ArtWatch at Thirty, Part II: The Artful Promotion of the World’s Worst Restorations

15 APRIL 2023. MICHAEL DALEY WRITES:
In Part I we set the 1980-1994 cleaning of Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel frescoes in the era’s ambitiously experimental and accident-prone restorations. Here, we examine the art-historically untenable scholarship that arose when Michelangelo’s debilitated frescoes were endorsed as if constituting revelations that merited a rewritten history of art. Three decades on, identifying and examining the polished art-political stratagems that draw so many scholars and art critics into supporting egregiously destructive restorations remains a matter of professional urgency.

Above, Fig. 1, Top: National Geographic’s iconic photo-record of the Sistine Chapel ceiling which captured the last moments of the most acclaimed late stage of Michelangelo’s painting, including his The Crucifixion of Haman, the Prophet Jonah, and the Libyan Sibyl. Above, the post-cleaning, LED-lit chapel. When unveiled in 1512, the then brilliantly lit and shaded figures set in deep architectural spaces were eulogised for having made surfaces which physically advanced towards the viewer recede optically through Michelangelo’s powers of design and unprecedented deployment of lights and shades. At the time, no one spoke of Michelangelo’s colour – “brilliant” or otherwise.
TWIN AND CROSS-LINKED ASSAULTS ON A CRITIC
On 8 October 1987, halfway through the cleaning of the Sistine Chapel Ceiling, the restoration’s leading scholarly critic, Professor James Beck, Chairman of Columbia University’s Art History and Archaeology Department, was branded the “most culpable of the critics” by Sir John Pope-Hennessy in the New York Review of Books (“Storm Over the Sistine Ceiling”). Two months later, that attack was followed by another in the December Apollo magazine by Kathleen Weil-Garris Brandt (“Twenty-five Questions about Michelangelo’s Sistine Ceiling”). Like Pope-Hennessy, Brandt was a professor of Renaissance art at New York University’s post-graduate art history school, The Institute of Fine Arts (which incorporates a Samuel H. Kress Program-sponsored conservation department), and she was considered a long-standing friend by him.
Brandt characterised the restoration’s critics as “a tiny, heterogenous and vociferous cadre”. She likened their arguments to “the wild cries of some ferocious mutant of Chicken Little” and added “Many believe that the critics, like that benighted bird, were misunderstanding insufficient evidence, to draw mistaken conclusions to the alarm and detriment of the neighbours.” She conceded the issue “is a serious one” but only the better to sting: “Are the critics merely opportunists, bodysurfing in a wave of publicity they would never otherwise have enjoyed?” In his 2016 memoir, Michelangelo and I, Gianluigi Colalucci, the restorer/co-director of the Sistine Chapel restorations, described Brandt as “sweet and gentle in appearance but with a character of steel” who, having “obtained her own office in the museum complex”, had “put just about everybody under pressure with her inflexible activity”.
“THINGS ARE NOT AS YOU THINK”
There were degrees of hypocrisy in both attacks. Pope-Hennessy’s charge of professional culpability had followed his invitation to Beck to serve on a Metropolitan Museum Advisory Committee. As Colalucci would later disclose, Brandt’s denigration was not made as the self-effacing and disinterested scholar she had implied in Apollo – “Like many Renaissance scholars, I have held a kind of informal watching brief for the cleaning operation since its inception in 1981 [sic] and I talk on the subject with groups and individuals of all kinds.” Formally speaking, Brandt had two dogs in this fight. First, she had obtained her Vatican office as the official spokesman on “Scholarly and General information” for Arts and Communications Counsellors, a division of the New York Public Relations firm Ruder and Finn Inc. which had been retained by the Vatican to handle the restoration crisis. Second, she was a member of a shadowy, secretive scientific advisory committee the Vatican had set up, ostensibly, to monitor the controversial restoration. On learning of that committee, Colalucci threatened to resign but was dissuaded by his restoration co-director, Fabrizio Mancinelli, who urged him to calm down because: “You’ll see that things are not as you think…” In due course, Colalucci recalled, “we were given to understand that the findings were positive”.
As will be shown in Part III, the ploy of an institutionally self-appointed, supposedly invigilating but intended exonerating body, had been honed at the National Gallery in 1947 and 1967. Given the importance of the greatest art, whenever major restorations are started, they must, of political necessity, be defended unequivocally for the duration and at length thereafter, for fear of triggering institutional melt-downs. When a restoration of sacred art in a sacred place is funded in advance by a foreign corporation in a commercial exchange for film and photography rights, any admission of error becomes doubly inconceivable. Little surprise therefore that, as Colalucci disclosed, the Vatican’s own scientific advisory committee remained in place as a supportive “working group” throughout the entire restoration of Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel frescoes. Headed by André Chastel, this group’s members, in addition to Brandt, were:
“Carlo Bertelli of Lausanne University, initiator of the restoration of Leonardo’s Last Supper executed by Pinin Brambilla [See: The Perpetual Restoration of Leonardo’s Last Supper, Part I: The Law of Diminishing Returns]; Pierluigi De Vecchi, an expert on Michelangelo; Sydney J. Freedburg from Washington; Giovanni Urban[i] former director ICR [the Istituto Centrale di Restauro]; Luitpold Frommell and Matthias Winner, directors of the Bibliotecca Hertziana in Rome; Umberto Baldini, director of the ICR [and head of the Brancacci Chapel restoration]; Michael Hirst, an expert on Michelangelo’s drawings; John Shearman, an expert on Raphael and the Sistine Chapel…The restorers were Alfio Del Serra from Florence…and Paul Schwartzbaum from New York, head of the ICCROM school and projects in Rome. Norbert Baer from New York University was the only chemist.”
THE SAMUEL H. KRESS FOUNDATION INTERVENTION
Colalucci aired a secondary grievance concerning the advisory committee in 2016: “By express desire of Chastel and the other members, we were not allowed to inform the press of the work of this group of experts, even though it would have been of great benefit to us because” [the quasi-invigilators] “wished to keep a low profile and avoid the attention of the already overly excited public opinion”. However, “Shortly afterwards, Marilyn Perry, the pleasant and dynamic president of the Kress Foundation, set up another working group, this time consisting almost exclusively of restorers on her own initiative.”
“The members were Mario Modestini, the foremost restorer in America; John Brealey, director of the restoration department of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York; the young Dianne Dwyer, then assistant to John Brealey [see Fig. 11 below]; Andrea Rothe, director of the restoration department of the J. P. Getty Museum in Malibu; David Bull, director of the restoration department of the National Gallery in Washington [see Figs. 2 and 3 below]; and Leonetto Tintori, a highly skilled restorer from Florence [see Fig. 3 below].
“The group’s task was to monitor our work, give advice and put forward criticisms. The [single] meeting was very fruitful and ended positively with a report drawn up [by] the members of the group aimed in particular at public opinion in the United States.”
The resulting open letter from this committee to the American press executed its expressly intended effect to perfection. In April 1987, Time’s art critic, Robert Hughes, claimed:
“…most experts on Renaissance art, and on Michelangelo in particular, strongly endorse it and reject out of hand the anti’s allegation of haste or insufficient study…Last week a further vote of confidence came from the Samuel H. Kress Foundation, a long-established non-profit organisation concerned with the care and preservation of Italian art. Six of the world’s leading conservators… reported in an open letter that the ‘new freshness of the colours and the clarity of the forms on the Sistine Ceiling, totally in keeping with 16th century Italian painting, affirm the full majesty and splendor of Michelangelo’s creation’”
John Russell reported in the New York Times:
“An international Group of leading conservators of Italian paintings has given its unanimous and strongly enthusiastic approval to the current restoration of Michelangelo’s frescoes in the Sistine Chapel in Rome…Though not intended as a riposte to recent criticism of the restoration the report could be said to rebut the attacks that have been made upon it. Among those who have opposed the restoration are Prof. James Beck of Columbia, Alexander Eliot, formerly of Time Inc. and a group of 14 American artists who asked the Pope to halt the work…”
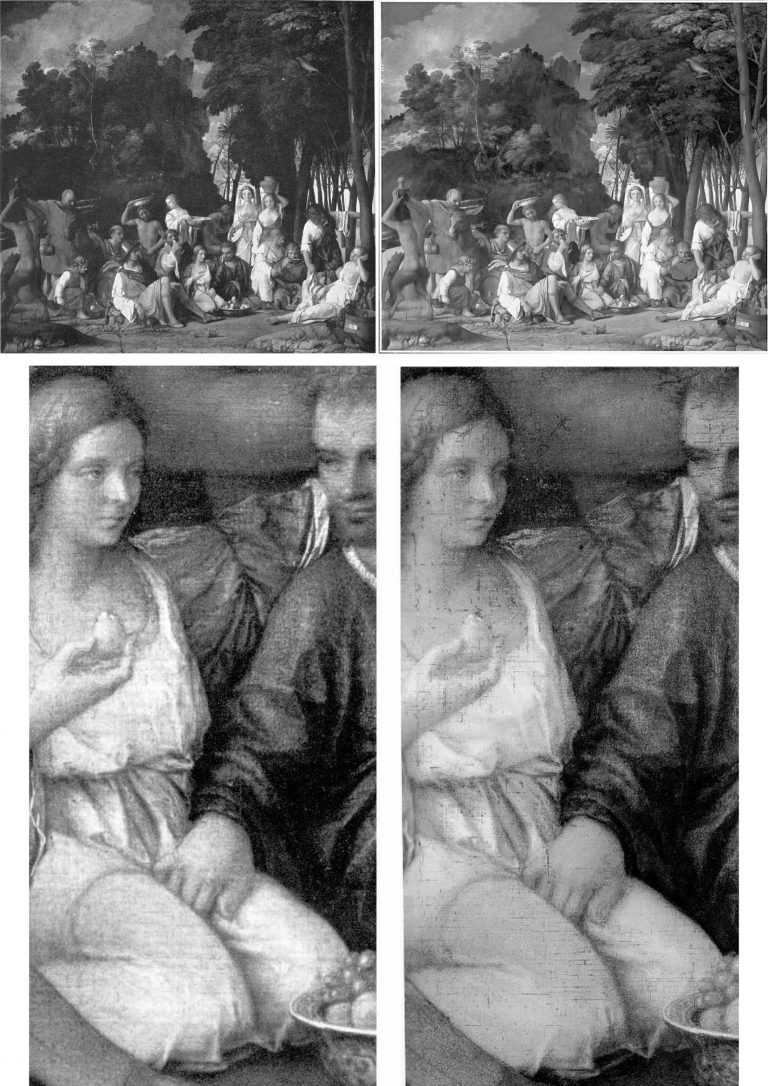
Above, Fig. 2: Top, the David Bull-restored Bellini/Titian Feast of the Gods, (before cleaning, left; after cleaning, right); below, a detail before cleaning, left, and immediately after cleaning, right. If Bull had simply removed a discoloured film of varnish, the previously discernible tonal values would have emerged enhanced – and not, as seen, diminished, compressed, and with a flattening of previously tangible forms. Such losses were Bull’s forte: when he restored Turner’s Rockets and Blue Lights (Fig. 3, below), one of the picture’s two distressed steamboats disappeared and its plume of once-black smoke was painted into a waterspout. (When that restorations-wrecked picture was sent to the UK on a tour, credulous British art critics took their lead from a Tate Gallery press release and gushingly proclaimed it “One of the stars of the show”.)
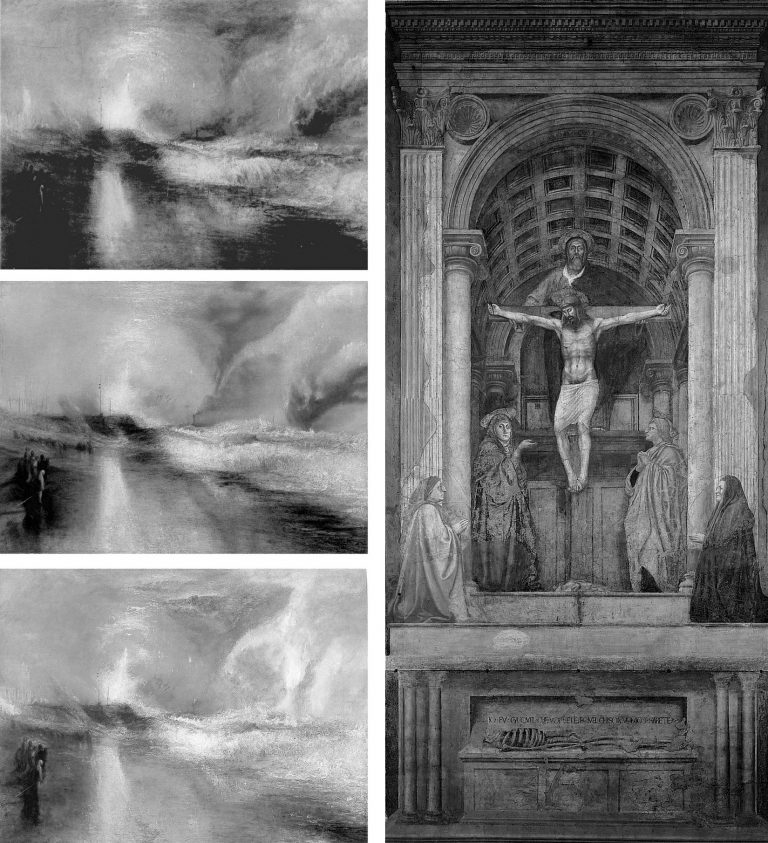
Above, Fig. 3: Left, Turner’s painting of two steamboats in distress, “Rockets and Blue Lights…” as seen in: 1896 (top); 1934 after restoration by William Suhr (centre); 2003 after restoration by David Bull (above). Right, Massacio’s Holy Trinity in the Santa Maria Novella, Florence, after restoration by Leonetto Tintori.
SUCKERED ART CRITICS
Where the Kress Committee’s open letter achieved immediate propagandistic effect, it took time for the claimed unanimity of its expert endorsement to dissolve. In a 28 April 2012 post we made the following (uncontested) disclosures:
“ArtWatch has been haunted for two decades by a nearly-but-not-made restoration disclosure. In the 1993 Beck/Daley account of the Nippon TV sponsored Sistine Chapel restoration (Art Restoration: The Culture, the Business and the Scandal), we reported that in the late 1980s Leonetto Tintori, the restorer of Masaccio’s Holy Trinity in the Santa Maria Novella, Florence [Fig. 3, above] and a member of the international committee that investigated the controversial cleaning, had urged the Sistine team privately to preserve what he termed ‘Michelangelo’s auxiliary techniques’ which in his view included oil painting as well as glue-based secco. What we had not been able to say was that Tintori (who died in 2000, aged 92) had prepared a dissenting minority report expressly opposing the radical and experimental cleaning method.
“Shortly before the press conference called to announce the committee’s findings, Tintori was persuaded by a (now-deceased) member [Fabrizio Mancinelli] of the Vatican not to go public with his views. He was assured that his judgement had been accepted and that what remained on the Sistine Chapel ceiling of Michelangelo’s finishing auxiliary secco painting would be protected during the cleaning. With a catastrophically embarrassing professional schism averted, the restoration continued and the rest of what Tintori judged to be Michelangelo’s own auxiliary and finishing stages of painting was eliminated. Without knowledge of Tintori’s highly expert dissenting professional testimony, the public was assured that despite intense and widespread opposition the cleaning had received unanimous expert endorsement. Critics of the restoration were left prey to disparagement and even vilification.”
Our 1993/2012 claims on the dissent within the international committee had been double-sourced by James Beck and the Florence-based art historian Richard Fremantle in conversations with Tintori (a member of ArtWatch). They became triple-sourced and document-backed on 8 June 2011 when the Titian expert and former director of the Warburg Institute, Professor Charles Hope, gave the following account when delivering the third James Beck Memorial Lecture (“The National Gallery Cleaning Controversy”) at the Society of Antiquaries, London:
“It would be unrealistic to suppose that those directly involved in the restoration would willingly concede that large areas of Michelangelo’s own work were removed. But even those who believe that the restorers did a good job ought to recognise that much of the controversy could have been avoided if a more careful assessment of the art-historical evidence had been carried out before the restoration began. But no serious investigation was made of the records of earlier restorations, the issues raised by Wilson were not addressed, and Vasari’s testimony was accepted as conclusive evidence that Michelangelo only used buon fresco, without any recognition of its problematic character (which was well understood in the nineteenth century) and without any discussion of the evidence of Armenini. In this context, one might also mention an article in the 1995 Revue de l’art by Leonetto Tintori, the most experienced restorer of Tuscan frescoes of his generation, who died in 2000 at the age of 92. Tintori was consulted about the desirability of restoring the ceiling, and I understand that he opposed it. The most important point in his article is that the technique supposedly used by Michelangelo on the ceiling, buon fresco alone, with only very small additions in secco, was entirely inconsistent with the practice of other painters in Tuscany, from Buffalmacco to Lippi and Sarto; and the same point was made by Eve Borsook [art historian and author of the 1960 and 1980 The Mural Painters of Italy] in the same journal. Tintori ended his article by deploring the modern practice of ever deeper cleaning, concluding, ‘This new orientation aimed at the total restitution of the original paint has had the paradoxical effect that the appearance of pure authenticity has become increasingly rare.’ Given his membership of the [Kress-assembled] committee that recommended, apparently against his own advice, the restoration of the ceiling, he could hardly have attacked the results explicitly, but it cannot be by chance that he chose to say what he did, a year after the publication of the [Vatican’s] final restoration report.
WHO HAD KNOWN OF TINTORI’S DISSENT?
In his 2016 memoir, Colalucci made no mention of Tintori’s opposition or his 1995 Revue de l’art views on the destructiveness of the Sistine Chapel restorations – his sole reference to the opposing restorer came in his above-cited composition of the Kress committee. Presumably, all other members of the working group – Modestini; Brealey; Dwyer [-Modestini]; Rothe and Bull had known of his opposition, as had Mancinelli. Perhaps Marilyn Perry and Colalucci had not known, but, certainly, Robert Hughes, John Russell, and very many other journalists were duped. Brandt gave no hint of Tintori’s opposition in Apollo but she stopped fractionally short of claiming unanimity:
“Everyone agrees with David Bull, Head of Paintings Conservation at Washington’s National Gallery of Art, that ‘the work being done on the frescoes should be meticulously watched, examined and questioned… (Fresco conservators seem not to be disturbed by the cleaning.)”
POPE-HENNESSY’S ATTACK ON BECK
When dubbing Beck the most culpable scholar/critic, Pope-Hennessy detached himself from his professional obligations:
“If you are an art historian, it is essential to free yourself from the fetters of your profession. The Sistine Ceiling is no more the property of art historians than the Ninth Symphony is the property of musicologists.”
The analogy was perversely inapt: in the Sistine Chapel, two recently appointed young officials – an art historian/curator and a quasi-scientific restorer – were rewriting a score they had ignorantly/wilfully misread in defiance of their predecessors’ views and reports and they were demanding that musical history be re-written to sanctify their systematic adulterations.
Pope-Hennessy was not alone in standing on such treacherous ground – he was running with a pack. His denunciation of Beck was made in a review of the 1986 book The Sistine Chapel: The Art, the History, and the Restoration (- published in the UK as The Sistine Chapel: Michelangelo Rediscovered). The book carried accounts from the three principal Vatican agents of the restoration: Professor Carlo Pietrangeli (Director General of the Vatican Museums); Dr Fabrizio Mancinelli (Curator of the Vatican Museums’ Byzantine, Medieval and Modern collections); and Gianluigi Colalucci (the Vatican’s Chief Restorer) – the latter two being the restoration’s co-directors. Their views were implicitly endorsed by accompanying scholarly essays from André Chastel, Pierluigi de Vecchi, Michael Hirst, John O’Malley, and John Shearman. The book was co-published by the Nippon Television Network Corporation which had sponsored the 1980-1994 restoration for $3million in exchange for all film and photography rights throughout each of the restoration’s three stages (the upper wall lunettes; the ceiling; and the Last Judgement altar wall) and for three years afterwards on each part.
INDEFENSIBLE METHODS
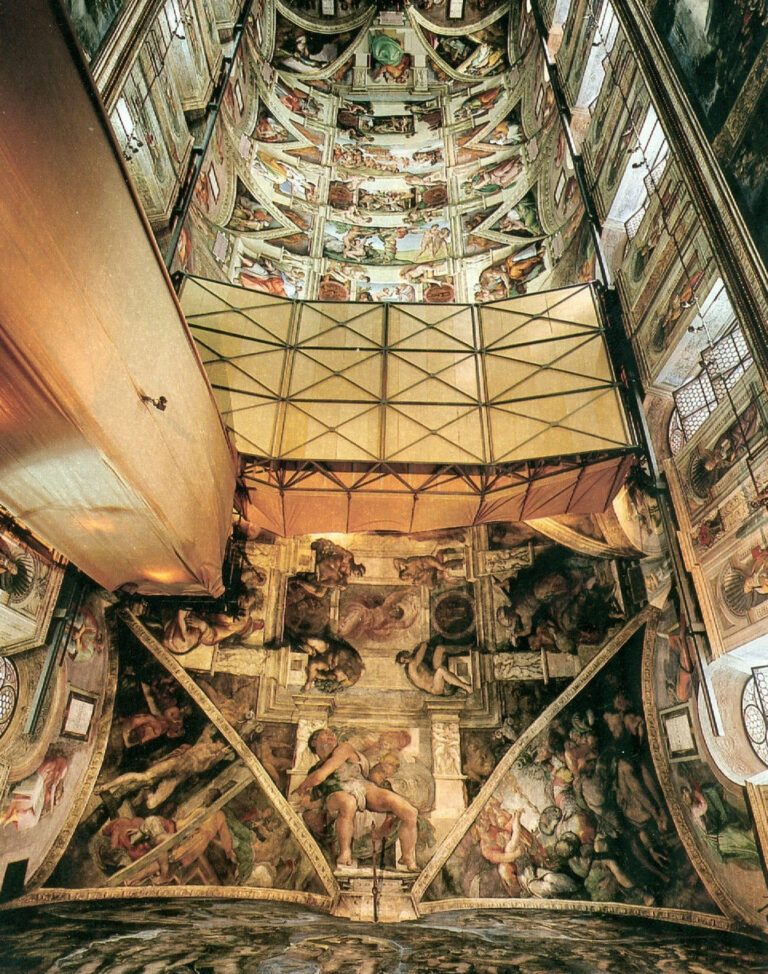
Pope-Hennessy appreciated that the restoration breached fundamental protocols by being conducted piecemeal on a narrow, enclosed platform when under intense film-set lighting that denied the restorers any means of appraising the actions and artistic effects of their radical, oven cleaner-like gelled cocktail of soda, ammonia, and detergents. (See Figs. 1 and 4.)
The cleaning paste, AB57, had been formulated to strip all historic organic materials from the plaster surface in two three-minute applications set twenty-four hours apart and removed each time with copious amounts of sponged water. The solvents-contaminated rinse water saturated the fresco plaster so completely that underdrawings on a lower plaster layer became visible. Empty assurances were given that a new air-conditioning system would protect the newly exposed bare plaster surfaces from the Chapel’s notoriously high levels of dirt, humidity, and fluctuating temperatures. Reports later emerged of secret night-time removals of white powder accumulations on the ceiling frescoes. By 2013 the ceiling had been lit to brighter and more colourful effect with powerful LED lights, when the chief defence of the restorers had been their supposed recovery of originally brilliant colours. See “The Twilight of a God: Virtual Reality in the Vatican” where we asked:
“Given this recent history, might Prof. Brandt – or any of the restoration’s supporters at that time – ever have imagined that within a couple of decades the Vatican would conclude that the chromatically brilliant ‘New Michelangelo’ would require artificial lighting ten times more powerful than that installed at the time of the restoration?”
In 2016, Colalucci blamed the chapel’s initially too-powerful levels of artificial lighting for the cleaning controversy itself:
“None of us had realized that after cleaning, these frescoes needed minimal lighting in order to be seen correctly. We should have considered the fact that, having been painted to be seen solely in light from the windows or candles and torches, they would look wrong in very brights lights such as television crews use.”
Despite the claim that the restoration had recovered an original intense chromaticism in Michelangelo’s painting that required low levels of lighting, the apparently natural light entering through the chapel’s windows was subsequently turbo-charged:
“…in the end the entire lighting system was revolutionized and moved outside with quartz lamps behind the window panes in accordance with a project devised by the technical department for a combination of natural and artificial light. Today with the new [LED] technologies, the Vatican Museums have installed a new lighting system with good results.”
THE STILL-UNSOLVED ATMOSPHERIC POLLUTION PROBLEM
On 10 January 2013 we reported:
“It is now clear that having first engineered a needless artistic calamity, the Vatican authorities have additionally contrived a situation in which the already adulterated remains of Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel frescoes are presently in grave physical peril. On January 2nd 2012 Art Daily carried an Agence France-Presse report on the panic that has beset the Vatican authorities over the present and worsening environmental threat to the Chapel’s frescoes:
“The Vatican Museums’ chief warned that dust and polluting agents brought into the Sistine Chapel by thousands of tourists every-day risk one day endangering its priceless artworks. Antonio Paolucci told the newspaper La Repubblica in comments published last Thursday that in order to preserve Michelangelo’s Last Judgment and the other treasures in the Sistine Chapel, new tools to control temperature and humidity must be studied and implemented. Between 15,000 and 20,000 people a day, or over 4 million a year, visit the chapel where popes get elected, to admire its frescoes, floor mosaics and paintings. ‘In this chapel people often invoke the Holy Spirit. But the people who fill this room every day aren’t pure spirits,’ Paolucci told the newspaper. ‘Such a crowd… emanates sweat, breath, carbon dioxide, all sorts of dust,’ he said. ‘This deadly combination is moved around by winds and ends up on the walls, meaning on the artwork.’ Paolucci said better tools were necessary to avoid ‘serious damage’ to the chapel… The Sistine Chapel, featuring works by Michelangelo, Botticelli and Perugino, underwent a massive restoration that ended in the late 1990s. The restoration was controversial because some critics said the refurbishing made the colours brighter than originally intended.”
POPE-HENNESSY’S MANIFEST AMBIVALENCE
Without addressing the invasive actions of AB57 – the use of which had been condemned by restorers, scientists, artists, and art historians – or the abnormal film lighting – Pope-Hennessy did acknowledge some of their artistically disruptive consequences:
“On the other hand, it must be recognised that the effect made by any section of the fresco is contingent on the cleaning not only of that section but of the areas contiguous to it. The figure of God the Father in the Creation of the World could be cleaned faultlessly, but it would appear less dominant if the equation between the figure and the fictive moulding around it were disturbed. This has occurred in the first half of the ceiling…where the upper strip of the [fictive architectural] framing is now too light. If this happened in the second half of the ceiling, there would be protests that the Genesis scenes had been diminished or spoiled. The present width of the scaffolding is the equivalent roughly of one bay of the ceiling, and it is extremely difficult when standing on it to judge the relationship of the part of the ceiling that is within touching distance to the cleaned part beyond. I have repeatedly wondered whether it would not be prudent in the second half of the ceiling to employ a platform of double width, even at the cost of denying a larger area of the fresco to current visitors.” (Emphases added.)
Above, Fig. 4: The Sistine Chapel ceiling showing the restorers and film-makers’ platform approaching the most brilliant, deep-space final stages of Michelangelo’s painting.
“TO RESTORE OR NOT TO RESTORE” – COLALUCCI’S BREACH OF PROTOCOLS
Had Pope-Hennessy’s suggestion been made and accepted (thereby tacitly acknowledging an unsound seven-year long procedure) it would have had no effect. Colalucci had stipulated the pre-set, no variations, two three-minute AB57 applications precisely to prevent his restorers from making individual appraisals for fear of undermining his desired aesthetic homogeneity. As he put it in 2016: “I wanted to have every square centimetre under my control and was reluctant to expose others to the risk of failure or controversy.” We can now be clear that this restoration truly was one man’s folly. On his unwarranted and unfounded insistence that Michelangelo had not painted on the fresco surface, the restoration was reduced to the brutally simplistic and non-artistic goal of executing the most technically expeditious removal of all historic materials from the plaster surface – which, in truth, was to say, primarily, the last stages of Michelangelo’s own work. For this reason, even if the restorers had been able to compare the already cleaned fresco sections with the one being cleaned, they had no authority to depart from Colalucci’s twin, three-minutes AB57 applications procedure. Later, in self-exculpation at a Kress-organised conference in New York, Colalucci claimed that the heat and the brilliant film-set lighting had “fatigued the eyes” and made aesthetic appraisals impossible – when the decision to clean with AB57 had been taken before the deal with the Japanese film-makers had been struck.
On his own admission, Colalucci had sanctioned a procedure that breached the most fundamental restoration protocol of all – and one that had recently been stated by Professors Paolo and Laura Mora, the inventors of AB57 – that, at all times, the restorer and not the cleaning agent itself must assume responsibility for all the resulting changes of appearance in the work of art. The absence of declared support for the Sistine restorations by the Moras themselves is conspicuous. My (Leonardist) colleague, Jacques Franck, recalls – and may still possess – a 1980s Italian newspaper report in which it was claimed that the Moras had resigned from a Vatican committee because they had judged AB57 (which had been developed to remove traffic pollution from Rome’s marble buildings) unsuitable for Michelangelo’s frescoes. Had they been invited to serve on the Kress-assembled committee, along with Tintori – and if not, why not? Or on the Vatican’s own committee? Our researches had found a single enigmatic comment on the subject. In the Summer 1987 Art News (“Michelangelo Rediscovered”), M. Kirby Talley, Jr. wrote: “The decision to restore the Sistine frescoes was not taken lightly. ‘To restore, or not to restore, that’s the question you have to ask yourself every time you are confronted with a problem.’ cautioned Professor Laura Mora, restorer at the Istituto Centrale del Restauro and a leading authority on fresco conservation.” Talley continued: “This question was posed by the Vatican authorities, and the pros and cons were scrupulously weighed before the final go ahead was given”. No doubt they were, but the fact remains that contrary to the Kress-driven propaganda coup that may have turned Pope-Hennessy, three – and arguably, the top three – leading fresco authorities had not been on the scales. Brandt brought no clarification on the matter in Apollo with her gnomic observation “Fresco conservators seem not to be disturbed by the cleaning”.
SACRIFICING MICHELANGELO’S “COMMUNICATIVE POWER”
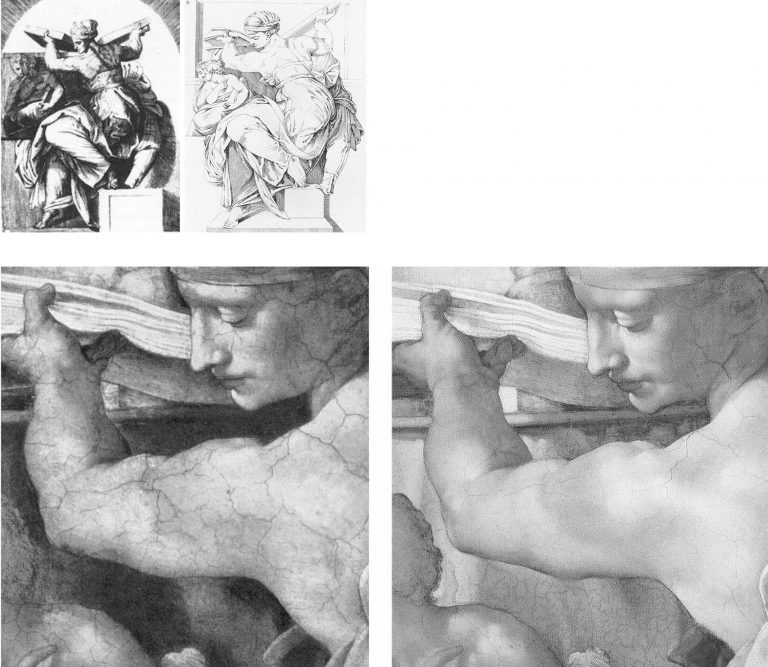
Above, Fig. 5, top: two engraved copies of the Libyan Sibyl, both of which showed the Sibyl’s left arm relieved by a tonally dark background; above, a detail of Michelangelo’s Libyan Sibyl before (left) and after (right) Colalucci’s cleaning and showing the profound and systematic losses of Michelangelo’s secco-extended tonal range of shading and aerial placements. As well as making broad-brush tonal adjustments, Michelangelo had – as Charles Heath Wilson had testified in the late nineteenth century (when very closely examining the ceiling from a special scaffolding) – also drawn secco revisions to contours and to many details such as hair and eyes. In the above photo-comparison, it can be seen that many lines which had clarified and reinforced details like the Sibyl’s thumb, lower jaw, the hair band, and the edges of the giant book, had all perished in Colalucci’s soda/ammonia/detergent double-washing. Further, Wilson had supplied an incontrovertible material/scientific proof that the secco painting was Michelangelo’s own: the secco painting had cracked as the plaster had cracked. The ceiling had begun cracking in Michelangelo’s own lifetime. Had the painting been applied centuries later by subsequent restorers, as the Vatican claimed on no evidence, it would have run into the cracks. It had not run into the cracks – but the world heard nothing of this: Wilson’s crucial, utterly subverting testimony on the secco painting had been air-brushed out by all players at the Vatican and, wittingly or unwittingly, by all of their art historical supporter/apologists.
For his part, Pope-Hennessy harboured and instanced futher (well-founded) aesthetic and historical anxieties:
“…you come in, as you have always done, through the little door under the Last Judgement and look up, speechless at the rebellious Jonah, the melancholy Jeremiah, and the Libyan Sibyl heroically supporting her colossal book [Fig. 5, above]. But about halfway down the chapel is a scaffolding resting on rails along the walls, covered with mustard-coloured fabric on which appear the shadows of ordinary mortals busily at work. [Fig. 4, above.] Beyond it you look towards the Zechariah, the Joel, and the Delphic Sibyl, suffused with light and seemingly the work of another, more lively, more decorative artist…Inevitably, judgement contains a strong subjective element, the more so as two kinds of verdict are involved, short-term judgement dominated by pleasure at the unwonted freshness of paint surface and long-term judgement in which one asks oneself whether the image has the same communicative power that it possessed before… Each time I go back to the chapel and sit, as I have so often sat, before the pitted surface of the Jeremiah, I feel concern that future generations may be denied an experience that raised the minds and formed the standards of so many earlier visitors. This is the basis of the claim of Beck and many others that the cleaning should be suspended at this point.” (Emphases added.)
Against all of which, he baldly insisted: “If there were the least reason to believe that the late frescoes would be overcleaned, this would be a valid view. But there is no evidence of overcleaning in the restored section of the chapel and there is no reason to suppose that the later frescoes will be treated less judiciously.”
THE WILFULLY DISREGARDED HISTORICAL VISUAL RECORD
On Pope-Hennesy’s own – albeit limited – admissions, there was every reason not to take the Vatican restorers’ methods on trust, not the least of these being the fact that, as any visually alert scholar should have appreciated, the many copies of the Ceiling made from Michelangelo’s day to our own, had all testified to his secco overpainting:
Above, Fig. 6: Top, left, the ink and wash copy of Michelangelo’s Sistine Ceiling figure Jonah, made between 1524 and 1534 by Giulio Clovio; top, right, a c. 1800 etched copy of Michelangelo’s Jonah by the Irish painter James Barry, R. A.; above, left, a detail of Michelangelo’s Jonah before Colalucci’s cleaning and showing the then surviving secco remains of the Clovio-copied dramatic shadow cast from the Prophet’s left foot; above, right, Jonah’s left foot after Colalucci’s elimination of the secco-enhanced shadows.
Disregarding all such historical visual testimony, the Vatican insisted that what had been understood since the 1512 unveiling to be Michelangelo’s own shadows, were arbitrary accumulations of soot trapped in “glue-varnishes” applied centuries later by successive restorers with sponges tied to thirty-feet long poles – poles of which, we established, no record existed and which, had they existed, would have stopped thirty-feet short of the ceiling. The phantom poles were summoned by Vatican officials in the absence – which we also established – of Vatican records of ceiling-high restoration scaffolding.
THE BOOK THAT WOULD HAVE BLOCKED THE SISTINE CHAPEL RESTORATION:
Above, Fig. 7: Left, the compendious 1990 book of historic copies of Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel frescoes; centre, the book’s reproduction of Giulio Clovio’s Jonah drawing; right, the book’s reproduction of 19th century engravings (after lost copies) of the two lunettes Michelangelo had painted on the Chapel’s altar wall and would later destroy when preparing that wall for his Last Judgement.
Had the above book been published before 1980 and due consideration been given to Wilson’s account, a cleaning of the ceiling would have been stopped dead by the testimony of the above two images. The Clovio drawing alone constituted a proof positive that Michelangelo’s instantly-acclaimed lights and shadows had not only been present on the Ceiling but were also present on Michelangelo’s upper wall lunette frescoes – just as Colalucci’s Vatican restorer predecessors had reported. It did so because the two lunettes part-shown in its lower corners, were the very ones that Michelangelo destroyed to paint his Last Judgement. Thus, the sharply pronounced shadow that had been cast along the ground by Jonah’s left foot had been painted before any restorer had been near the frescoes. It could not, therefore, have been a freakishly artistic by-product of soot trapped within successive “glue varnishes” applied by restorers. Moreover, the glimpses of the shadows cast by Michelangelo’s lunette figures in Clovio were in turn confirmed by the etched copies of the two destroyed lunettes on the altar wall. Even the Clovio-recorded nude boy supporting Jonah’s name tablet had originally cast his own shadow on the wall before Michelangelo painted his Last Judgement.
Above, Fig. 8: The name tablet for the Prophet Zacherias – top, before cleaning: above, after cleaning.
THE ELEPHANT ON THE CEILING
Michelangelo had not been the first artist to depict cast shadows. What stunned his contemporaries had been the thunderous force of spatial illusionism within which his figures had realised an unprecedentedly vivid sculptural presence-in-space. It was precisely in the wake of the illusionistic shading’s evisceration that Pope-Hennessy had (correctly) noted that where the name tablets had previously been “firmly integrated in the [real and fictive] architecture of the chapel…they [now] read like supertitles in an opera house” – see Fig. 8, above. To repeat: that tragically late-published book had shown beyond any dispute that there had been no break in the visual record of Michelangelo’s shadows from his day to ours – and, therefore, that the Vatican’s restorers had destroyed the finishing stages of Michelangelo’s own painting throughout the ceiling. In retrospect – and after all the account/demonstrations we have published (see, for example, Cutting Michelangelo Down to Size) – it might increasingly seem that this visually self-evident truth was a truth too big and too inconvenient in its implications ever to be ceded by the Vatican and the compliantly supportive art historical establishment it had garnered.
UNDERSTANDING POPE-HENNESSY’S SCHOLARLY BLANK CHEQUE
As a former director of both the Victoria and Albert Museum and the British Museum; a professor of art history at New York University’s post-graduate Institute of Fine Arts; and the very recently retired Chairman of European Paintings at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, Pope-Hennessy’s essay had effortless clout despite his self-subverting acknowledgements of both disturbing artistic results and – even – a wide distrust of the restoration among professionally sound peers. He opted to berate the critics while lauding the restorers, not on what they had done (on some of which he was critical) but on what he expected them to do next. Perhaps he had been privy to Mancinelli’s assurance to Tintori? He had certainly registered concern over of a group of cleaned Prophets and Sibyls:
“Optically, seen from the altar end of the chapel, they look a little smaller and less weighty than they did before. In the heads, a gain in definition is accompanied by a loss of ambiguity.”
Given that the visual arts work on and through their optical reception, how could Pope-Hennessy discount his own art historically informed, optically received, reading of diminished volumes and weights in Michelangelo’s figures? Perhaps he, like the art critics Hughes and Russell, had been swayed (or cowed) by the sheer authority of the supposedly unanimous Kress Foundation report? In any event, he wrote:
“…a gulf opened between those who adhered to the old concept of the ceiling and those who embraced the ceiling as it seemed originally to have been. The dispute was taken up in the American press, in largely polemical terms. There were demonstrations; and vociferous protests were made by both academic and non-figurative artists. The Vatican authorities went so far as to explain publicly, in two days of conferences in New York, the restoration program and the data on which it was based. Not unnaturally American criticism was reported throughout Italy, and had a disturbing, though not demoralizing, effect on the restorers involved. Arrangements, however, were made for a number of restorers of acknowledged excellence (three of them specialists in fresco decoration) to visit Rome, and they one and all endorsed the wisdom of what was being done.” (Emphases added.)
LEARNING TO LOOK
Aside from this explicit professional deference to a Higher Technical Authority in matters of aesthetic appraisal, other possible explanations for Pope-Hennessy’s stance emerged in his 1991 memoir, Learning to Look. This most distinguished scholar had a visual Achilles Heel – of time spent in an art school, he recalled “I disliked this too, and to this day I cannot draw.” Moreover, he had developed aversions to fellow art historians – and even (like Colalucci) to subjective judgements:
“One of the things about art history that I found puzzling from the first was that clever art historians (there were stupid ones too, of course, but a lot of them were really clever) should reach diametrically opposite conclusions on the basis of a tiny nucleus of evidence. The reason, so far as one could judge, was that the subjective element in art history was disproportionately large. If this were so, it was not only works of art that needed to be looked at in the original but art historians too, since their results were a projection of their personalities. So for some years, I made meeting art historians a secondary avocation.”
From the first, Pope-Hennessy had indeed made it his business to meet as many art historians as possible. When he left Balliol College, Oxford, with a second-class degree in history and an alumnus’s legendary “tranquil consciousness of an effortless superiority” (- in his case, specifically: “in the form of a self-confidence that sometimes verged on arrogance and a clear understanding of the difference between success and a succès d’estime”) he sold some inherited coconut islands off Borneo as income to be devoted “to travelling and to the preparation of a book” – and all this when, like Max Beerbohm’s Young Arnold Bennet, already having “a life plan in my mind.” During the Second World War he “found himself” in the Intelligence Department of the Air Ministry and there, for the first time, “met ordinary people” whom he considered “congenial and interesting”. In later life he expressed a preference for works of art over people of any kind:
“Objects mean more to me than people. It is not that I am frigid or reclusive, but that object-based relationships are more constant than human ones (they never change their nature and they do not pall).”
THE CHURNING “RAW MATERIAL” OF SCHOLARSHIP – AND A NEW SPECTATOR SPORT?
However, and despite his avowed attraction to the constancy of objects, as a self-made art historian, Pope-Hennessy came to welcome their radical alteration by restorers:
“People sometimes complain that there is nothing new to be said about Italian painting. They mean by this there are now monographs on many minor painters and that the works of great artists have been discussed in a large number of books. But the truth is that the raw material of Italian painting is in a constant state of flux. When paintings change through cleaning, our view of the artist who produced them changes as well.”
Above, Fig. 9: Top, the National Galley’s Piero della Francesca The Nativity before its latest restoration (left), and afterwards (right); above, a comparative detail showing the recently repainted shepherds and wall, with (inset) their previous state.
Like many of their scholarly peers, newspaper art critics have come to welcome the easy copy-generating potential of restorers’ alterations. In December 2022, Waldemar Januszczak of the Sunday Times, extolled the National Gallery’s controversially reconstructed Piero della Francesca Nativity (Fig. 9, above) and claimed that museums themselves now welcome “the inevitable brouhaha that follows any big restoration” because it “provokes interest and gets people through the door.” However, the art historian Giorgio Bonsanti deplored the intervention in IL GIORNALE DELL’ARTE and fears that such “controversies are destined not to subside but to remain and grow in future years, because the problem exists, and will remain evident to the millions of visitors to the National Gallery”. Scarcely less alarming to the Gallery must have been the Guardian critic, Jonathan Jones’, (earlier) assault on the repainted Nativity.
Jones had been the newspaper art critic of choice who was embedded within the Gallery’s conservation department during the restoration of its version of the Leonardo Virgin of the Rocks. The Evening Standard art critic, Brian Sewell, a student of Anthony Blunt at the Courtauld Institute, and a long-time scourge of National Gallery restorations, had been similarly co-opted within the restoration of Holbein’s The Ambassadors (Fig. 10, below). When so embedded, Jones predicted (wrongly) that “ArtWatch will attack the restoration”. On the Nativity, Januszczak similarly predicted: “There will be those, of course, who will howl at the changes – there always are.” In this case, at least three have now done so on the record – in addition to Jones and Bonsanti, in the March/April 2023 issue of the Jackdaw, its editor, David Lee (“Abbronzatura Solaire”), complained that aside from imposing complexions on the shepherds that are “more appropriate to Love Island than Bethlehem”, the Gallery has confounded a manifestly un-finished painting with a damaged finished painting.
Having previously studied the Nativity’s historic and restoration dossiers, we would add that this panel painting has likely suffered more accumulated restoration blunders than any other in the collection – with the possible exception, perhaps, of Giovanni Bellini’s Madonna of the Meadow. Both of those two pictures received disastrous “structural surgery” from a restorer (Richard D. Buck) who had been hired and brought over from America in 1948 by the National Gallery’s Director, Sir Philip Hendy, to introduce supposedly advanced conservation methods. Januszczak, who defends the Nativity’s recent repainting make-over on the grounds that “an active artwork that is doing what it is supposed to be doing must always trump a charming ruin”, begs the crucial question – “What is an historic picture supposed to do?” – and he clearly fails to appreciate that it is not Time and Neglect but, rather, restorers who, through their ceaseless Un-doing and Re-doing of pictures, create ruins. Where no auction house or dealer would dream of boasting that a picture on offer has had multiple restorations, museum pictures are treated today like so many bags on an airport carousel waiting to be picked up and done over on the whims and fancies of the next available restorer.
(Incidentally, Jones, Bonsanti, and Lee have by no means exhausted the many due criticisms of the Nativity’s latest restoration makeover. The ruined stone wall behind the repainted Shepherds, for example, has itself been repainted in a manner that robbed it of thickness and perspectival placement and left it running flatly across the picture plane, like so much stone-patterned wallpaper, to serve as a backdrop foil to the hypothetically reconstructed heads, as seen at Fig. 9.)
PROCLAIMED RESTORATION TRANSFORMATIONS – AND THINGS THAT CRITICS OVERLOOK
Where Pope-Hennessy had likened the Sistine Ceiling to Beethoven’s Ninth and noted that “another, more lively, more decorative artist” was emerging, Januszczak whooped at the spectacle of the transformation:
“The thin and neat scaffolding bridge moved elegantly along the ceiling like a very slow windscreen wiper. In front of it lay the old Michelangelo, the great tragedian, all basso profundo and crescendo. Behind it the colourful new one, a lighter touch, a more inventive mind, a higher pitch, alto and diminuendo. It was being able to see both of them at once – Beethoven turning into Mozart before your eyes – that made this restoration such a memorable piece of theatre.”
Unlike Januszczak, Pope-Hennessy had not always welcomed restoration-induced changes. In his 1970 book, Raphael, he observed: “But Raphael restored is Raphael interpreted; it is different from the real thing” – and in 1987 he would likely have known that a recent “Raphael restored” at the Vatican had proved disastrously different from the real thing. In 1982, Mancinelli had said of a bungled, chemically experimental restoration that required extensive repainting by Colalucci in Raphael’s Loggia, “It is the best demonstration that a restoration can also not go along well.” In 2016, Colalucci recalled that the Vatican had faced “a serious problem” when “a new inorganic substance that had not been sufficiently tried and tested” was used.
In 1991, as the Sistine Chapel restorations neared completion, Pope Hennessy reverted to his younger self’s restoration-critical stance and noted:
“In London since 1945 the National Gallery had been the target of ceaseless criticism. There had been intermittent controversies in the press over the cleaning of paintings, but successive directors had enjoyed the support of a passive, compliant board. The policy of Radical Cleaning had been espoused by Philip Hendy (who must have suffered from some retinal defect which made him see pictures as flat areas of colour) and had continued under his successors for so long that proof of the damage done to the collection over thirty years could be seen in almost every room.”
That judgement on National Gallery cleanings was sound and it constituted an international commonplace. Mario Modestini wept for half an hour at the sight the Gallery’s “flayed” restorations; in 1970 Pietro Annigoni painted “MURDERERS” on the National Gallery’s doors in protest; in March 1999 when I visited the Gallery with Professor Anatoly Alyoshin, head of the Repin Institute, St. Petersburg (Russia’s leading institute for the training of picture restorers), he was shocked by the paintings’ uniform brightness and seeming newness. Stopping between galleries, he swept his arm around and said “See! Everything in every school looks as if it was painted in the same studio at the same time.” In a sense, everything had been – after stripping paintings of all they judge extraneous, National Gallery restorers are permitted to this day to paint onto them whatever they take to have been an artist’s original intentions, even with pictures as old and venerated as Holbein’s The Ambassadors and Piero’s Nativity. Old masters are being treated like neglected scores awaiting the life-restoring interpretation of a would-be pictorial Furtwängler, von Karajan or Barenboim – but with the difference that where musical scores outlive their successive interpreters, a painting is its own score.
PURISM AND FAKISM: FALSE AGE CRACKS AND RE-INTERPRETATIONS ON RESTORED PAINTINGS
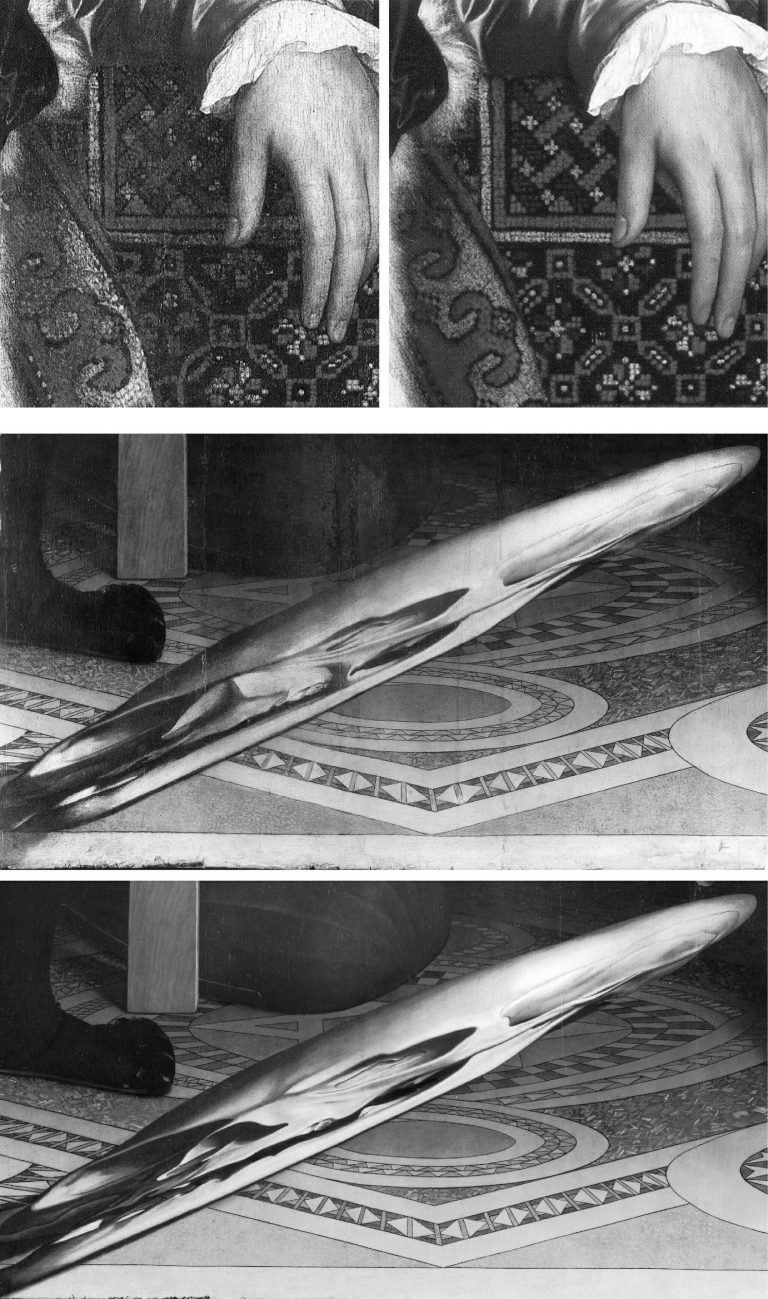
In the 1990s the National Gallery’s then head of restoration, Martin Wyld, contended: “The ‘Good Restorer’ is the one who ‘does the minimum necessary but not too little… we remove everything not put on by the artist and then use our judgement to get back to the original.” On 8 April 2023, the Financial Times (“Behind the seams at the museum”) reported that the present head of restoration, Larry Keith, said of his restoration of Parmigianino’s Saint Jerome’s vision of John the Baptist revealing the Virgin and Jesus, “We are editing, in a way. The work is informed by science and objective criteria, but there are decisions you take, which on some level are interpretive”. In an Esso-sponsored, BBC-filmed restoration of the Ambassadors (which has ceased to be available), Wyld was seen to have repainted much of the carpet to a new design on the authority of a “carpet expert”, and to have repainted much of Holbein’s famous anamorphic skull to a new and elongated design derived from a computer-distorted photograph of another skull. The Gallery’s defence of Wyld’s first-ever insertion of a Virtual Reality image into an old master painting was its claim that “modern imaging techniques” offered more “scope for exploring possible reconstructions” than the perspectival and optical conventions by which the skull had been produced. The pronounced differences between the Ambassadors’s old original paint and Wyld’s newly redesigned and presumptuously repainted parts of the skull, were concealed by his painting fake lines of cracking onto his own newly painted hypothetical reconstructions to match the real cracks on the real old paint.
Above, Fig. 10: Top, a detail of Holbein’s The Ambassadors, showing a section of redesigned and repainted carpet, before treatment (left) and after treatment (right); centre, the pre-restoration anamorphic skull in Holbein’s Ambassadors; above, the Wyld-extended, computer-generated skull in the Ambassadors.
PRODUCING “DIFFERENT, MORE POWERFUL” IMAGES
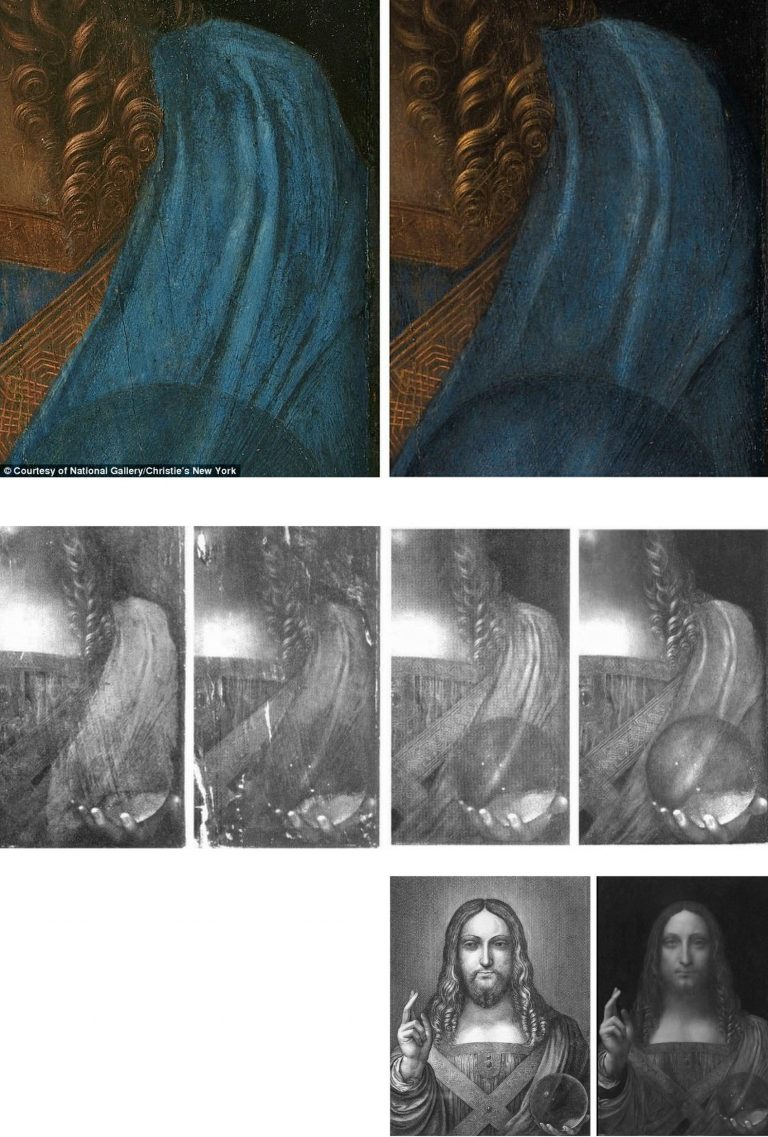
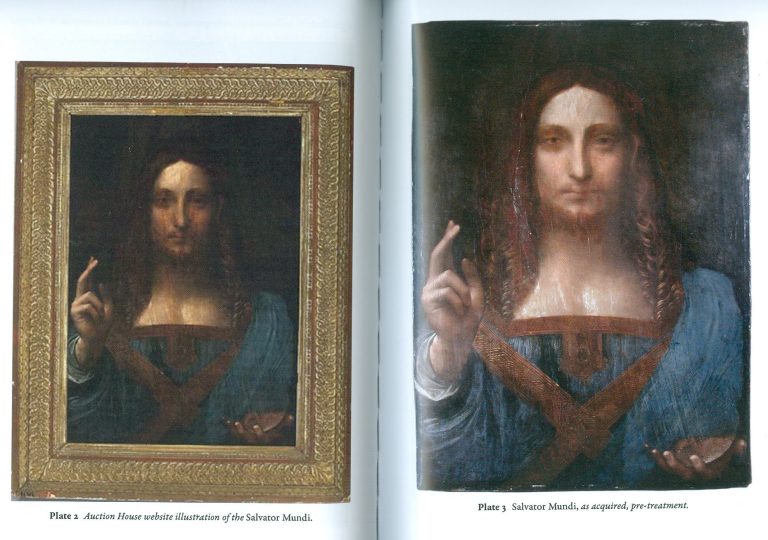
The New York restorer and Kress-appointed Sistine Chapel invigilator, Dianne Dwyer Modestini (formerly Clinical Professor, Kress Program in Paintings Conservation at NYU’s Institute of Fine Arts) – very extensively repainted and artificially distressed the much-damaged Leonardo School Salvator Mundi that fetched a world record $450 million in 2017 at Christie’s, New York – prompting Thomas Campbell, a former director of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, to ask: “450 million dollars?! Hope the buyer understands conservation issues – #readthesmallprint”. Dwyer Modestini had published this small-print report of an early intervention in her decade long undoing and redoing of the picture:
“The initial cleaning was promising especially where the verdigris had preserved the original layers. Unfortunately, in the upper parts of the background, the paint had been scraped down to the ground and in some cases to the wood itself. Whether or not I would have begun had I known, is a moot point. Since the putty and overpaint were quite thick I had no choice but to remove them completely. I repainted the large missing areas in the upper part of the painting with ivory black and a little cadmium red light, followed by a glaze of rich warm brown, then more black and vermilion. Between stages I distressed and then retouched the new paint to make it look antique. The new colour freed the head, which had been trapped in the muddy background, so close in tone to the hair, and made a different, altogether more powerful image. At close range and under a strong light the new background is obvious, but at only a slight remove, it closely mimics the original [paint work] … Most of the retouching was done with dry pigments bound with PVA AYAB. Translucent watercolours, mainly ivory black and raw siena, were used for final glazes and to draw [false age-] cracks…” (Emphasis added.)
Above, Fig. 11: Top, a section of drapery on the $450million Leonardo school Salvator Mundi, as seen in 2011-12 at the National Gallery (left), and (right) as when sold in October 2017 at Christie’s, New York; centre row, showing left, and second left, the picture detail, as when acquired in 2005 and taken to Modestini for restoration; third left, the Modestini-restored picture detail when shown as an autograph Leonardo in 2011-12 at the National Gallery; and, right, the Modestini re-modified feature, as sold in 2017 as an autograph Leonardo, at Christie’s, New York; bottom row, left, the Wenceslaus Hollar engraving that was said by the National Gallery to have been copied from the National Gallery-exhibited Salvator Mundi picture (bottom right) when in the collection of Charles I. That claim was subsequently disproved when the lost Charles I Salvator Mundi emerged in Moscow and was seen to be of an entirely different composition – at which point, the previous resemblance of the painting’s complex shoulder drapery folds to those in the Hollar etching had become more of a disqualification than a potential corroboration.
CHRISTIE’S RESPONSE
In December 2017, Christie’s was presented with photographic evidence (Fig. 11, above, top) assembled by Dr Martin Pracher, a lecturer in technical art history, that showed the changed states of the Salvator Mundi’s (true left) shoulder drapery between 2012, when exhibited at the National Gallery as an autograph Leonardo prototype painting, and 2017, immediately before the $450million October 2017 sale at Christie’s, New York, in which the picture was offered as a then different but supposedly still-autograph Leonardo prototype that enjoyed “an unusually strong consensus” of scholarly support. Under Press questioning (see Dalya Alberge in the Daily Mail) a Christie’s spokeswoman said Modestini had “partially cleaned the passage of paint in the shoulder and the dark streaks disappeared… To imply something incorrect has taken place would itself be incorrect”. Thus, it was insisted that the recently “disappeared” multiple folds, were not folds but mere “dark streaks” that had appeared during Modestini’s 2005-2010 restorations only to disappear under her 2017 ministrations.
INSTITUTIONALLY SEALED LIPS
Of whatever it consisted, Modestini’s last-minute intervention had been made under sworn secrecy at NYU’s Institute of Fine Arts conservation studios, as she disclosed in her 2018 memoir, Masterpieces: Based on a manuscript by Mario Modestini. That is, when the Salvator Mundi returned to New York in July 2017 ahead of Christie’s November sale, Modestini, was instructed “not to inform anyone” when the painting was “delivered to the Conservation Center under guard and in great secrecy”. Modestini further disclosed that a deal brokered by Christie’s ahead of the sale whereby the vendor would receive at least $100million had also been “successfully kept under wraps.”
THE NATIONAL GALLERY’S ABIDING INFLUENCE ON RESTORATION “REVELATIONS”
When Pope-Hennessy deviated in 1987 from his earlier soundness on transformative restorations, he bought into the National Gallery’s longstanding picture cleaning rationale by endorsing two of the 20th century’s most spectacularly controversial restorations:
“In its cleaned form the [Sistine] ceiling has become again what Michelangelo’s contemporaries considered it, one of the supreme achievements of mankind. With Titian, the revelation started in the National Gallery in London, when the Bacchus and Ariadne was freed of centuries of dirt and proved to be painted in an altogether different tonality from any that had previously been supposed.”
That there had been no “centuries of dirt” to remove from the Titian will be shown in Part III. A fuller understanding of Pope-Hennessy’s late-life restorations lapse and an appreciation of the methodological and promotional similarities between the two most controversially transformative restorations in the second half of the twentieth century will be tracked through the records of the two successive National Gallery directors from 1934 to 1967, Sir Kenneth [later Lord] Clark, and Sir Philip Hendy. By the 1980s, that pair’s polished formulations had come to serve as an internationally infectious template for the unbridled techno-experimentalism seen in the Brancacci and Sistine chapels during what, for Colalucci, had constituted the terminus of “the golden age of restoration in Italy, the halcyon era from the late 1940s to the mid-1990s.”
In Part III, we correlate the false scholarship that flowed from the Titian Bacchus and Ariadne and Michelangelo Sistine Chapel restorations, along with the artfully engineered professional endorsements both restorations received from the then highest authorities.
Michael Daley, Director; 15 April 2023
Books on No-Hope Art Attributions
The latest addition to the fast-growing but least-estimable art book publishing genre – The Book of Art Attribution Advocacy – has finally arrived. It comes eight years late and on the second anniversary of Christie’s, New York, 15 November 2017 sale of the formerly attributed-Leonardo, Salvator Mundi picture – which disappeared the following day.
Fig. 1: The above book,Leonardo’s Salvator Mundi & the Collecting of Leonardo in the Stuart Courts, constitutes the first official published account in support of the Salvator Mundi painting that was exhibited as an autograph Leonardo painting at the National Gallery in the 2011-12 exhibition, “Leonardo da Vinci: Painter at the Court of Milan” (see Fig. 10) and that was sold at Christie’s two years ago for $450 million. The authors are: Margaret Dalivalle, a provenance specialist; Martin Kemp, Professor Emeritus and Leonardo specialist; and, Robert Simon, a New York art dealer and one of the two original buyers of the Salvator Mundi in 2005. The book contains no contributions by those who examined the painting technically and worked on its successive restorations. In their introduction and in defence of these startling omissions, the authors liken their book to a three-act opera: “However it is not intended to be an exhaustive treatment of the subject. As with an opera having a grand and intricate plot, this book will consider three facets of the story, each in depth, while necessarily bypassing many ancillary issues.”
There is no mention of the catcalls it has elicited. A glance at the illustrations shows the book to carry a new mystery: there would now seem to have been an undisclosed restoration.
Above, Fig. 2: In this photo-spread, the first image shows the painting as illustrated by the auctioneers in 2005. The second image is said to show the picture as acquired by Robert Simon (and one other) at the auction. The restorer chosen by the new owners was Dianne Dwyer Modestini who worked on the painting in a number of restorations between 2005 and 2017. She has recalled (see Fig. 4) that when the painting was taken to her home in 2005 its surface was still sticky. The painting would thus seem to have been restored at some point after the sale catalogue was prepared and before it was taken to Modestini.
Above, Fig. 3: Simon Hewitt’s long-promised and compendious 2019 book (pp.352), Leonardo da Vinci and the Book of Doom, is written in support of the attributing to Leonardo of a mixed media drawing that was dubbed “La Bella Principessa” by Martin Kemp – and which remains unsold in a Swiss freeport. Now said by Hewitt to have been drawn by Leonardo in 1496 from Bianca Sforza, the illegitimate daughter of “Il Moro”, the 7th Duke of Milan, this book demonstrates – but does not expressly acknowledge – that no record of such a drawing exists before its sale at Christie’s, New York, in 1998 when it was sold as early 19th century German for $22,850 to a New York dealer who sold it on to Peter Silverman in 2007 for $19,000. In 2008 Silverman introduced himself to Hewitt by jumping into his cab saying: “May have a story for you one day! I’ll let you know.” In 2009 Silverman summoned Hewitt to Paris and a facsimile of “La Bella Principessa”. Having taken it at first sight to be early 19th century German, Hewitt produced an article for the Antiques Trade Gazette headed “Is this the greatest art market discovery of the century”.
Above, Fig. 4: Although Dianne Dwyer Modestini’s 2018 memoir, Masterpieces, is not strictly-speaking a book of art attribution advocacy, it contains as an epilogue, a chapter on the Salvator Mundi. In it, Modestini reproduces the photograph of the Salvator Mundi as shown in Fig. 2 above, right, and she describes it as being “as I first saw it in 2005”. We report in the ArtWatch UK Journal No. 32 (p. 47) how Modestini further commented on the picture in Masterpieces:
“When the Salvator Mundi returned to New York in July 2017 ahead of Christie’s November 2017 sale…having been instructed ‘not to inform anyone’ when the painting was ‘delivered to the Conservation Center [of the Institute of Fine Arts, New York University, where Modestini works as Senior Research Fellow and Conservator of the Kress program in Paintings Conservation] under guard and in great secrecy.’ Modestini writes approvingly of the fact that a deal brokered by Christie’s ahead of the sale whereby the vendor would receive at least $100million ‘was successfully kept under wraps’.”
For that late-stage re-restoration work in 2017, see Dalya Alberge, Mailonline, 22 December 2017, (“Auctioneers Christie’s admit Leonardo da Vinci painting which became the world’s most expensive artwork when it sold for £340m has been retouched in the last five years.”)
Above, Fig. 5: Although Martin Kemp’s 2018 Living with Leonardo is a professional lifetime memoir, he too includes chapters in support of the two Leonardo attributions he has championed – those of the Salvator Mundi and the mixed media drawing he dubbed “La Bella Principessa” that is owned by Peter Silverman – as seen above right. Kemp, like Hewitt, devotes much of his advocacy to attacking critics of the two attributions – including ArtWatch UK’s officers and associates.
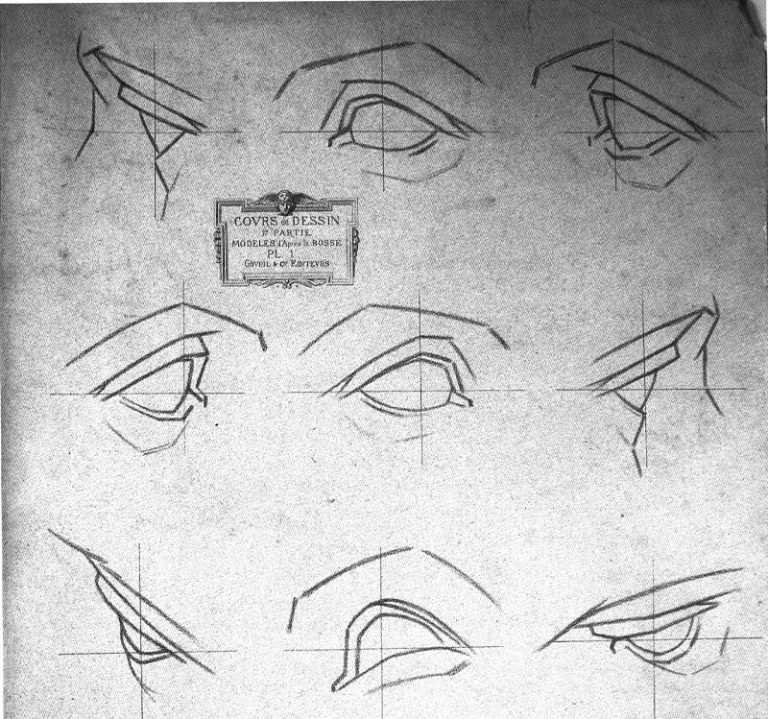
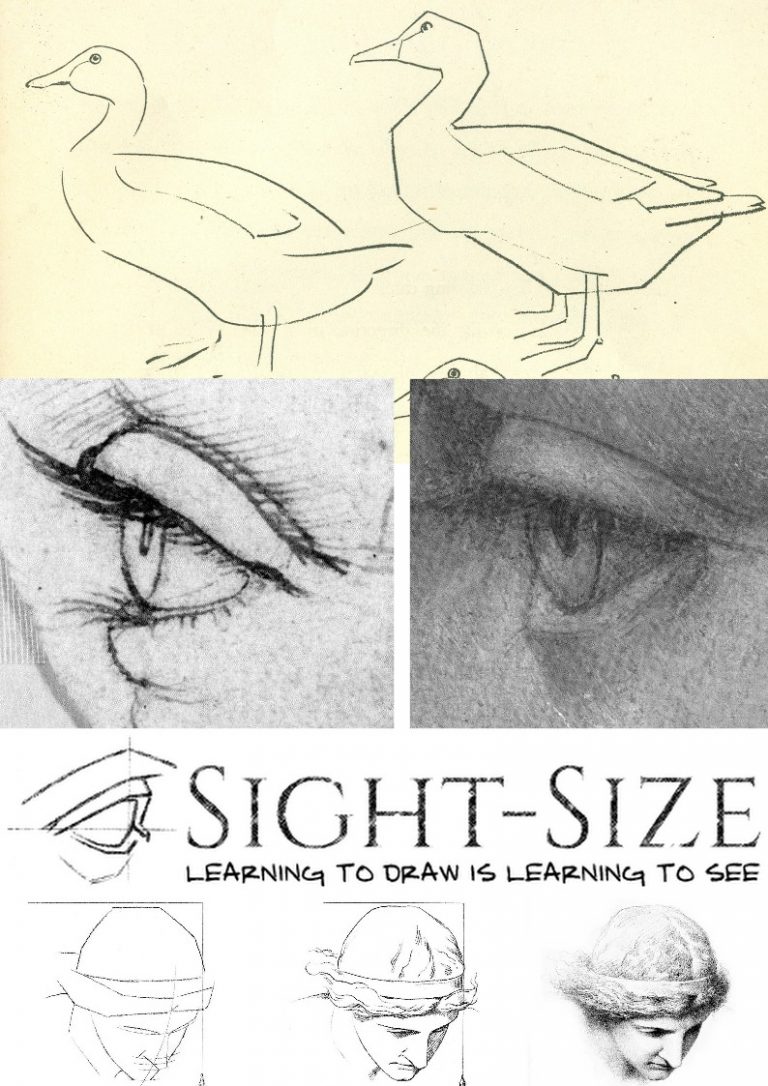
Above, Fig.6: Kemp’s publishers, Thames and Hudson, asked to reproduce a four-part graphic (top) which we had published on 3 May 2016 (“Problems with “La Bella Principessa” – Part II: Authentication Crisis”) precisely to demonstrate why, on stylistic grounds, the eye of “La Bella Principessa” could not possibly have been drawn by Leonardo. A crucial part of our cross-linked visual comparisons was an eye from a 19th century sheet of demonstrations to art students on how best to sketch eyes with short, straight lines. When Kemp’s book was published it carried a three-part diagram as shown above and as if it were the four-part one we had published. In Kemp’s reduced graphic, the embarrassing testimony of the guide to students had been omitted.
Above, Figs. 7 and 8: In the top image we show the sheet that had carried the eye which Kemp dropped. In the second image above we show (top) instructions in one of the “How to draw…” books, a guide to students on the relative merits of drawing ducks with curving lines or straight lines. Below it we show an eye drawn by Leonardo, with curving lines, and the eye of “La Bella Principessa”, drawn with straight lines. (As it happens, the eye that Kemp declined to publish is used as the logo for a drawing school – Sight-Size.)
Above, Fig. 9: This book of 2012 is something of a rarity within the genre of advocacy books in that it is written not by a professional art historian or art critic but by the work’s owner. It makes a fascinating and instructive read. We learn from the horse’s mouth, exactly who approached whom and when in the attempted formation of a sufficiency of experts to constitute an art-market “consensus of support”. We learn how Silverman planned his own media campaign to introduce both the work and its assembled supporters to the world. Such inside disclosures and resulting cross-linked accounts of the campaigning, can become sources of friction. In his 2018 memoir Kemp takes Silverman to task in a number of respects. Firstly (p.152), in terms of how the championing of the attribution should best have been managed:
“I had already written an extended report for Peter Silverman – longer than a standard academic article, shorter than a book. What I had seen and what I was gleaning from my continuing research persuaded me to write a book with Pascal [Cotte of Lumière Technology – see Fig. 11]…We also decided to include a short chapter by fingerprint specialist Paul Biro, who compared the inky fingertip with likely Leonardo prints. Ideally, nothing more should have appeared before our book [Kemp and Cotte’s, at Fig. 11] was launched. I was very concerned that the piecemeal, erratic and sensationalized release of incomplete stories was proving prejudicial. Early in 2009 I circulated a strategy to Peter and his supporters proposing that the drawing should be ‘exposed to a wholly non-commercial venue at the same time as all the research data had been released in full.’ I emphasized that all the material in the planned book should be embargoed before its publication. This placed considerable demands on Peter’s uneven reserves of discretion and patience…”
With so much cross-linking of players mishaps can arise. Members of tightly-knit groups of advocates can come collectively to see all opposition not as differing viewpoints but as quasi-pathological manifestations of “hostility” from rival “gangs”. For example, Hewitt reports:
“On July 1 Peter Paul Biro alerted Kemp and Cotte that the next edition of the New Yorker would be running a ‘potentially prejudiced and cherry-picked article about me, my work and the drawing.’ The New Yorker, he pointed out, was ‘owned by Condé Nast, which in turn is owned by Si Newhouse – a major client of Christie’s.’ ‘Christie’s and their friends are getting as much as they can in the public domain rubbishing the portrait and those who have worked on it’ replied Kemp – who had assured the New Yorker that Biro’s work on the [“La Bella”] portrait was exemplary.’ David Grann’s 16,000 word article on July 12th implied Biro was sleazy and incompetent. When Biro [unsuccessfully] sued the New Yorker for libel, a Federal judge paid implicit tribute to Grann’s verbal craftiness – declaring that his article did not make express accusations against Biro, or suggest concrete conclusions about whether or not he is a fraud.” Kemp, too, discusses Biro in his memoir:
“The strategy I had outlined fell apart when the fingerprint became the explosive subject of international attention before our book was published. Paul Biro, working from his studio in Montreal, compared Pascal’s amplified image of the fingerprint with prints in Leonardo’s unfinished St Jerome in the Vatican. Paul identified a print in the St Jerome which he saw as showing eight points of resemblance with that on the vellum. The most characteristic part of a fingerprint is the complex whorl at the centre of each fleshy pad. This was not apparent [– was not present?] in the print on the portrait which was made by the very tip of a finger. Paul’s ‘eight characteristics’ would not have been enough to secure a criminal conviction, but they were suggestive [of what?] and supportive. I could more or less see what he was seeing, if I tried hard, and I was happy to accept that he possessed a more expert eye for such things. [And besides:] The fingerprint evidence was a small part of the total fabric of evidence I was building up. But a ‘Leonardo fingerprint’ is news; it has a ‘cops and robbers’ dimension. The story was broken in the Antiques Trade Gazette by Simon Hewitt, a journalist with whom Peter had developed a trusting relationship. On 12 October 2009 the Gazette announced:
“‘ATG correspondent SIMON HEWITT gains exclusive access to the evidence used to unveil what the world’s leading scholars say is the first major Leonardo da Vinci find for 100 years…ATG have had exclusive access to that scientific evidence and can reveal that it literally reveals the hand – and fingerprint –of the artist in the work. The fingerprint is ‘highly comparable’ with one in the Vatican’.”
Kemp went on to say: “David Grann threw a lot of unpleasant mud at Paul Biro.” He then threw some of his own: “The source of much of the mud was Theresa Franks, founder of the Fine Art Registry, who had developed a reputation as an effective and litigious polemicist about the vagaries of the art world…The New Yorker piece was hugely damaging for Paul – and for the portrait, because our limited use of his evidence was used to taint the whole of the case we were making.”
Kemp’s remarks on Hewitt’s journalistic prowess might have disappointed the journalist/author whose book begins:
“INTRODUCTION
‘Is this the greatest art discovery of the century?’
“That was the front-page headline [he reproduces the front-page] in Antiques Trade Gazette on 17 October 2009, placed above my story about the portrait…It was one of the biggest stories of my career and, in terms of internet hits, the biggest story ever covered by the respected, if slightly fusty, art market weekly I had served on as Paris correspondent since 1985…”
Another attribution, another “gang” of opponents… Hewitt adds: “What Kemp dubbed ‘the New York gang’ were ‘almost bound to be hostile in an act of closing ranks, since they all missed it.’” Yet another is the “Polish gang”. Under a heading “POLES APART” Hewitt writes:
“Soon after Leonardo’s portrait of Bianca Sforza had gone on show in Monza, Katarzyna Pisarek [books editor of the AWUK Journal] published a 17,000-word article in Artibus & Historiae – a twice yearly journal edited by her Polish compatriot Józef Grabski, whose advisory committee included the Metropolitan Museum’s Everett Fahy (cited by Richard Dorment as a ‘vehement opponent of the Leonardo attribution’)…Pisarek was aping her Communist-era compatriot Bogdan Horodski, a former director of the Polish National Library…Pisarek harped on about Peter Paul Biro’s ‘dubious’ fingerprint evidence, omitting to mention that this had been removed as inconclusive from the second edition of the Kemp Cotte book…”
Hewitt seemed not to grasp the full import of the fact that an entire chapter of the Kemp/Cotte book had been excised. He pursued his Polish Conspiracy slur: “ ‘Why was Pisarek ‘suddenly so concerned to address this portrait when she had no record as a Leonardo scholar?’ wondered Martin Kemp. He presumed it ‘resulted from a kind of Polish solidarity’…On November 29 Waldemar Januszczak [Sunday Times art critic and TV broadcaster] – born in England to Polish parents…” and so on. Kemp/Cotte had had very good professional reasons to disassociate themselves from Biro. Kemp puts it with some delicacy in his memoir but the urgency is clear: “It transpired that Paul had previously achieved some notoriety in the detection of a purported Jackson Pollock discovered by a truck driver in a thrift shop. This discovery had been chronicled in a 2006 TV documentary, Who the #$&% is Jackson Pollock? Grann went on to tell a complex tale of Biro’s engagements with other Pollock authentications, in which the artist’s fingerprints appeared on paintings that were subsequently rejected by important Pollock scholars. It was alleged that Biro forged the Pollock fingerprints.”
In the first edition of the Kemp/Cotte book, the authors described the partial fingerprint as a full fingerprint in their introduction: “Following Lumière Technology’s discovery of a fingerprint and a handprint on the portrait, the authors turned to Peter Paul Biro, Director of Forensic Studies, Art and Access & Research, Montreal, to analyse this evidence in the context of what was known of Leonardo’s work…” And Kemp wrote (in his concluding chapter headed: “What constitutes proof?”): “…We have been able to detect extensive left-handed execution, not least in the layers below those we can see with our naked eye. Finger- and hand-prints have come to light in the way we have come to recognize as characteristic of Leonardo’s working methods. Indeed the isolated fingerprint near the left margin has strong if not conclusive evidential value that Leonardo himself touched the vellum.”
Above, Fig. 10: The catalogue to the National Gallery’s 2011-12 exhibition “Leonardo da Vinci: Painter at the Court of Milan”. Normally such a scholarly publication would not become ensnared in attribution controversies because public galleries do not, on principle, include privately owned, unpublished and un-attributed works without provenances that are on the market, but it did so with the Salvator Mundi – even though the identity of the picture’s by-then three owners (one of whom had bought-in with a $10 million stake) was undisclosed. Also undisclosed was: the venue at which the picture had been bought; the price at which it had been purchased; the identities of the leading scholars who were supposed to have endorsed the Leonardo attribution. Crucially, the supporters included the National Gallery’s director, one of its trustees and the curator and organiser of the Leonardo exhibition. The catalogue entry described the work as an autograph Leonardo painted prototype for the many similar Leonardo school Salvators that exist. Its author, Luke Syson, wrote: “This discussion anticipates the more detailed publication of this picture by Robert Simon and others. I am grateful to Robert Simon for making available his research and that of Dianne Dwyer Modestini, Nica Gutman Rieppi and (for the picture’s provenance) Margaret Dalivalle, all to be presented in a forthcoming book.”
As mentioned above, that book has finally been published over eight years after the opening of the National Gallery exhibition and we now see that there are only three authors of Leonardo’s Salvator Mundi & the Collecting of Leonardo in the Stuart Courts: Margaret Dalivalle, Martin Kemp and Robert Simon. Modestini and Gutman-Rieppi have been dropped. In Living with Leonardo, Martin Kemp discusses the failure of Peter Silverman to get “La Bella Principessa” included in the National Gallery exhibition – on the organisation of which he (Kemp) had, at one point, been under consideration as co-curator:
“Looking back over the different fortunes of the attribution of the Salvator Mundi and the portrait of Bianca Sforza, there are some clear lessons to be drawn. The first concerns how a work of art enters the scholarly and public domains. Robert quietly introduced the Salvator Mundi to a judicious selection of experts, who – remarkably, given the usual leakiness of the art world kept their counsel for three years. By the time the painting emerged in public, there was a critical mass of influential voices who would speak in the painting’s favour. By contrast a series of incontinent leaks to the press, as happened with the Bianca prejudices a work in the eyes of specialist commentators. I regret that I did not have more influence on when and how La Bella Principessa emerged…
“Ownership also plays its role. The owners of the Salvator played their hand cleverly, fostering the idea that they wanted to do right by Leonardo’s masterpiece and were interested in it entering a public collection. Peter Silverman, on the other hand, has become a conspicuous presence in the art world…he has what is conventionally called ‘a good eye’. I believe that his intuition about the portrait of Bianca Sforza will be vindicated in the longer term, but unfortunately his variable declarations about its ownership, even if well-intentioned, did not induce trust and made him vulnerable to media criticism.”
This was in pointed contrast to Kemp’s view of Robert Simon:
“…Robert Simon, the custodian of the picture (whom I later learnt learned was its co-owner), outlined something of its history and restoration. He seemed sincere, straightforward and judiciously restrained, as proved to be the case in all our subsequent contacts…All of the witnesses in the [National] gallery’s conservation studio were sworn to confidentiality, and the painting travelled back to New York with Robert. It was becoming ‘a Leonardo’.”
Above, Fig. 11: The 2010 edition of Leonardo da Vinci, “La Bella Principessa” The Profile Portrait of a Milanese Woman. Since 2014 we have reviewed this work in the following posts:
“Problems with ‘La Bella Principessa’ – Part I: The Look”
“Problems with ‘La Bella Principessa’ – Part II: Authentication Crisis”
“Problems with ‘La Bella Principessa’ – Part III: Dr. Pisarek responds to Prof. Kemp”
“Fake or Fortune: Hypotheses, Claims and Immutable Facts”
The day before the subsequently disappeared Salvator Mundi painting was sold at Christie’s, New York, we published a post explaining why the attribution was unsound and the provenance implausible:
“Problems with the New York Leonardo Salvator Mundi Part I: Provenance and Presentation”
Weeks before the sale and before criticisms of the Salvator Mundi erupted in New York, we had spoken against the attribution in a Guardian interview – “Mystery over Christ’s orb in $100m Leonardo da Vinci painting”
Michael Daley, Director, 15 November 2019
“Leonardo scholar challenges attribution of $450m painting”
Dalya Alberge reports in the Guardian that a Leonardo scholar, Matthew Landrus, believes most of the upgraded Salvator Mundi was painted by a Leonardo assistant, Bernardino Luini.
THE LUINI CONNECTION
In her Guardian article, “Leonardo scholar challenges attribution of $450m painting”, Dalya Alberge further reports that the upgraded version of the Salvator Mundi that Matthew Landrus has de-attributed to Leonardo’s assistant, Bernardino Luini, is the very painting that was attributed to Luini in 1900, when acquired by Sir Charles Robinson for the Cook collection.
Above, Fig. 1: Left, the Salvator Mundi that was bought for $450m as a Leonardo for the Louvre Abu Dhabi in November 2017 as it was seen in 2007 when only part-repainted and about to be taken to the National Gallery, London, for a viewing by a small group of Leonardo scholars who are said to have been sworn to secrecy. (For the many subsequent changes to the painting see our “The $450m New York Leonardo Salvator Mundi Part II: It Restores, It Sells, therefore It Is” and Figs. 4 to 6 below.) Above, right: A detail of the National Gallery’s Luini Christ among the Doctors.
BIG CLAIMS ON INCOMPLETE EVIDENCE
Even after being sold twice (in 2013 and 2017) for a total of more than half a billion dollars, the painting’s 118 year long journey from a Luini to a Leonardo and now back to Luini again, remains a mystery: no one has disclosed when, from whom and where the painting is said to have been bought in 2005. Professor Martin Kemp recently disclosed that the work was bought for the original consortium of owners “by proxy”. Long-promised technical reports and accounts of the provenance have yet to appear and keep receding into the future. These lacunae notwithstanding, the painting is scheduled to be launched at the Louvre Abu Dhabi in September, and also to be included in a major Leonardo exhibition at the Paris Louvre in 2019.
THE ROLE OF LEONARDO’S ASSISTANTS IN THE LOUVRE ABU DHABI SALVATOR MUNDI
As Dalya Alberge reports, a number of Leonardo scholars have contested the present Leonardo attribution and held the work to be largely a studio production that was only part-painted by Leonardo himself. Frank Zöllner, a German art historian at the University of Leipzig and author of the catalogue raisonné Leonardo da Vinci – the Complete Paintings and Drawings, believes it to be either the work of a later Leonardo follower or a “high-quality product of Leonardo’s workshop”. Carmen Bambach, of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, holds it to have been largely the work of Leonardo’s assistant Giovanni Antonio Boltraffio. One scholar, Jacques Franck, suggested in a 29 November 2011 interview in the Journal des Arts that an attribution to either Luini or Leonardo’s late assistant (and effective ‘office manager’) Gian Giacomo Caprotti, called Salai or Salaino seemed plausible and persuasive. More recently, in January 2018, he tipped to Salai as the author because of strong similarities revealed by penetrating technical imaging examinations – see Figs. 2 and 3 below and “Salvator Mundi LES DESSOUS DE LA VENTE DU SIECLE”.
Above, Fig. 2: Left, an infra-red reflectogram of the Louvre Abu Dhabi Salvator Mundi; above, right, an infra-red reflectogram of Salai’s Head of Christ, signed and dated 1511, Pinacoteca Ambrosiana (Milan).
Above, Fig. 3: An infra-red reflectogram detail of the Louvre Abu Dhabi Salvator Mundi. Jacques Franck writes: “This close-up view of the Fig. 2, left, document, reveals in the Saviour’s face, neck and head, the same typical underlying sketching-out technique using very thick dark lines to define the preliminary contours and modelling that are seen in Fig. 2, right. None of this underlying graphic/roughing out process is ever encountered in original Leonardo painting where the graphic/painterly stages are more subtle.”
CHANGING FACES: FOUR STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT IN THE LOUVRE ABU DHABI SALVATOR MUNDI
ABOVE, FIG.4: From the left, Face 1 – The former Cook collection Salvator Mundi when presented in 2005 (– when still “sticky” from a recent restoration) to the New York restorer, Dianne Dwyer Modestini.
Face 2: The former Cook collection painting after the panel had been repaired and the painting had been stripped down.
Face 3: The former Cook collection Salvator Mundi after several stages of repainting and as exhibited as a Leonardo at the National Gallery’s 2011-2012 Leonardo da Vinci, Painter at the Court of Milan exhibition.
Face 4: The face after yet further (- and initially undisclosed) repainting by Dianne Dwyer Modestini at Christie’s, New York, ahead of the 2017 sale – as was first published by Dalya Alberge in her Mail Online revelation: “Auctioneers Christie’s admit Leonardo Da Vinci painting which became world’s most expensive artwork when it sold for £340m has been retouched in last five years”.
Above, Fig. 5: Left, the former Cook collection painting’s face as in 2005; right, the face, as transformed over twelve years by Modestini, when presented for sale at Christie’s, New York, in November 2017.
Alberge’s current Guardian article, “Leonardo scholar challenges attribution of $450m painting” has gone viral – see for example: CNN’s “Leonardo’s $450M painting may not be all Leonardo’s, says scholar”, and the ABC (Spain) “Crecen las dudas sobre la autoría del «Salvator Mundi» de Leonardo”.
In the CNN report, it is said that:
“Others are in less doubt. Curator of Italian Paintings at London’s National Gallery, Martin Kemp, sent the following statement to CNN Style by email: ‘The book I am publishing in 2019 with Robert Simon and Margaret Dalivalle (…) will present a conclusive body of evidence that the Salvator Mundi is a masterpiece by Leonardo. In the meantime I am not addressing ill-founded assertions that would attract no attention were it not for the sale price.’”
We make the following observations. Although Professor Martin Kemp is not a curator at the National Gallery he does seem to have been considered at one point as a possible co-curator of the National Gallery’s 2011-2012 Leonardo exhibition, which, in the event, was curated solely by the Gallery’s own then curator, Luke Syson, who is now at the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Syson drew heavily for his 2011 catalogue entry on the painting on the researches of one of the owners of the Salvator Mundi, the New York art dealer, Robert Simon: “This discussion anticipates the more detailed publication of this picture by Robert Simon and others. I am grateful to Robert Simon for making available his research and that of Dianne Dwyer Modestini, Nica Gutman Rieppi and (for the picture’s provenance) Margaret Dalivalle, all to be presented in a forthcoming book.” That book has now been coming for some time. First promised by the National Gallery in 2011, it was more recently promised for 2017, and then for this year, and now, for next year – and possibly in time for inclusion in the catalogue of the Paris Louvre’s planned major 2019 Leonardo exhibition?
Professor Kemp also promised a conclusive body of evidence for his attribution to Leonardo of the drawing he dubbed “La Bella Principessa”. In his 2012 book Leonardo’s Lost Princess, Peter Silverman, the owner of “La Bella Principessa”, wrote: “Martin believed that the fingerprints [compiled by the now discredited fingerprints expert Peter Paul Biro], though not conclusive on their own, added an important piece to the puzzle. He wrote to me, ‘This is yet one more component in what is as consistent a body of evidence as I have ever seen. I will be happy to emphasize that we have something as close to an open and shut case as is ever likely with an attribution of a previously unknown work to a major master. As you know, I was hugely skeptical at first, as one needs to be in the Leonardo jungle, but now I have not the slightest flicker of doubt that we are a dealing with a work of great beauty and originality that contributes something special to Leonardo’s oeuvre. It deserves to be in the public domain.’” In the event, the “La Bella Principessa” drawing did not enter the public domain. Unlike the Salvator Mundi, which sold for $450m, it was not included in the National Gallery’s 2011-2012 Leonardo exhibition and it presently remains, so far as we know, unsold, in a Swiss free port.
Kemp’s present lofty disinclination to address “ill-founded assertions that would attract no attention were it not for the sale price” marks a change of policy. Last year, immediately ahead of the sale that produced the astronomical price of the Salvator Mundi, Kemp was happy to engage polemically with those who rejected the Salvator Mundi’s Leonardo attribution. As he has recently disclosed: “I was approached by the auctioneers to confirm my research and agreed to record a video interview to combat the misinformation appearing in the press – providing I was not drawn into the actual sale process.”
SCHOLARS’ NEED FOR FULL AND DETAILED REPORTS AND FOR OPEN DEBATES
Above, Fig. 6: Left, the small-scale published (infra-red) technical image of the Salvator Mundi; centre, the painting as exhibited in 2011-2012 as a Leonardo at the National Gallery; right, the painting as presented for sale at Christie’s, New York, in 2017.
Much remains to be examined with this restoration-transformed but still, effectively, unpublished work where the promised reports on technical examinations and provenance seem perpetually trapped in the post like Billy Bunter’s postal order. Note in Fig. 6 above, for example, the radical changes made to the true left shoulder draperies; to the orb and the sole of the hand that holds it; and, above all, to the face. We must hope that the painting’s new owners will encourage the old 2005 consortium of owners to publish their privately commissioned researches as soon as possible. In general terms, it would be a much better thing if new and elevating attributions were once more published by single scholars, taking full responsibility in a scholarly publication, so that the case for a work’s re-attribution might be examined widely and discussed openly on a fully informative account and presentation of technical evidence and history of provenance. The recent tendency for owners to hold and selectively part-release researches during promotional campaigns of advocacy is not conducive to best scholarly practice.
Michael Daley, Director, 9 August 2018
Coming next:
Professor Martin Kemp and ArtWatch – Part 1: Twenty-four years of abuse on photo-testimony