the face of it, Grosvenor was openly campaigning against the interest of a Mould/Bader client who, reportedly, had already paid £12.5m and delivered a £4.2m profit to Mould/Bader on an £8.3m picture, and yet, at the same time, he was commanding the country to come to the aid of a public institution so as to help it buy the picture for £12.5m from a dealer and his “progenitor of adventures in old masters” partner/backer.
“ULTIMATE BUYERS”
Again, concerning the price, in his 25 November 2013 post, when scolding Sewell for challenging the attribution and for claiming the NPG could have bought for less than £12.5m had it acted sooner, Grosvenor retorted: “How does Brian know where we, as the ultimate buyers (in partnership with Alfred Bader fine arts) would have stopped bidding? I can tell you now that the NPG would not have got it at auction for less than the asking price today.” Thus, we learn that the Bader-backed Mould gallery had been prepared to buy the supposed Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait for very appreciably more than £12.5m. Having already routed all opposition in 2009 with an £8.3m bid, who – other than the NPG – might have been expected to buy the picture after four years of no-sale? We say “no-sale” because if the picture had belonged to Stunt it would have been reputationally reckless behaviour for the vendor, after taking payment, to seek to block the buyer.
In November 2013 Grosvenor complained “Waldemar [Janusczcak] is mounting a one-man campaign to have my employer donate the picture to the NPG…” – which tacitly disclosed that Mould/Bader were still the owners. An anonymous, but evidently well-informed reader commented on Grosvenor’s website: “…Mould and co are entitled to profit from 1) saving the Van Dyck four years ago by taking the risk of purchasing it at auction during a very difficult period 2) holding the painting for four years with a lot of someone’s capital in it 3) researching the picture to add to its value all that is now known about it.”
THE PRESS WEIGHS IN
When Stunt’s reported bid to remove the picture spurred the NPG’s attempt to retain the picture in Britain at £12.5m, many journalists urged the public to contribute to the “Save-the-Picture” fund. In the Times Ben Macintyre hailed Van Dyck as an exemplary immigrant who had enriched his adopted home – a mongrel nation avidly open and welcoming to foreign talents, in which he was knighted, married into the aristocracy, buried in St Paul’s and had left as his legacy a transformed British school of painting that, having passed through Gainsborough and Reynolds to Singer Sargent, “is still felt nearly four centuries later”. That was a perfectly fair and attractive (if by no means original) analysis. Van Dyck’s last and greatest of all self-portraits, Macintyre assured readers, depicts a man who has found his home from home, “and that is where he should stay.” Against that somewhat sentimental reading, evidence suggests that, ahead of the end of Charles I’s reign, Van Dyck was looking to jump national ships.
Jonathan Jones in the Guardian asked “£12.5m for a self-portrait by Anthony van Dyck? That’s what the National Portrait Gallery and the Art Fund are trying to raise in an appeal launched today. Is it worth it?” Sporting hyperbolic philistinism, he self-answered: “Absolutely. I think this is one of the most worthwhile campaigns in years to ‘save’ a work of art for the nation. Van Dyck’s Self-Portrait would make a spectacular addition to the National Portrait Gallery. Quite frankly, it could make the place. It would give a gallery stuffed with pictures of primarily historical interest a true artistic masterpiece, by the man from Antwerp who gave birth to British art.”
In the Spectator the historian Andrew Roberts wrote: “Of all the great British portrait painters, Van Dyck is by far the most important not to be represented by his own portrait in one of the great British public collections, considering how central he is to the history of the British school of painting and how his influence has grown over the centuries. ‘We are all going to heaven’, Gainsborough said on his deathbed, ‘and Van Dyck is of the company.’ For the National Portrait Gallery, the story of Britain that it attempts to tell through portraiture is simply incomplete without a portrait of Van Dyck, which has long been identified as one of the major lacunae in its otherwise superb collection. This is the only chance a museum or a gallery in the United Kingdom has of acquiring the masterpiece and it’s the only portrait of the artist ever likely to be made available for acquisition by a British public collection…”
Grosvenor purred on his 28 November 2013 post: “excellent piece by historian Andrew Roberts in the Spectator on the NPG’s campaign” without disclosing that since May 2013 Roberts had been an NPG trustee. Nor did he demur when Roberts assured the public that this was “the only chance” of acquiring what was the “only portrait of the artist ever likely to be made available for acquisition”. Not the slightest hint was given that three Van Dyck self-portraits were in the offing and on 8 December 2013, the Sunday Times prodded laggards: “James Stunt, who is married to Bernie Ecclestone’s younger daughter Petra, has already put in an offer of £12.5m and hopes to hang the piece in his Los Angeles mansion.”
A PROLONGED STRUGGLE TO RAISE THE READIES…
On 17 February 2014 Grosvenor announced:
“The National Portrait Gallery has successfully argued for an extension to the export bar on Van Dyck’s c. 1640 Self-Portrait. This means they have another 5 months to try and raise £12.5m, which is the sum required to match the picture’s sale price. The NPG has already raised a quarter of that amount, from bodies such as the Art Fund, the Monuments Trust, and also (impressively) nearly a million from smaller donations made by members of the public…” That left some £8.2-3m to find – effectively the full original world record price paid at auction. Once again, Grosvenor reminded his readers: “I’m in something of a quandry [sic] on this one, given that Philip Mould & Co., for which I work, sold the picture to an overseas buyer.” (Emphasis added.)
AN EMPLOYEE HELPS BROKER A NEW CUT-PRICE MYSTERY DEAL
On 26 March 2014 Grosvenor announced he had been working on “a new deal to help the National Portrait Gallery’s campaign to acquire Van Dyck’s final Self-Portrait” and that the target price “has now been reduced from £12.5m to £10m.” Who exactly was working with whom – and how – on this deal? What role had Grosvenor played? Stunt, he reported, had issued a statement: “When I agreed to buy [not when I bought] this great portrait I didn’t expect the huge swell of public opinion and strength of emotion its export would generate…I have reconsidered my position and have decided, with Dr Bader and Mr Mould’s agreement, to withdraw from the process.” Had Stunt owned the painting he would neither have been able to withdraw from a process, nor have required the agreement of Bader and Mould to sell his own picture to the NPG at a supposed-billionaire’s public-spirited £2.5 million loss, should he have wished. Presumably, Stunt meant only that he was withdrawing both an earlier undertaking to purchase and a declared threat to remove the painting on purchase.
Had Stunt feared opprobrium on removing the picture from the country, he could have bought it on an agreement not to remove it – he had three homes in London at that time. Given that, for whatever reason, the well-publicised Stunt purchase had vaporised, and that Mould/Bader still had no buyer in view – other than the NPG which was clearly struggling to match the reported sale at £12.5m – why did they not revert to their earlier £9.5m offer to the gallery?
At that price, Mould/Bader would still have made £1.2m profit on their £8.3m purchase – almost as much as the £1.4m contributed by the donations of 10,000 members of the public – while earning kudos for contributing to the public weal. Grosvenor reported that Mould and Bader had responded separately. Mould had said: “I am delighted to be able to help the National Portrait Gallery’s campaign in this way”. In what way had he helped? Had he volunteered a £2.5 million cut on a painting he (or he and Bader) still owned but could not sell? Or, had the elderly Bader been the near- or actual owner, with Mould and Grosvenor having acted as his agents in an attempt to flip a £8.3m painting to the National Portrait Gallery?
A CHEERLEADER CONSTRAINED
“And, for what it’s worth”, Grosvenor continued, on 26 March 2014, “here’s what I have to say. Regular readers will know that previously I’ve had to tread carefully when it came to the NPG’s campaign. Van Dyck is my favourite artist, and I’d naturally like to see his final Self-Portrait stay in the UK and on public display. But my responsibilities towards our clients meant that I couldn’t be as much of a cheerleader for the [fund-raising] campaign as I’d liked. Now that Mr Stunt is no longer buying the picture, and Dr Baders [sic] and Philip Mould have agreed this new plan in favour of the NPG, however, all efforts can be focused on the Gallery’s fundraising. I’m pleased with the outcome.” (All emphases added.)
Ostensibly, that was inscrutable: Grosvenor talks of clients when only Stunt had reportedly been in the picture; Stunt is now not buying and therefore, contrary to all previous claims, he had not bought. How real, then, had been the threat to remove the picture from the country? Had it become apparent to Mould/Bader that even with the extended leave to raise funds, the NPG was unlikely to raise the necessary £12.5m? Was it not the case that no one was interested in buying the picture and that to be sure of a sale, the high asking price to the NPG would have to be slashed; that having paid £8.3m for a stealthily upgraded former copy, Mould/Bader had simply bitten off more than they could chew?
As for who was making the twenty per cent price reduction, Bader made no comment. His family responded: “Alfred Bader CBE, an established philanthropist on both sides of the Atlantic, has been impressed by the public’s response to the painting, and the efforts that both the Art Fund and the National Portrait Gallery have made to keep the picture on public display. He very much hopes that the National Portrait Gallery is able to complete the rest of its fundraising challenge.” That would fit with the view some held at the time that (the then ailing) Bader and his family were impatiently seeking the return of his undisclosed investment/stake in the picture.
THE SECOND “LAST VAN DYCK SELF-PORTRAIT”
In the light of a £2.5m reduction after four years of no-sale, it might again be wondered at what point the now Grosvenor-owned True “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait” that today hangs in the Rubenshuis Museum had emerged. In his December 2015 BAJ article, Grosvenor disclosed that his painting had undergone a long and “sensitive conservation, leaving us with the picture we see today”. Skipping an owner’s obligatory guff on “sensitive conservation”, for how long was it in restoration? Answer: “over the last few years”. That is a lot of sensitivity on a modest painting and it suggests that Grosvenor might have acquired the picture no later than c.2013. [*] Had he at any point advised his employer or the National Portrait Gallery that he had single-handedly acquired a supposedly artistically superior Van Dyck self-portrait with a supposed royal provenance that he would shortly publish and lend to a foreign museum as the True Last Van Dyck Self-portrait? For that matter, had Mould and Grosvenor jointly advised the National Portrait Gallery when the third Van Dyck self-portrait (Figs. 1, 15, 19 and 20) – that would be sold privately and thereafter loaned to the Minnesota Institute of Arts – first came to their attention?
[* Although Grosvenor gives no indication of when or where he acquired the picture, he does track its history as far as 2006 when it fetched $3,120 at Christie’s, NY, in a 6 June sale, as lot 40, ‘After Van Dyck’.]
A RESEARCH AND ADVOCACY-LED BREAK-THROUGH
“Well, hurrah”, Grosvenor had cheered on 1 May 2014, “the National Portrait Gallery in London has successfully raised £10m to buy Van Dyck’s late ‘Self-Portrait’” – but note Grosvenor’s new description of the soon-to-become National Portrait Gallery picture: “Van Dyck’s “late ‘Self-Portrait’”. Why late and no longer last?
“I may write more about the acquisition process later”, Grosvenor went on, “but I’m quite proud to have been involved in both that and the process of research and advocacy that has resulted in the [NPG] portrait becoming what it is today. It’s certainly been a privilege to have handled the picture here at the Philip Mould Gallery. Seeing Sir Anthony in our offices every day made it feel as if he was part of the family. I don’t mind admitting that most days I would greet him with a quiet ‘Morning Ant’, and if I was the first in I’d positively shout it, and even give him a wave. He never waved back of course, but that vivid, knowing expression made it seem as if he was reciprocating in some way. And then there was the strange feeling of having Van Dyck look over us as we made the occasional discovery of a new work by him. These have included – if you’ll forgive the boast – the Portrait of Olivia Porter in the Bowes Museum, the Portrait of a Young Girl now hanging at the Ashmolean, two male full-length portraits painted by Van Dyck while he was in Italy, a Holy Family painted in Sicily, three important head studies, and his last Portrait of Queen Henrietta Maria as St Catherine. There are others which unfortunately I can’t tell you about – at least, not yet. I hope, now that he’s left us, the discoveries don’t dry up.”
THE THIRD VAN DYCK SELF PORTRAIT
Above, Fig. 20: Left, a photo accompanying Grosvenor’s 5 March 2015 post on a painting loaned as an autograph Van Dyck self-portrait to the Minneapolis Institute of Arts, Minnesota; right, a Grosvenor photo carried on 31 March 2015 with the caption: “Wanted – good homes for second-hand picture crates.”
So, yet other Van Dyck Discoveries-in-Waiting – but which would emerge next? Well, the one now hanging in the Rubenshuis museum had first been written up by Grosvenor in the December 2015 British Art Journal but, in 2018, Gleadell had reported in the Telegraph that Mould’s favourite Van Dyck upgrade “is a self-portrait that he found at auction in Germany, in 2012. Thought to be a copy and with a €30,000 estimate, he bought it for €572,000. By 2015 he had sold it on privately, since it appeared at the Minneapolis Institute of Art on loan from the American investment financier, Scott Minerd. Taking some credit for the change in status was Mould’s researcher, Bendor Grosvenor, now a TV presenter [etc….]” Presumably, with Mould having bought for only half a million, Minerd will have paid very considerably less for his attributed Van Dyck self-portrait than had the NPG for its now Grosvenor-shunted former “Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait”?
KNOCKING SIR OLIVER MILLER
Grosvenor had claimed his own credit on the upgrading of the Mould-to-Minerd self-portrait on 5 March 2015:
“The Art Newspaper seems to have scooped a story I’ve been dying to tell you about for some time; the re-discovery of an important self-portrait by Van Dyck. The picture was one of the last important portraits I worked on with Philip Mould in London.” Grosvenor then cited Martin Bailey’s Art Newspaper coverage:
“Martin Bailey writes: ‘A self-portrait by Van Dyck that was dismissed a decade ago as a copy is now hanging in the Minneapolis Institute of Arts, Minnesota, as an original work. The painting which has been authenticated by experts, was quietly put on display in February…An unpublished paper on the self-portrait, prepared for the owner, dates the work to around 1629 and states that this attribution is accepted by four key experts: Susan Barnes, a co-author [one of four] of the 2004 Van Dyck catalogue raisonné, Christopher Brown [*], the former director of the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford, David Jaffé [**], a former senior curator at the National Gallery in London, and Malcolm Rogers, the outgoing director of the Museum of Fine Arts Boston. The attribution is also accepted by Patrick Noon, the head of paintings at the Minneapolis Museum…The late Oliver Millar, another co-author of the 2004 catalogue raisonné, dismissed the work as ‘possibly a very early copy’. He assumed that the original painting was missing…’”
[* As senior curator at the National Gallery in 1982, Christopher Brown had been instrumental in the gallery’s £2.5m 1980 purchase of the Rubens Samson and Delilah. **David Jaffé, a successor as senior curator, strongly defended the picture’s acquisition and in 2005-6 organised the National Gallery exhibition, Rubens: A Master in the Making that showcased the Samson and Delilah. Conspicuously, neither of the contemporary copies of the original lost Rubens Samson and Delilah – which, as mentioned, had both testified to a wider composition in which Samson’s toes had not been cut off at the edge of the painting – were brought to the exhibition.]
Grosvenor continued: “The unpublished paper referred to above was written by me, and I’ll share further details with you soon. There’s a great deal to discuss. I think the picture was probably painted in late 1628. A few quick additional points: The Art Newspaper mentions that the late Sir Oliver Millar ‘dismissed the work’ – but in fact when he saw it at an Agnews exhibition in 1968 he pretty much accepted it. [Source?] Indeed, although the picture was little known and only exhibited once, it was continuously published as ‘a Van Dyck’ right up until 1999, and it was only in the 2004 Catalogue Raisonné co-written by Sir Oliver Millar that the picture was first doubted. I’m not sure why Sir Oliver changed his mind, but it was probaby [sic] due its pre-conservation condition; it had been substantially over-painted, and was also really quite dirty under old varnish. I believe Sir Oliver was perhaps also misled by the gold chain, thinking that chain was that given to Van Dyck by King Charles I, and that the portrait must therefore be an English-period work (that is, in the section of the catalogue that he was responsible for), dating to after 1632 – when Van Dyck’s technique was rather different. In fact, I linked hte [sic] portrait to a a [sic] gold chain Van Dyck was given earlier, in 1628 by the Archduchess Isabella in Brussels, when she appointed him her court painter…”
The paper for which Grosvenor claimed credit may well have formed the whole or part of this entry in the Mould gallery’s Historical Portraits Picture Library.
The Minneapolis picture, too, Mould reports, had gone into restoration. Had that been in London and, perhaps by the same restorer who sensitively “retrieved” the now Rubenshuis picture over a couple of years? Given that Grosvenor had researched this second, 2012 acquired, rival Van Dyck self-portrait and prepared a scholarly paper on it for the Mould Gallery, had either sleeper hunter informed the NPG of its presence in London before the gallery paid £10m for it’s then – but now Grosvenor-demoted “Last Van Dyck Self-portrait”?
If it might be thought a remarkable coup for all three Mould/Grosvenor Van Dyck self-portraits to have found homes in museums – the NPG, the Rubenshuis and Minneapolis – on this aspect, Grosvenor has shown a certain professional diffidence. Writing in the Financial Times of 3-4 March 2018 on the subject of collectors lending works to museums, he weighed the pros and cons of collectors lending and held: “Critics claim that museums are being used by lenders to enhance the value of their work…It is true that in some circumstances a period on loan can make an artwork better known, and thus more saleable. And there are other benefits to lending, too; the former National Gallery director Sir Nicholas Penny points out that museums can offer collectors the ‘double service of a free safety deposit with a shop window.’” Grosvenor hastened to add: “But the suggestion that a period of display can transform an artwork’s value is overblown…And while there undoubtedly are unscrupulous art owners, most collectors are driven not just by a passion for art, but by a passion to share it, too (disclaimer, this includes me; I have lent works anonymously since I started collecting over a decade ago)…at the Rubenshuis museum in Antwerp, which has only a small collection of its own and an even smaller budget, the well-publicised loan of a Tintoretto that once belonged to David Bowie helped increase visitor numbers by 30 per cent…It is time for museums to become the liggers of the art world, and borrow as much as they can. There’s a good chance they’ll get to keep it.” Grosvenor made no mention of his own loaned Last Van Dyck Self-Portrait, but we all get the picture, so to speak.
“CALL THE CONNOISSEURS!” – MOULD, GROSVENOR AND STUNT BID TO PRODUCE A NEW VAN DYCK CATALOGUE RAISONNÉ
Above, Fig. 21: Top, the entrance to the Paul Mellon Centre, London. Above, left, Bendor Grosvenor; centre, James Stunt; right, Philip Mould.
Leaving the Minneapolis Museum picture aside for Part II, we can now disclose that in 2014, Grosvenor and Mould jointly sought support from the Paul Mellon Centre to write a new catalogue raisonné on Van Dyck – and, also, that James Stunt had presented himself to the centre in support of the two dealers’ proposal with an offer to fund the costs of their proposed venture. It was a combined offer and proposal that could not be accepted, a) because the above-mentioned major catalogue – written by the four specialist Van Dyck authorities, Susan J. Barnes, Nora De Poorter, Oliver Millar, and Horst Vey – had been published by the Mellon Centre in 2004 and which work was then, as it remains today, widely regarded as an indispensable reference source; and, b) because the two would-be revisers were considered to have no real scholarly credentials to conduct such a massive and monumentally important art historical project.
When Mould and Grosvenor parted company (the latter with the rumoured £1m payoff) Waldemar Januszczak declared support for Grosvenor – and the pair now give joint podcasts (“WALDY AND BENDY’S ADVENTURES IN ART” on the Sunday Times’ fire-walled website.)
At 9.44 on 10 January 2021 Grosvenor tweeted the above “in-restauro” picture with this comment: “Ever fancied a go at cleaning a painting. In this week’s #WaldyandBendy we talk conservation and I have a go myself. It’s easy!”
GROSVENOR’S PROLONGED CALLS FOR A NEW VAN DYCK CATALOGUE RAISONNÉ
In August 2014 Grosvenor began disparaging past catalogues of Van Dyck’s work. Thus, of one painting on 19 August: “The above picture has recently gone on display at the Courtauld Gallery in London. It’s currently catalogued as ‘Van Dyck’. I think it was last published by the late Erik Larsen (whose Van Dyck catalogue raisonné is, alas, probably the worst single demonstration of connoisseurship ever published).” Ten days later in another post: “Surely, the most important pre-requisite in compiling a catalogue raisonné is not a degree in art history[*], but the confidence that you will be able to know for certain that your chosen artist really did paint the picture that some label/institution/scholar says they did…Now, I haven’t written a catalogue raisonné[**], but I have (and I hope this doesn’t sound too much like boasting, but there’s no other way of saying it) a proven track record of having a good ‘eye’. So for the benefit of any budding connoisseurs out there, I would add the following three crucial tips (obviously, this is all mostly relevant to Old Masters, and not modern and contemporary catalogues)…”
[* Although Grosvenor does not possess a degree in art history, having read modern history, his PhD dissertation on “The Politics of Foreign Policy: Lord Derby and the Eastern Crisis, 1875-8” might well have developed the usefully transferable research skills that were sometimes in evidence on the BBC’s Fake or Fortune programme. For sure, such desirable skills are not always inculcated within today’s university art history departments, so many of which prefer to fry almost any fish other than those of art and its history, but, as mentioned, Grosvenor has gone further and contended (AHN post, 29 August 2014) that “Actually, I’d be tempted to argue that a degree in history is more useful, as it gives a better training in how to evaluate evidence.”]
[** Tantalisingly, in a footnote, Grosvenor added: “Though that might be about to change!” But then… no further dangled hints of a new Grosvenor Van Dyck catalogue raisonné. As for Grosvenor’s not wishing to boast, some might chuckle – before relinquishing his career as a dealer and when temporarily shutting down his own website, he likened what he described as his “enemies” within the art trade to Salieris. As boasts go, likening oneself to Mozart might take some beating.]
FRUSTRATION AND IMPATIENCE WITH ACADEMIC IMPARTIALITY
Perhaps Grosvenor’s fullest expression of dissatisfaction with art historical scholarly expertise came in a March 2015 Art Newspaper piece (“Spare us the so-called experts and call for the connoisseurs”) which carried another Larsen-was-rubbish diatribe with an added slur: “The late Eric Larsen was a hopeless ‘expert’ on Van Dyck, and (it is said) took cash for attributions…Larsen’s example demonstrates two things. First, that it is dangerously easy to become ‘an expert’: all you need is a publishing contract. And second, that the art world – especially the art market – believes that if a painting is published in the latest book, it must be authentic no matter how bad or good that book is…In the quest for academic impartiality, however, we often ignore actual ability. True attributional expertise…can only be gained through years of experience…”
When Gleadell reported in 2018 that Grosvenor now prefers to keep his finds and is “quietly accumulating a small collection of discoveries of his own”, he added: “At this rate, the 2004 [Van Dyck] catalogue raisonné is going to need updating fairly soon – if everyone can agree on things, that is.” Perhaps Mould and Grosvenor have not altogether abandoned hopes of pulling off The Great Connoisseurship Double of being the art trade’s most proactive sleeper hunters and the arbiters of their own field?
In Part II we consider the Two Last Van Dyck Self-portraits on their relative artistic merits.
Michael Daley, 27 January 2021
The Art World’s Toxic Assets – Part III: Failures of Scrutiny
Within a couple of years of our warnings on the art world’s accumulating toxic assets of upgraded Old Master attributions, that sphere has been rocked by a spate of discovered/alleged old master forgeries that have recently deceived and embarrassed leading experts and major institutions alike.
In the midst of this turmoil, a Raphael-esque painting of insecure provenance (which is to say, of none before 1841), that relates to no known Raphael work, that is said to be good in parts and perhaps to have been a fragment of a lost unknown painting by Raphael, was launched to the world in the Guardian on October 3rd as a provisional “discovery” (“Raphael ‘copy’ once valued at £20 may be a £20m original”) to be shown on 5 October in a new three-part BBC4 series, “Britain’s Lost Masterpieces” [see Figs. 1a and 1b below]. The programmes were co-presented by an art historian, Jacky Klein, and a fast rising young player in the Old Masters attributions field, Bendor Grosvenor. Formerly of the Philip Mould Gallery and the BBC “Fake or Fortune” series, Grosvenor doubles as an art market commentator on a blog site, “Art History News” and, occasionally, for the Financial Times.
In the 8/9 October Weekend FT (“An eye for the real thing”) Dr Grosvenor held that the recently exposed failures of judgement constituted a scandal that threatens “to undermine the art world’s long established system of deducing authenticity”. He suggested that this danger stemmed from too great a reliance on the judgements of “independent, usually academic” experts who have published works on the artists they appraise, and from insufficient heed being paid to those (by implication like himself) who have not studied art history or published on artists but who, nonetheless, possess a “good eye”.
This recommendation was advanced even as Grosvenor admitted that he, along with France’s National Centre for Research and Restoration at the Louvre; a leading Louvre curator; numerous Frans Hals scholars; the Burlington Magazine; Christies (on scholarly advice); the Weiss gallery; and, Sotheby’s (at first), had been deceived by a recently exposed fake Frans Hals [Fig. 2, above], and, that he had come within a whisker of being deceived by a Gentileschi fake that snared the Guardian art critic and blogger, Jonathan Jones, and the National Gallery which had accepted the work as authentic when it was offered on loan (“Was the National Gallery scammed with a fake Old Master painting?”).
Where we held in the April 2006 ArtWatch UK Journal [Fig. 3, above] that too many in the art world were disregarding Mark Twain’s admonition to “buy land because they are not making it anymore” when buying upgraded school works as autograph masterpieces, Bendor Grosvenor often declares a state of rude good health in the old masters market. Because so many old masters have already been taken off the market and into museums, and because, by definition, old master paintings are no longer being produced, market growth increasingly depends on the discovery of “sleepers” – which is to say, of suspected hitherto unrecognised major works whose true identities will emerge during dealers’ un-monitored, sometimes radical stripping-down, repairing and retouching of paintings. (More recently we published a post that indicated means by which restorations might slide towards outright fakery in cases which, coincidentally, involved earlier “Frans Hals” paintings. See “A restorer’s aim – The fine line between retouching and forgery”.) On 13 August 2014 we called in a letter to The Times for a statutory requirement for vendors to disclose all that is known on a work’s provenance and conservation history [see Fig. 4, below]
On the BBC4 series “Britain’s Lost Masterpieces” Bendor Grosvenor got very excited at the prospect of a distinctly Raphael-esque painting in Haddo House in Scotland being an autograph Raphael [Fig. 1a]. BBC coverage of the visual arts rarely airs dissenting voices and this programme was constructed with many narrative layers all of which sang the same encouraging tune: Although this work has little provenance we should be assured by the fact that it had been bought in the early 19th century as an autograph Raphael by the 4th Earl of Aberdeen, George Hamilton-Gordon (1784-1860), who, in his early years and travels, was an impassioned devotee of the classical arts of Greece and Italy, and who somehow managed, despite being “flat broke”, to acquire a fine collection through a “shrewd nose for bargains”. Particular assurance was seen in the fact that the picture had been exhibited as a Raphael at the British Institution in 1841. However, an old hand-written label attached to one of two oak bars that reinforced the back of the poplar panel says, in English, “The Virgin Mary, Raffael or after Raffael” [see Fig. 1b]. As that is the only documentation (other than an indecipherable fragment of a wax seal) on the back of an assumed 500 years old panel, it would seem likely that the label was present when the painting was exhibited in 1841 as a Raphael. If it had not been present in 1841, why would its owner have added such a weakening document to his own painting?
The question of the label’s origin is the more perplexing because, as we now learn from Dr Grosvenor, the canny Scottish Fourth Earl of Aberdeen, George Hamilton-Gordon, had not bought the painting while on his early travels in Italy because he had not bought it all. Rather, he had inherited it more than a generation later from his brother, Robert Gordon, when he died in 1847 (by choking on a fish bone). The provenance thus descends entirely from Robert Gordon who was born in 1791 and would not likely have bought the painting (from whomever – for no one knows) much before 1810. Although Robert Gordon was the owner when the picture was exhibited at the British Institution, there are no family inventories listing the painting before 1867 and none thereafter lists it as a Raphael. In two entries it is priced at £80 and later at £20. On both occasions it was listed as a copy. In the television programme, the co-presenters describe seeing their perceived challenge as being to reverse a hypothecated “increasing scepticism” with which the painting was viewed after George Gordon’s death in 1860. But what if the Raphael attribution had always been appreciated within the family as being uncertain? Or, might not a contrary reading have been considered of the possibility that it only became politic for independent scholars to dissent on a claimed Raphael attribution after the death of the fourth earl who had been an extremely powerful and well-connected political figure – and one with with a sarcastic turn to boot?
Against the fragmentary picture’s distinctly weak provenance, it was claimed (- but not demonstrated) that a close fit existed with secure Raphael Madonnas. The belief that this work might be an autograph Raphael received high level scholarly and (implicit) institutional endorsement as Bendor Grosvenor is filmed ascending the grand stairs of the National Gallery’s Sainsbury Wing in the company of the Gallery’s former director, Sir Nicholas Penny. The camera catches the pair passing the monumental carved Roman Letters “RAPHAEL” [see Fig. 5, below] and jumps in a nanosecond to a painting in the Gallery’s substantial Raphael holdings – but not to one its finest, instead to the least secure, most recent, so-called Madonna of the Pinks that had been attributed to Raphael in 1992 by Nicholas Penny when a curator at the Gallery, and that was later bought by the Gallery for nearly £35millon after a public appeal. Towards the end of the film [Fig. 6, below] Nicholas Penny places the putative Grosvenor-Raphael, somewhere between “probably by Raphael” and “by Raphael” and suggests that with a little “more time and courage” he might well go the whole hog.
Above, (top – and running clockwise), Figure 5: Bendor Grosvenor passes the monumental carved “RAPHAEL” in the National Gallery’s Sainsbury Wing; the National Gallery’s (disputed) Raphael Madonna of the Pinks; the Bendor Grosvenor-proposed Haddo House Raphael Madonna, before restoration; and, the National Gallery’s Madonna of the Pinks, as presently framed. Above, Fig. 6: Jacky Klein, Bendor Grosvenor and Nicholas Penny seen examining the Haddo House Madonna in the 5 October BBC4 “Britian’s Lost Masterpieces” programme.
Although a caveat was offered in the programme (and reported in the Guardian) with an admission that there had not been the time and money to run all appropriate tests, Grosvenor nonetheless claimed that all the evidence seemed to point in the right direction. As if to dispel any doubts, the television programme (which was produced by Tern TV and commissioned by Mark Bell, Head of Arts Commissioning, BBC, under the Executive Producer for the BBC, Emma Cahusac) carried a strong implicit message that the Grosvenor-proposed Raphael is as sound as the National Gallery’s Penny-attributed Raphael Madonna of the Pinks. We would counter that, with both pictures, such assurances were misleading and that the principal evidence on the strength of these attributions is found in the look of the pictures, which testify in different ways[ see Fig. 5] against Raphael’s authorship, as will be shown in Part IV.
We would add two points here. First, that Dr Grosvenor seems unaware of the extent to which the Madonna of the Pinks had been rejected as by Raphael in the 19th century and more recently by scholars including Professor James Beck, the founder of ArtWatch International who devoted three chapters of his last (2006) book, From Duccio to Raphael – Connoisseurship in Crisis, to problems with the present attribution [see Fig. 7, below]. Although Nicholas Penny is a highly respected Renaissance specialist, and his Raphael attribution had been fittingly proposed in a long, thorough scholarly article in the Burlington Magazine (“Raphael’s Madonna dei garofani” Rediscovered, 134, 1992) that had impressed Professor James Beck, the attribution itself received only majority approval from a group of specialist scholars assembled at the National Gallery. Contrary to initial Gallery press claims, there had been no firm consensus of scholarly opinion – a fifth of the invited scholars dissented from the attribution when questioned directly by Beck.
At the time, we pointed out that the then majority for support had reversed over a century’s scholarly consensus of judgement. The Penny-Raphael had been rejected as early as 1854 by Gustav Friedrich Waagen as “the small picture in the Camuccini collection which I do not consider to be original. The tone of the flesh has something insipid and heavy. The Treatment makes me suspect a Netherlandish hand.” Professor Martin Kemp rejected the Penny-Raphael Madonna on the grounds of her most disconcerting and uncharacteristic teeth-baring opened mouth: “In reality, for any Renaissance woman to be portrayed showing her teeth, American-style, is unthinkable”. (Leonardo, Oxford/New York, 2005, p. 242.)
There were structural problems with the picture, as well as stylistic incongruities. In the 2003 ArtWatch UK Journal 29, we drew attention to the disturbing fact that the National Gallery’s Madonna of the Pinks Raphael – like the Gallery’s (challenged) Rubens Samson and Delilah painting – had lost vital physical and documentary evidence. With both paintings the original, evidence-bearing back is missing, as is also the case in the drawing that has been dubbed “La Bella Principessa” and given to Leonardo da Vinci by Martin Kemp, even after it emerged that the supposedly 500 years old work had been sold anonymously and without a shred of provenance by the widow of a restorer who was the work’s first known and sole owner. That atypical drawing on an atypical medium has been (unusually) glued down onto an oak panel, thereby preventing an appraisal of drawings known to be present on its reverse.
The Samson and Delilah panel painting had been planed down to wafer thinness and glued onto a modern sheet of blockboard in an operation of which no record exists. The back of the Madonna of the Pinks was “polished”, coated and given three wax seals in the 19th century when in the hands of its first known owners, the notorious Camuccini family
of artists, copyists, restorers, art dealers and art smugglers. We cited much else that was problematic about the Madonna of the Pinks:
“It possesses, for example, an irregular border of unpainted wood that is ‘unusual’ for Raphael. The picture’s unusually highly-wrought finish, ‘jewel-like, as Dr Ekserdjian and associates put it; made up of ‘tiny, almost invisible brushstrokes’, as the National Gallery puts it, is said to have been the result of the work’s especial execution for the close contemplation of a nun…Even if this fanciful explanation for the unusual brushwork were to be accepted, it would not also explain the picture’s atypical colour scheme [which] Dr Penny suggests, may reflect ‘a particular moment of indebtedness by Raphael to Leonardo…’ ”
We complained that “Dr Penny’s case seems to rest on the belief that the outcome of technical analysis carried out at the National Gallery somehow displaces or neutralises all accumulations of otherwise awkward evidence…A manifest weakness of Dr Penny’s case is that no technical analysis or even photographic comparison is offered on any of the picture’s forty or so rival contenders…” It was later learned that scientific analysis had identified the wood of this most unusual artefact as being, not poplar, as might have been expected, or even a fruit wood, as is the case with one large Raphael panel, but yew – a wood nowhere encountered in Raphael or, so far as we know, in any Italian Renaissance painting. As will be seen in Part IV, the proposed Grosvenor-Raphael bears many handicaps.
Michael Daley, 20 October 2016