Problems with “La Bella Principessa”~ Part I: The Look
The world famous drawing that was dubbed “La Bella Principessa” by Professor Martin Kemp is insured for $150 million and lives in a “secure vault in Zurich”. It is not a portrait of Bianca Sforza by Leonardo da Vinci, as has been claimed, but a twentieth century forged or pastiche Leonardo.
WHITHER “LA BELLA PRINCIPESSA”
In 1998 the now so-called “La Bella Principessa” appeared from nowhere at Christie’s, New York. A hybrid work made in mixed media that were never employed by Leonardo (three chalks, ink, “liquid colour”), on a support that was never used by Leonardo (vellum), and portraying a woman in a manner that is nowhere encountered in Leonardo, it was presented as “German School, early 19th century” and “the property of a lady”. It went for $22,850 to a New York dealer who sold it nine years later on a requested discount of 10 per cent for $19,000 to an art collector, Peter Silverman, who said he was buying on behalf of another (unidentified) collector whom he later described as one of “the richest men in Europe”. Thus, at that date, it was not known who owned the drawing or by whom it had been consigned to Christie’s and it remained entirely without provenance. In its nine years long life, no one – not even its new owner(s) – had taken it to be by Leonardo.
In a 2012 book (Lost Princess ~ One man’s quest to authenticate an unknown portrait by Leonardo da Vinci), Silverman claimed a successful upgrading to Leonardo and described how he had gained the support of distinguished scholars including Professor Martin Kemp who had formulated an elaborate hypothetical history in which the drawing was said to be a Leonardo portrait made either from a living subject in celebration of her wedding or in commemoration after her death in 1496.
Nonetheless, the drawing failed to gain a consensus of scholarly support and is rejected in centres like New York, London and Vienna. Carmen Bambach, the Metropolitan Museum’s Renaissance drawings authority dismissed “La Bella” on the grounds that “It does not look like a Leonardo”. Thomas Hoving, a former Metropolitan Museum director, held it to look “too sweet” to be Leonardo. ARTnews reported that the Albertina Museum’s director, Klaus Albrecht Schröder, had noted “No one is convinced it is a Leonardo”. In the Burlington Magazine Professor David Ekserdjian suspected it to be “counterfeit”.
THE LOOK OF “LA BELLA” AND THE COMPANY SHE BEST KEEPS
In matters of attribution the most important consideration is the look of a work. Many things can be appraised simultaneously but, conceptually, the “look” of a work might be broken down into two aspects: an initial at-a-glance response to a work’s effects and appraisal of its internal values and relationships; and, a comparison of the effects, relationships and values with those of bona fide productions of the attributed artist, or with those of the artist’s students, associates or followers. It can also be useful to compare the looks of works with those of copyists and known forgers. It might fairly be said that in connoisseurship, as in the evaluation of restorations, visual comparisons are of the essence. (In ArtWatch we take pride in the extent to which we seek out all possible comparative visual material and regret that some institutions still hinder our efforts in this regard.)
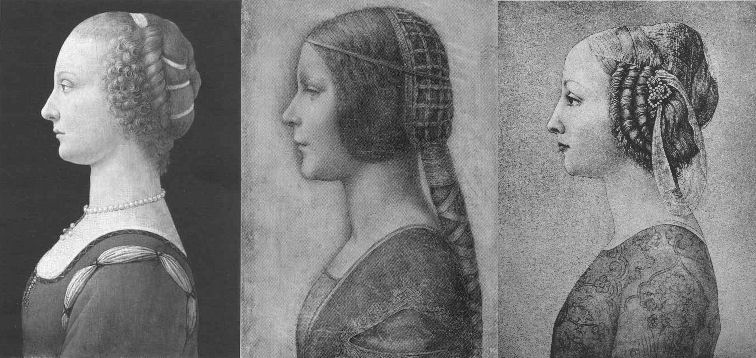
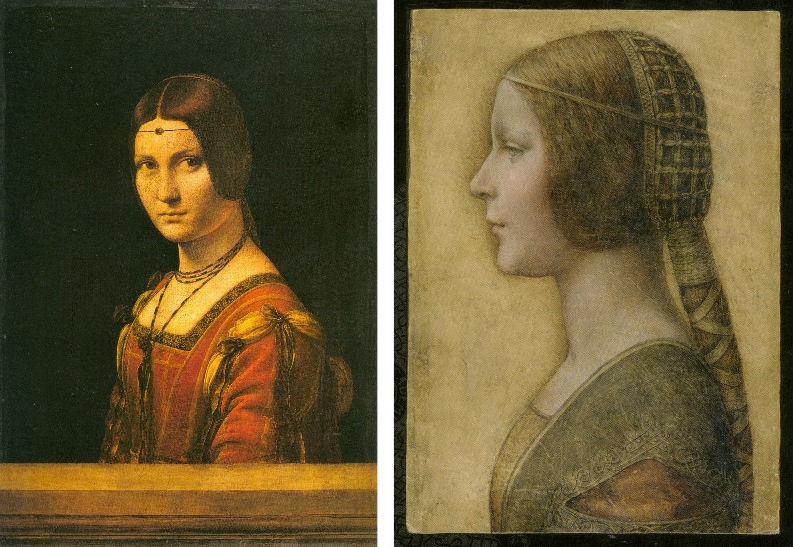
Above, Fig. 1. If we put aside questions of attribution and simply look at the group above, we find works of remarkably similar figural motifs and formats that clearly relate to and derive from a most distinctive type of 15th century Italian profile female portrait. These similar-looking works are similarly sized, being, respectively from left to right:
A Young Woman, 14 and 1/4 x 10 inches;
“La Bella Principessa”, 13 x 9 and 3/4 inches; and,
A Young Woman, 18 x 12 1/2 inches (here shown mirrored).
All show young women depicted in the strict early Renaissance profile convention made in emulation of antique relief portraits on coins and medals. Although very widely encountered (see Fig. 4), Leonardo side-stepped the type in order to intensify plastic and expressive values with sculpturally-purposive shading and axial shifts in the bodies and gazes of his portraits (see Fig. 6). The portrayals above are strikingly similar in their head/torso relationships; in their absences of background; in their highly elaborated coiffures which offset ‘sartorially’ skimped and unconvincing simplifications of costume; in their sparse or wholly absent depictions of jewellery; and, even, in their almost identically cropped motifs. Collectively they might be taken as a suite of variations on a simple theme. We take all three to be twentieth century Italian artefacts. At least two of them are linked to Bernard Berenson and the two on which reports have been published have unusual and problematic supports.
As mentioned below, the Detroit picture is painted on top of photographic paper. It is suspected that it might have been a photograph of the Frick sculpture to which the painting was initially related. The “La Bella Principessa” is drawn, exceptionally for Leonardo, on a sheet of vellum which appears to have been removed from a book and it is, most unusually, glued to an oak panel. The panel itself is a curiosity: although a number of “butterfly keys” have been inserted into its back, as if to restrain splitting, there is no evidence of splits in the panel and, if there were, the present four such keys in such a small panel might be considered restoration “over-kill”. If the panel had split while the vellum was glued to it, the drawing would have split with the panel. The fact that the vellum has been “copiously glued” to a (possibly pre-restored) oak panel makes it impossible to examine the back of the drawing which is said by one of its proponents, (Cristina Geddo, an expert in Leonardo’s students and Milanese “Leonardesques”) to bear “superimposed numbers…a written inscription…[and a] little winged dragon – at least that is what it seems.” For Geddo, this unexamined content is reassuring: “This feature, too, counts in favour of an attribution to Leonardo, who, even though he never to our knowledge used a parchment support in his work, was in the habit of re-using the paper on which he drew.”
(In reading the compendious literature on this proposed attribution, we have sometimes wondered what might be allowed by its supporters to count as evidence against the attribution.)
CONSIDER THE HISTORIES
The portrait on the left, A Young Woman, was bought in 1936 by the Detroit Institute of Arts as by Leonardo da Vinci or Andrea del Verrocchio. The institute’s director, W. D. Valentiner, made this attribution on the strength of clear correspondences with the curls in the hair of Leonardo’s painting Ginevra de’ Benci (see Fig. 6) in the National Gallery of Art, Washington, and with those found in the above-mentioned marble sculpture in the Frick Museum, A Young Woman, given to Andrea del Verrocchio. (Valentiner had made a study of Leonardo’s work in Verrocchio’s workshop.) In 1991 Piero Adorno, specifically identified the Detroit picture as Verrocchio’s lost portrait of Lucrezia Donati. Notwithstanding seeming correspondences with secure works, this picture is now relegated to “An Imitator of Verrochio” – and this is an extremely charitable formulation. In Virtue and Beauty, 2001, David Alan Brown described it as “a probable forgery by its anachronistic materials and unorthodox construction”. “Probable” [!] because: “after a recent technical examination, the picture turns out to have been painted on photographic paper applied to a wood panel that was repaired before it was readied for painting. And at least one of the pigments employed – zinc white – is modern…” Valentiner judged one of two Leonardo studio works of the Madonna with a Yarnwinder to be “more beautiful than the Mona Lisa”.
The portrait on the right, A Young Woman, was attributed to Piero Pollaiuolo by Berenson in 1945. While this figure is perhaps the most attractive of the above three, with its nicely constructed counterbalancing of the thrusts in the neck/head and torso, and its credibly proportioned arm, the work itself has, so far as we can ascertain, sunk without trace. In truth, this female profile portrait type has been assailed by forgeries. Alison Wright notes in her 2005 book The Pollaiuolo Brothers, that “Complications for the historian lie both in the fact that the subjects of most female portraits are no longer identifiable and that, because of their exceptional decorative and historical appeal, such portraits were highly sought after by later nineteenth- and early twentieth-century collectors, encouraging a market for copies, fakes and over-ambitious attributions.”
The portrait in the centre (“La Bella Principessa”) has been precisely attributed by Kemp to Leonardo as a book illustration portrait of Bianca Sforza of 1495-96.
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE LOOKS OF THEN OF NOW

Above, Fig. 2. In My dear BB (an incalculably valuable new resource edited and annotated by Robert Cumming), we learn that in November 1930 Kenneth Clark’s wife, Jane, wrote to Berenson: “K has seen Lord Lee’s two new pictures…The Botticelli Madonna and Child you probably know too. K thinks the latter may be genuine about 1485 or rather part of it may be, but it is not a pretty picture…” A footnote discloses that Lee had bought The Madonna of the Veil, a tempera painting on panel in 1930 from an Italian dealer for a then huge sum of $25,000 (Fig. 3). It was widely accepted by scholars as autograph Botticelli and published by the Medici Society as a “superb composition of the greatest of all Florentine painters”. Clark, doubting the attribution on sight, objected that it had “something of the silent cinema star about it” – and he likened the Madonna to Jean Harlow (Fig. 3). Lee donated the picture to the Courtauld Institute Gallery in 1947. In June 2010 Juliet Chippendale (a National Gallery curatorial intern working in association with the Courtauld Institute MA course) disclosed that scientific examination had identified pigments not known before the 18th and 19th centuries and worm holes that had been produced by a drill. It is now designated a work of the forger Umberto Giunti (1886-1970), who taught at the Institute of Fine Art in Siena and forged fresco fragments.
ART HISTORICAL SILENCES
Four months later Clark wrote to Berenson: “Just in case Lee has sent you a photograph of his new Botticelli may I ask you to forget anything Jane may have reported me as having said of it. It is one of those pictures about which it is best to be silent: in fact I am coming to believe it is best for me to be silent about every picture. Did I tell you that my Leonardo book was a mare’s nest. The man had sent photographs of two drawings from the middle of the Codice Atlantico. They must have been early copies done with some fraudulent motive – perhaps the book really did belong to Leonardo – he certainly had read it – & some pupil thought to enhance its value.”

Above Fig. 3. The young Kenneth Clark (then twenty-seven years old) displayed an admirable “eye” by spotting a fraud on sight some eighty years ahead of the pack. Is it better for a connoisseur to see but not speak than it is not to see at all? Undoubtedly, it is. Would Clark have enjoyed his meteoric rise had he humiliated the mighty and exposed the big-time fraudsters of his day? (That question might be taken as self-answering.) If Clark bided his time on Berenson, eventually he delivered an unforgiving former-insider’s repudiation in 1977 by chronicling how Berenson had “sat on a pinnacle of corruption [and] for almost forty years after 1900… [done] practically nothing except authenticate pictures”
PRETTY – AND NOT SO PRETTY – WOMEN
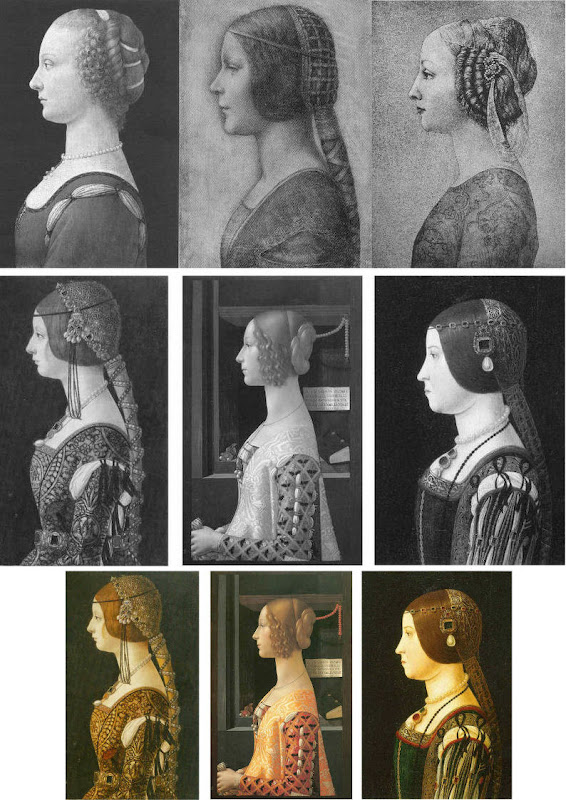

Above, Fig. 4. In the middle and bottom rows we see three bona fide works of the female profile type – respectively:
Portrait of Bianca Maria Sforza, c. 1493, by Ambrogio de Predis, The National Gallery of Art, Washington;
Domenico Ghirlandaio’s 1488-1490 Giovanna degli Albizzi Tornabuoni, Museo Thyssen-Bornemisza, Madrid; and,
a portrait of Beatrice d’Este tentatively attributed by Kemp to Ambrogio da Predis.
The differences between this trio and the works in the top row are pronounced and eloquent. The secure works are highly individuated and immensely richer in their effects. Collectively, they do not constitute an inadvertent suite. Individually, they are greatly more various compositionally. Collectively, they are markedly richer in jewellery and ostentatiously sumptuous costumes. The distinctive physiognomies of their subjects derive from living persons, not from other art or photographs of other art. Flattery and loving attention are channelled more into the costume and bling than into the facial features. In every respect the opposite is the case in the top row where prettiness has been held at a premium with an eye on the modern photographically-informed market.
LEONARDO BREAKS THE MOULD
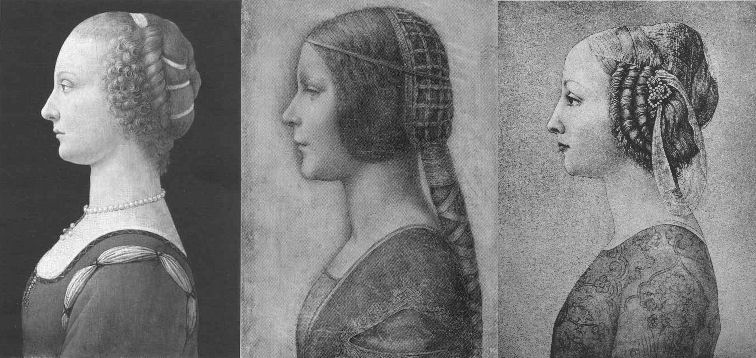
Above, Fig. 5: As mentioned, “La Bella Principessa” and her two companions are of a piece, and of a type never followed by Leonardo whose female portraits (see below) pioneered an unprecedentedly complex and sophisticated evocation of real, sculpturally palpable women in tangible spaces or landscapes. To include the figurally impoverished and stylistically anachronistic “La Bella Principessa” in Leonardo’s oeuvre would disjunct his revolutionary arc of insights and innovations in portraiture. Such inescapably disruptive consequences have been ceded tacitly by Kemp, “La Bella Principessa’s” principle defender – some say advocate. In “La Bella Principessa ~ The Story of the New Masterpiece by Leonardo da Vinci” (Kemp’s 2010 book jointly written with Pascal Cotte of Lumiere Technology and including chapters by the drawings scholar Nicholas Turner and the recently discredited fingerpints expert Peter Paul Biro), Kemp converts an intractable problem into an asset by begging the essential question. That is, he underwrites “La Bella’s” credibility on an assertion that “Any important new work, to establish itself, must significantly affect the totality of Leonardo’s surviving legacy over the longer term.” Without question, the de-stabilising inclusion of “La Bella Principessa” would produce knock-on effects, but arguing backwards from that predictable disturbance to some endorsement of its source is patently unsound methodologically – the inclusion of any atypical work, whether bona fide or forged, into an oeuvre would affect its “legacy”.
LEONARDO’S ACCOMPLISHMENTS
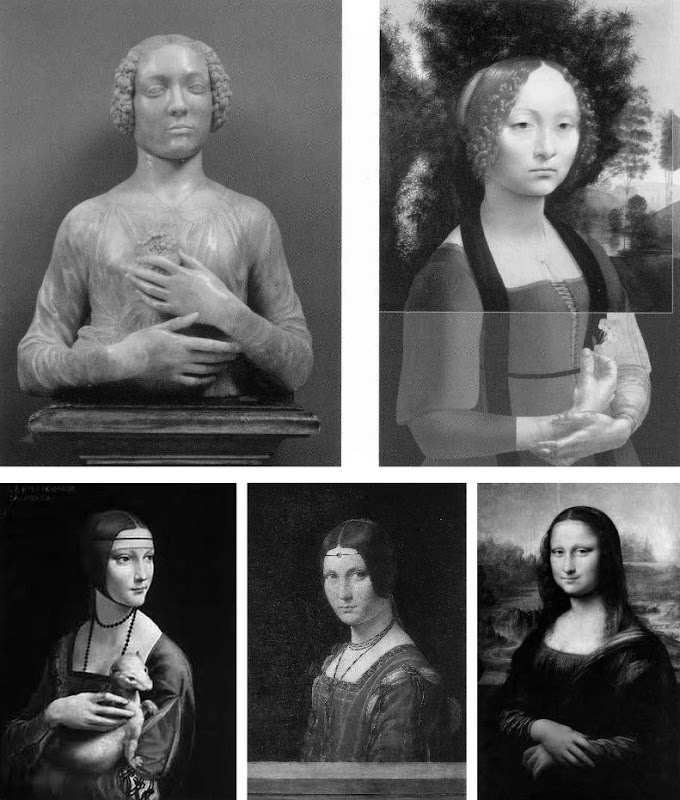

Above, top, Fig. 6: Left, Andrea del Verrocchio’s Lady with a Bunch of Flowers of c. 1475; and (right) Leonardo’s (hypothetically extended) Ginevra de’ Benci of c. 1474-1478.
Above, Fig. 7: Left, Leonardo’s The Lady With an Ermine of about 1489-90; centre, Leonardo’s La Belle Ferronnière of about 1495-96; right, Leonardo’s Mona Lisa (La Giaconda) of about 1503-06 onwards.
In the group above we see extraordinary development in Leonardo’s portraits of women over the last quarter of the fifteenth century as he strove to incorporate the entirety of sculptural, plastic, figural knowledge, and to surpass it by making it dance to an artistically purposive tune liberated from the happenstance, arbitrary lights of nature on which sculpture then necessarily depended. Some have attributed the Bargello sculpture, the Lady with a Bunch of Flowers, to Leonardo on the grounds that its subject was Ginevra de’ Benci, the subject of Leonardo’s painting. Others have seen Leonardo’s authorship of it in the beauty of the hands. In Leonardo da Vinci and the Art of Sculpture, 2010, Gary M. Radke holds that the two works show differences that emerged in the mid-1470s between the two artists. Against this, it has been suggested that the painting might originally have borne a closer relationship to the sculpture with a possible inclusion of hands in a fuller length treatment. A study of hands by Leonardo was incorporated in a hypothetical and digitally realised extension of the painting by David Alan Brown (Virtue and Beauty, 2001, p. 143). Frank Zollner sees the painting as marking the point (1478-1480) at which Leonardo broke away from “the profile view traditionally employed in Florence for portraits of women” in favour of the three-quarters view in order to impart “a pyschological dimension to his sitter – something that would become the hallmark of Renaissance portraiture”. Which is all to say that Leonardo had broken away from the profile convention some sixteen to eighteen years before, on Kemp’s hypothesis, he made a solitary and exceptional “return” to it.
Speaking of the reconstruction of Leonardo’s Ginevra de’ Benci painting, Brown writes:
“Ginevra’s portrait, the lower part of which was cut down after suffering some damage, may have included hands. A drawing of hands by Leonardo at Windsor Castle, assuming it is a preliminary study, aids in reconstructing the original format of the picture. As reconstructed, Leonardo’s portrait may be seen to have broken with the long-standing Florentine convention of portraying women in bust-length profile. In seeking an alternative to the static profile, Leonardo, like Botticelli, seems to have turned to Verrocchio’s Lady with a Bunch of Flowers in the Bargello, Florence. Because of the sitter’s beautiful hands which mark an advance over the earlier head-and-shoulders type of sculpted bust, the marble has even been attributed to Leonardo. But the highly innovative conception of the half-length portrait bust is surely Verrocchio’s achievement. What young Leonardo did was to was to translate this sculptural protype into a pictorial context, placing his sitter into a watery landscape shrouded in a bluish haze…”
A CASE CONSPICUOUSLY NOT MADE
For the owner and the art historical proponents of “La Bella Principessa”, the very chronology of Leonardo’s female portraits constitutes an obstacle. Given Leonardo’s famous eschewal of strict profile depictions of women, the onus is on those who would include “La Bella Principessa” (- albeit as a solitary and exceptional stylistic regression that was undertaken without ever attracting attention or comment) to make a double case.
First, they must show how and where “La Bella Principessa” might plausibly have fitted within the trajectory of Leonardo’s accepted works. Second, they must demonstrate by comparative visual means that “La Bella Principessa” is the artistic equal of the chronologically adjacent works within the oeuvre. Kemp has proposed the precise date of 1495-96 for the execution of “La Bella Principessa” but, conspicuously, has not presented direct, side-by-side visual comparisons with Leonardo’s paintings. Instead of comparing “La Bella Principessa” of 1495-6 directly with Leonardo’s La Belle Ferronnière of about 1495-6, Kemp writes:
“If the subject of Leonardo’s drawing is Bianca, it is likely to date from 1495-6. In style, it seems at first sight to belong with his earlier works rather than to the period of the Last Supper. However, Leonardo was a master of adapting style to subject. Just as his handwriting took on an earlier cast when he needed to adopt a formal script, so his drawing style could have reverted to a meticulous formality, appropriate for a precious set-piece portrait on vellum of a Sforza princess.”
“If”? “Could have”? “At first sight”? The pro-attribution literature is bedecked with daisy-chains of such tendentious and weasel words and terms. With which earlier works is “La Bella Pricipessa” deemed to be artistically comparable or compatible? With the Ginevra de’ Benci of c. 1474-1478? With The Lady With an Ermine of about 1489-90? Never mind the red herrings of handwriting and the giant, near-obliterated historical figures of the Last Supper, what of the relationship with Leonardo’s (supposedly) absolutely contemporaneous La Belle Ferronnière of 1495-96? (On this last we volunteer a pair of comparisons below.)
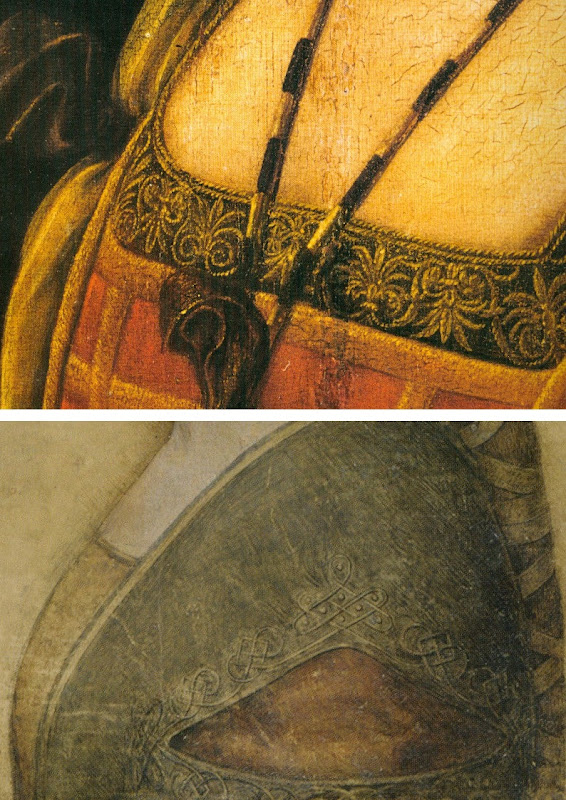


Above, Top, Fig. 8: Leonardo’s La Belle Ferronnière, left, and the “La Bella Principessa”.
Above, Fig. 9: Details of Leonardo’s La Belle Ferronnière, left, and the “La Bella Principessa”.
Kemp insists: “The Lady in profile [“La Bella Principessa”] is an important addition to Leonardo’s canon. It shows him utilizing a medium that has not previously been observed in his oeuvre…It testifies to his spectacular explosion and development of novel media, tackling each commission as a fresh technical challenge. It enriches our insights into his role at the Milanese court, most notably in his depiction of the Sforza ‘ladies’ – whether family members or mistresses. Above all, it is a work of extraordinary beauty.”
Even if we were to assume that for some reason Leonardo had opted to “revert” in 1496 to a type he had never employed, what might explain a pronounced indifference in “La Bella Principessa” to the detailed depiction of the “stuffs” of costume with which the artist was simultaneously engaged in La Belle Ferronnière? Given that Leonardo clearly appreciated and celebrated the fact that courtly costume required sleeves to be made as independent garments held decorously in place by ribbon bows so as to permit undergarments to peep through; and, given that Leonardo lovingly depicted not only the varying thicknesses of the costume materials but every individual twist in the threads of the elaborately embroidered band in La Belle Ferronnière, how could he possibly – when working for same ducal master, at the same time – have been so negligent and indifferent in the execution of “La Bella Principessa’s” costume? Kemp acknowledges and offers excuse for the distinct poverty of the costume: “It may be that the restraint of her costume and lack of celebratory jewellery indicates that the portrait was destined for a memorial rather than a matrimonial volume.” In so-saying, he jumps out of one frying pan into another.
If “La Bella Principessa” was made after Bianca Sforza’s death, from whence did the likeness derive? One reason why Kemp settled on Bianca as the preferred candidate subject for “La Bella Principessa” was that while (disqualifying) likenesses of the other Sforza princesses existed, none survives for her – she is an image-free figure. Kemp offers no indication of a possible means for Leonardo’s (hypothesised) post-death conjuring of Bianca’s supposed likeness other than to claim that “Leonardo has evoked the sitter’s living presence with an uncanny sense of vitality.” This again begs the crucial question and fails to consider any alternative explanations for the image’s qualities. (We will be showing how the profile of “La Bella Principessa” could well have been a “portmanteau” composite image assembled from one particular work of Leonardo’s and from that of another, unrelated painter.)
The most strikingly “Leonardesque” feature on the costume of “La Bella Principessa” – the knot patterning around the (implausible) triangular slash in the outer garment – is a source of further concern and constitutes evidence of forgery. First, the motif on which much effort will have been expended, is brutally cropped along the bottom edge of the sheet, as if by a careless designer laying a photograph into a book. Why would any Renaissance artist, let alone Leonardo, design a complicated feature so as to “run it off the page”? Further, the illusion of form (created by lights and shades) in the patterning is feeble in the extreme for Leonardo – as when compared with his treament of relief seen in the above embroidered passage in La Belle Ferronnière, for example. Leonardo probably better understood than any artist in history the vital connection between a thing made and a thing depicted. He took bodies and organs apart to understand their construction and he sought to create mental models that would make the otherwise terrifyingly arbitrary and capricious forces of nature graspable if not checkable. Most seriously of all, as our colleague Kasia Pisarek has noted and reported, while the patterning present on “La Bella Principessa” matches none found in any work of Leonardo’s, it more closely matches that found in a carved marble bust by Gian Cristoforo Romano in the Louvre – see “La Bella Principessa – Arguments against the Attribution to Leonardo”, Kasia Pisarek, artibus et historiae, no. 71, 2015. (To receive a pdf of Dr Pisarek’s article please write to: news.artwatchuk@gmail.com )
Michael Daley, 24 February 2012.
In Parts II and III we examine: the provenance of “La Bella Principessa” and the work’s problematic emergence from within the circle of Bernard Berenson; the claim by the forger Shaun Greenhalgh to have produced “La Bella Principessa” in Britain in the 1970s; the spurious “left-handed-ness” of “La Bella Principessa” and the low quality of, and the means by which the drawing was made…
Connoisseurship in Action and in Peril
“WHEN THE FIRST catalogue of the Ashmolean Museum’s Sculpture collection (in three volumes) was undertaken more than twenty-five years ago, the present author decided to exclude works made before 1540…”
“…The decision was partly determined by the quantity of the material but also in recognition of the special attention that the finest of the small bronzes given and bequeathed by Charles Drury Fortnum deserved. It is indeed because of these that the Ashmolean’s sculpture collection is the most important in the United Kingdom after that of the Victoria and Albert Museum, London…”

Above and below: The ‘Fortnum Venus’, attributed to Francesco Francia or his circle. c. 1500-05. Bronze, 26.1 cm. high. (Ashmolean Museum, Oxford).


Above, detail of St Jerome, by Cosimo Tura. c.1470. Panel, 101 by 57.2 cm. (National Gallery, London).
“The first of Jeremy Warren’s three volumes under review here includes these very figures. One of them is the
exquisite Venus associated with the Bolognese painter and goldsmith Francesco Francia (cat. No.20). It is one of the earliest responses in the Renaissance to the antique female nude, and perhaps belonged to a narrative group for, as her drapery falls, her hand is cupped as if to receive the apple from Paris…”
“…In conclusion it should be noted that the cataloguing of the permanent collection is not now often considered an essential part of the curator’s job. Any museum director who is chiefly an impresario is inevitably attentive to fashionable ideas and taste, whereas the cataloguer of a permanent collection is bound to give his or her attention to neglected artists, and to works by artists in which they are not initially interested, but which beg the question as to why the appealed to their predecessors – collectors, scholars and curators long deceased. This provides an antidote not only to the narrow outlook of the popular exhibition machine, but to that of academic institutions where scholars, having achieved promotion by imitating their seniors, are obliged to compete in appealing to the young consumers upon
whose favour the prosperity of the institution depends.”
~ NICHOLAS PENNY: “Sculpture in the Ashmolean”, Burlington Magazine, January 2016. A review of Catalogue: Medieval and Renaissance Sculpture. A Catalogue of the Collection in the Ashmolean Museum, by JEREMY WARREN, 3 vols., continuously paginated, 1188 pp. incl. numerous col. + b. & w. ills. (Ashmolean Publications, Oxford, 2014, £395.)
“FIVE NEW YEAR BLOCKBUSTERS
“It’s a new dawn, it’s a new day… what new art exhibitions will make you feel good? Read our list of the top five shows opening this season to get inspired.
“Discover the enduring impact of Botticelli and Delacroix on the art world and prepare to be star struck at exhibitions celebrating 100 years of British Vogue and the incredible beauty of our Solar System.
“Need a second opinion? Watch art historian Jacky Klein’s guide to the season’s unmissable art exhibitions.”
~ THE ART FUND, a mailing, 8 December 2016.
PERMANENT EVOLUTION – A JOB FOR LIFE
“Museums have become places where we take part in social as well as learning activity. It is easy to be cynical about
the impact of the café, restaurant or shop spaces on the culture and character of museums, but such facilities have made museums less daunting, more welcoming and more open to general visitors. However, such [democratization] needs to go deeper than the provision of opportunities to purchase or to consume.”
NICHOLAS SEROTA, the director (- since 1988) of the Tate, at the Leeum Samsung Museum of Art in Seoul.




HOW ART HISTORIANS CAN BE FOOLED BY CONDITION
“One of the most influential books in the twentieth-century art history was Erwin Panofsky’s Studies in Iconology. In this seminal work, the very latest German approaches and method were presented to an Anglo-Saxon audience for the first time. One of the dazzlingly learned chapters was devoted to the figure of Cupid wearing a blindfold, and Panofsky showed how this theme could be traced back to the writings of the medieval moralists. For thinkers of this Christian stamp, lovers were metaphorically blind, since they were ‘without judgement or discrimination and guided by mere passion’. But later, in the Renaissance, ‘moralists and and humanists with Platonizing leanings’ contrasted the figure of the blindfold Cupid with another kind of…”
~ PAUL TAYLOR. Introduction, CONDITION The Ageing of Art, Paul Holberton Publishing, 2016. ISBN 978 1 907372 79 7
Illustration: Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres, The Composer Luigi Cherubini with the Muse of Lyric Poetry, 1842, detail.

“…Although Bode was extremely learned in many branches of art history and had his information always ready – he had little need of written notes and photographs – he was no scholar in the true sense. He was more fond of action than reflection, and was far from having a just and objective mind. Moreover, the distracting practice of uninterrupted daily work hindered a comprehensive synthesis of realization. The deepest motive of the scholar, namely, disinterested love of truth, could not function productively in a nature always resolutely aiming for effectiveness and visible results. Bode was utterly unphilosophical, he considered no affair from more than one side. He saw black or white, good or bad, advantageous or inimical; he knew no intermediary steps. To forsee obstacles, to fear, to guard against them was not his way. Consequently he became angry as soon as he encountered opposition. He made more mistakes by acting than by failing to act. He was a hunter, not an angler.”
~ Max J. Friedländer – Reminiscences and Reflections, Edited from the literary remains and with a foreword by
Rudolf M. Heilbrunn, 1969, New York.

“…Anyway, getting back to the book that was sent to me, its title was rather grand and pompous: La bella Principessa – the beautiful princess. Or, as I knew her, ‘Bossy Sally from the Co-op’. I’m a bit unsure of how to talk of this because the book was written by an eminent Oxford professor and must have been quite an effort. I don’t want to ruffle any feathers or cause problems but I nearly swallowed my tongue on reading its supposed value – £150 million! It would be crazy for a public body to pay such a sum. So I feel the need to say something about it.
“The drawing is thought by some to be a work by Leonardo da Vinci, but it does divide opinion and it wasn’t included in the National Gallery’s Leonardo show of 2011, a show which I thought was really well done except for it being staged ‘underground’ in the Sainsbury Wing basement…
“I drew this picture in 1978…It was done on vellum, quite a large piece to find unfolded and without crease lines. I did it on vellum because at that time I couldn’t make old paper yet…The first thing I had to do was sand off the writing with 600-grit wet and dry paper. That done, it looked too new for anything old to look right on it, so I turned it over and did the drawing on the other side. That is why the drawing is done on the hair side of the vellum instead of the much-preferred ‘flesh side’. The texture of the sanding should still seen on its reverse.
“As I said, the face is of 1970s vintage, and I think that shows in the drawing…The drawings of Leonardo and Holbein especially have always impressed me with their fineness of line and detail, and in my view they must have been done under some magnification…The vellum is mounted on an oak board…before drawing on it, the vellum was stuck to the backboard with cabinet maker’s pearl glue, so it needed to be under a weighted press for a while to allow the glue to go off without ‘cockling’ the vellum. ‘Cockling’ is the effect you see on paper when you try to paint a watercolour without soaking and stretching the paper first. On vellum the dampness looks like blisters or a cockle bed on the shore. It’s caused by the water content of the glue, so the thing needs to be under a heavy press to dry it flat.
“After a bit of experimentation, and just to prove a point to myself, I lightly traced the drawing I’d invented onto the vellum (I’m sure the graphite can still be detected) and started to draw the image in hard black chalk – carbon black in gum arabic – using a pair of jeweller’s magnifying glasses. It took some time to get used to working like that, and I had to go to back to practising on papper for a while so as not to bugger things up…
“It was done in just three colours – black white and red – all earth pigments based in gum arabic, with the carbon black mostly gone over with oak gall ink. To be a bit Leonardo-like or even Holbein-like – they were both left-handers – I put in a left-hander’s slant to it…The Leonardo book [“La Bella Principessa ~ The Story of the New Masterpiece by Leonardo da Vinci”, By Martin Kemp and Pascal Cotte, with contributions by Claudio Strinati, Nicholas Turner and Peter Paul Biro] seems to put great store by the apparent leftyness of the drawing, but it can be shown up very easily. With the face on the vellum facing left, just turn the drawing clockwise to face her skyward, and hatch strokes from profile outwards in the normal manner…Incidentally, the book points out a palm print on the neck area, just the spot a right-hander doing an impersonation of a left-hander might rest their hand whilst doing the background hatching.
“Although I am no Oxford professor, I could list umpteen reasons for not thinking this drawing to be by leonardo…
The book mentions several holes on one margin as evidence that it has been bound into a volume, and also mentions some later ‘restoration’. I did not do these things, and don’t know who did, or where it went on its later travels. Looking closely at the picture in the book, it looks to have had the left margin peeled back an inch or so and has been restuck, not very well, especially at the bottom left. Could this be from when the left margin was pierced and roughly re-cut by someone else?
“I sold it for less than the effort that went into it to a dealer in Harrogate in late 1978 – not as a fake, or by ever claiming it was something it wasn’t. I can’t really say any more on it. At least it may now be known for what it is.”
~ SHAUN GREENHALGH – A Forger’s Tale, Published by ZCZ Editions in 2015
In the past it was customary for scholars to advance claims of attribution for particular works of art in scholarly journals and then wait to see how peers and colleagues responded to their evidence and arguments. Increasingly, we are seeing co-ordinated promotional campaigns of advocacy by players and owners who eschew venues of debate and sometimes denigrate sceptics and opponents. We invited two of the leading advocates of “La Bella Principessa’s” Leonardo’s authorship – Martin Kemp and Nicholas Turner – to speak at our recent conference on connoisseurship. Both declined. Neither our post of January 2014 (“Art’s Toxic Assets and a Crisis of Connoisseurship ~ Part II: Paper – sometimes photographic – Fakes and the Demise of the Educated Eye”) nor our colleague Kasia Pisarek’s article “La Bella Principessa: Arguments against the attribution to Leonardo” that was published in the June 2015 issue of the scholarly journal artibus et historiae have been challenged in print.
(For a pdf copy of Kasia Pisarek’s article, please write to: news.artwatchuk@gmail.com. For our conference, see Art, Law and Crises of Connoisseurship and Recap of Art, Law and Crisis of Connoisseurship Conference.)

The da Vinci Detective: Art Historian Martin Kemp on Rediscovering Leonardo’s Tragic Portrait of a Renaissance Princess – an ARTINFO Interview by Andrew M. Goldstein, 17 October 2011. Extracts:
…[Andrew Goldstein] “They weren’t the only ones to differ on the attribution of the painting, and when you first announced that you believed it to be a Leonardo, a lot of people disagreed. One museum director even told the Telegraph’s Richard Dorment, anonymously, that it was a “screaming 20th century fake, and not even close to Leonardo himself.” Has there been any reversal since then?
[Martin Kemp] “I don’t know who this anonymous person was, but we carbon-dated the parchment and that eliminates it from being a screaming modern forgery. If it were a forgery, it used things that we’ve only recently discovered about Leonardo’s technique in the last 20, 30 years. The fact that it was owned by Giannino Marchig takes it outside the period when it could be a forgery, knowing what we know now, so that’s not an option. The ultra-violet turns up retouching, and it’s very clear it has been heavily restored, but most objects 500 years old, including the “Salvator Mundi”, which is the new picture being shown in the National Gallery.
[…] “One thing that critics of your ‘Principessa’ attribution tend to bring up is the involvement in your research of Peter Paul Biro, a fingerprint expert whose credibility was questioned. What is your opinion of him?
“Well, Biro I knew of as someone who’d specialized in fingerprints and paintings, so we asked him to look at the fingerprint that is in the upper left side of the ‘Bella Principessa.’ I had data on finger prints and finger marks in other Leonardo paintings, and he said one of these matched – not astoundingly, because it’s just the tip of a finger, and one doesn’t rely on fingerprints on vellum. It wouldn’t convict anybody in a court of law. You need more than that. So he did a limited job here, and we didn’t depend too much on that evidence. The press liked it, of course because it was cops and robbers stuff.
“I would not now probably say much about it at all, because on reflection I don’t think we have an adequate reference bank of Leonardo fingerprints. I’ve talked to fingerprint specialists, and they typically require a full set of reference prints. We don’t have that for Leonardo. My sense is – and this is Pascal’s sense, too – that it’s probably premature, given what we know about Leonardo’s fingerprints, to come up with matches at all. But the job Biro did was perfectly straightforward. There were no grounds for dishonesty. Peter Paul Biro is suing the New Yorker*, but I can’t comment at all upon the court case because that’s about things that I know nothing about, so it’d be totally improper. But he did work for us, which I now, let’s say, place less reliance on, simply because, on reflection, I think the fingerprint evidence is rather slippery.
“Because of the work you have done to bring the ‘Principessa’ into the fold of acknowledged Leonardos, some say you have crossed from the realm of scholarship to something more like advocacy. How do you explain your passion for the portrait?
“I would say that one of the differences between being a historian of art and being a scientist, as I was trained, is that you’re dealing with objects that are deliberately communicating with something other than just our intellect. So, for me, it’s not a dry process. You begin with the feeling it’s special, and if it stands up to the research, you end with the feeling that it’s special, and I make no apology for that. I’ve been critized as acting as an advocate for it, but if I’m writing, as I am in ‘Christ to Coke’, about the ‘Mona Lisa’, I’m an advocate for that too, because it’s a miraculous picture. Also, when I’m writing about the Coke bottle, I’m not an advocate for Coke as a drink. I hate it. But it’s one of the all-time great
bits of product design and I’m happy to say that.”
“*THE MARK OF A MASTERPIECE” by David Grann, The New Yorker, 12 July 2010 ~ Extracts:
[1] “But he [Martin Kemp] also relies on a more primal force. ‘The initial thing is just that immediate reaction, as when we’re recognizing the face of a friend in a crowd,’ he explains. ‘You can go on later and say “I recognize her face because the eyebrows are like this, and that is the right colour of her hair,” but, in effect, we don’t do it like that. It’s
the totality of the thing. It feels instantaneous.'”
[2] “Moreover, according to [the curator of Drawings at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, Carmen] Bambach, there was a more profound problem: after studying an image of the drawing [La Bella Principessa] – the same costume, the same features, the same strokes that Kemp examined – she had her own strong intuition. ‘It does not look like a Leonardo’, she said.”
[3] “When such a schism emerges among the most respected connoisseurs, a painting is often cast into purgatory. But in January, 2009, Kemp turned to a Canadian forensic art expert named Peter Paul Biro who, during the past several years has pioneered a radical new approach to authenticating pictures. He does not merely try to detect the artist’s invisible hand; he scours a painting for the artist’s fingerprints, impressed in the paint on the canvas. Treating each painting as a crime scene, in which an artist has left behind traces of evidence, Biro has tried to render objective what has historically been subjective. In the process he has shaken the priesthood of connoisseurship, raising questions about the nature of art, about the commodification of aesthetic beauty, about the very legitimacy of the art world.Biro’s research seems to confirm what many people have long suspected: that the system of authenticating art works can be arbitrary and, at times, a fraud.”
[4] “Biro asserted that he had uncovered the painting’s ‘forensic provenance,’ telling a reporter, ‘The science of fingerprint identification is a true science. There are no gray areas.’ Having developed what he advertised as a ‘rigorous methodology’ that followed ‘accepted police standards,’ he began to devote part of the family business to authenticating works of art with fingerprints—or, as he liked to say, to ‘placing an artist at the scene of the creation of a work.'”
[5] “But the International Foundation for Art Research, a nonprofit organization that is the primary authenticator of Pollock’s works, balked, saying that Biro’s method was not yet ‘universally’ accepted.
[6] “In 2009, Biro and Nicholas Eastaugh, a scientist known for his expertise on pigments, formed a company, Art Access and Research, which analyzes and authenticates paintings. Biro is its director of forensic studies. Clients include museums, private galleries, corporations, dealers, and major auction houses such as Sotheby’s. Biro was also enlisted by the Pigmentum Project, which is affiliated with Oxford University.”
[7] “Biro told me that the divide between connoisseurs and scientists was finally eroding. The best demonstration of this change, he added, was the fact that he had been commissioned to examine ‘La Bella Principessa’ and, possibly, help make one of the greatest discoveries in the history of art.”
[8] “After he first revealed his findings, last October, a prominent dealer estimated that the drawing [‘La Bella Principessa’] could be worth a hundred and fifty million dollars. (The unnamed ‘lady’ who had sold it at Christie’s for less than twenty-two thousand dollars came forward and identified herself as Jeanne Marchig, a Swedish animal-rights activist. Citing, among other things, the fingerprint evidence, she sued the auction house for ‘negligence’ and ‘breach of warranty’ for failing to attribute the drawing correctly.)”
[9] “Ellen Landau, the art historian, said that she was ‘absolutely convinced’ that the paintings were by Pollock. Biro was sent a photograph of a fingerprint impressed on the front of one picture. He identified six characteristics that corresponded with the fingerprint on the paint can in Pollock’s studio—strong evidence that the work was by Pollock. But, as more and more connoisseurs weighed in, they noticed patterns that seemed at odds with Pollock’s style. Meanwhile, in sixteen of twenty art works submitted for analysis, forensic scientists discovered pigments that were not patented until after Pollock’s death, in 1956. At a symposium three years ago, Pollock experts all but ruled out the pictures. Ronald D. Spencer, a lawyer who represents the Pollock-Krasner Foundation, told me, ‘Biro can find all the fingerprints he wants. But, in terms of the marketplace, the Matter paintings are done. They are finished.'”
[10] “Reporters work, in many ways, like authenticators. We encounter people, form intuitions about them, and then attempt to verify these impressions. I began to review Biro’s story; I spoke again with people I had already interviewed, and tracked down other associates. A woman who had once known him well told me, ‘Look deeper into his past. Look at his family business.’ As I probed further, I discovered an underpainting that I had never imagined.”
[11] “During the eighties and early nineties, more than a dozen civil lawsuits had been filed against Peter Paul Biro, his brother, his father, or their art businesses. Many of them stemmed from unpaid creditors. An owner of a picture-frame company alleged that the Biros had issued checks that bounced and had operated ‘under the cover’ of defunct companies ‘with the clear aim of confusing their creditors.’ (The matter was settled out of court.) As I sifted through the files, I found other cases that raised fundamental questions about Peter Paul Biro’s work as a restorer and an art dealer.
[12] “Biro refused, multiple times, to divulge where he had obtained either of the paintings. According to the Wises, Biro insisted that the person who sold him the paintings was in Europe, and that it was impossible to contact him.
[13] “Sand sought proof of a financial transaction—a check or a credit-card payment—between Biro and Pap. Biro, however, said that he had obtained them in exchange for two musical instruments: a Steinway piano and a cello.
[14] “Sand was incredulous: ‘Is Mr. Pap a music dealer or is he an art dealer?’ After Biro could not recall where he had originally purchased the cello, Sand suddenly asked him, ‘You ever been convicted of a criminal offense, sir?’
‘No.’
‘You are certain of that?’
‘Yes,’ Biro said.”
[15] “Throughout the trial, the Biros and their attorneys maintained that the two paintings sold to the Wises were authentic, but to make their case they presented an art expert who was not a specialist on Roberts, or even on Canadian art. On September 3, 1986, the court found in favor of the Wises, and ordered Peter Paul and Geza Biro to pay them the seventeen thousand dollars they had spent on the pictures, as well as interest.”
[16] “Lawsuits had piled up against Peter Paul Biro and his family business. In two instances, there were allegations that art works had vanished under mysterious circumstances while in the care of Peter Paul. In one of the cases, Serge Joyal, who is now a senator in Canada, told me that he left a nineteenth-century drawing with the Biros to be restored. Before he could pick it up, Peter Paul notified him that it had been stolen from his car and that there was no insurance. Biro, however, never filed a police report, and Joyal says that Biro pleaded with him to wait before going to the authorities. During their conversations, Joyal says, Peter Paul acted evasive and suspicious, and Joyal became convinced that Biro was lying about the theft. As Joyal put it, ‘There was something fishy.’ Though Peter Paul said that there was nothing ‘suspect’ about his behavior, and that he should not be held liable, the court awarded Joyal seven thousand dollars, plus interest.”
[17] “Within Montreal’s small art world, there were whispers about Peter Paul Biro and his father. But the lawsuits appear to have attracted virtually no public attention. In 1993, Peter Paul Biro filed for bankruptcy, and he never paid many of the judgments against him, including what he owed the Wises and Joyal. Lipsz’s lawyer said of Biro, ‘He oiled his way out of that whole thing. . . . He got away scot-free.'”
[18] “Biro was part of an effort to launch a venture named Provenance, which would provide, as he put it, the ‘clever strategy’ necessary to sell ‘orphaned’ paintings for tens of millions of dollars. According to a business prospectus, marked confidential, Provenance would acquire art works that had been forensically validated by Biro and several colleagues, and sell them in a gallery in New York City. The company chose a thumbprint for a logo.”
[19] “Provenance was cleverly tapping into the public’s desire to crack open the art world, offering the tantalizing dream that anyone could find a Pollock or a Leonardo or a Turner languishing in a basement or a thrift shop. The company combined the forensic triumphalism of ‘C.S.I.’ with the lottery ethos of ‘Antiques Roadshow.’ (An associate producer at ‘Roadshow’ had already sent Biro an e-mail about possibly doing a segment on the Parkers’ ‘unbelievable discovery.’)
[20] “Biro previously had been suspected of creating an investment scheme around a seemingly precious object, with the promise that it would eventually reap huge profits. In the late nineteen-nineties, he persuaded a Canadian financial adviser, Richard Lafferty, who is now dead, to invest in a venture to authenticate and sell a work purportedly by Raphael’s disciple Perino del Vaga. Three of Lafferty’s colleagues confirm the story, as do letters, memorandums, and other documents.”
[21] “By the fall of 2005, Ken Parker had begun to look into the people behind Provenance. It turned out that Tod Volpe, in the nineties, had defrauded his art clients, including Jack Nicholson, of nearly two million dollars, and had served two years in prison. Parker discovered that one of Volpe’s principal partners in Provenance was also an ex-con, who had done time for tax evasion and for running a drug-smuggling operation in the United States. (Volpe told me, ‘We all have skeletons in our past.’) Parker confronted Biro, who, in a subsequent e-mail, told Parker that he had ‘severed all communication with Volpe.’”
[22] “And only months after rescinding his request for money he asked the Parkers to fund another new project: a privately endowed department for him and a colleague at Oxford University. ‘Naturally it is 100% tax deductible,’ Biro wrote, in an e-mail. ‘Those who support the foundation of a bold and new department for us at Oxford will have their name on a plaque or have the department named after them such as “The Ken Parker Department for Forensic Art History.” Sounds cool?'”
[23] “When a forgery is exposed, people in the art world generally have the same reaction: how could anyone have ever been fooled by something so obviously phony, so artless? Few connoisseurs still think that Han van Meegeren’s paintings look at all like Vermeers, or even have any artistic value. Forgers usually succeed not because they are so talented but, rather, because they provide, at a moment in time, exactly what others desperately want to see. Conjurers as much as copyists, they fulfill a wish or a fantasy. And so the inconsistencies—crooked signatures, uncharacteristic brushstrokes—are ignored or explained away. “
[24] “In the case of ‘La Bella Principessa,’ Biro did not handle the drawing, and was sent multispectral images from another laboratory, which he then developed and enhanced. Martin Kemp, the Leonardo scholar, told me, ‘In terms of what Biro did for us, I have absolutely no problems with any potential ethical issues.’ He emphasized that his opinion of the drawing did not depend on the fingerprint evidence: ‘I’m entirely confident that it is by Leonardo.'”
[25] “A final verdict on whether ‘La Bella Principessa’ is genuine may not be reached for years, but more and more connoisseurs have voiced doubts. Skeptics express surprise that there is no apparent historical record for the drawing, given that Leonardo was one of Italy’s most famous painters during the Renaissance. They note that vellum lasts for centuries, and that it would be easy for a forger to obtain old sheets. Many of the critics share the view of the Met’s Carmen Bambach: it just doesn’t look like a Leonardo. ARTnews, which has reported on Wertheim’s findings, recently interviewed Klaus Albrecht Schröder, the director of the Albertina Museum, in Vienna. ‘No one is convinced it is a Leonardo,’ he said. David Ekserdjian, an expert on sixteenth-century Italian drawings, wrote in The Burlington Magazine that he ‘strongly suspects’ it is a ‘counterfeit.’ Other art critics have suggested that Kemp has succumbed to a fantasy.
[26] “Whereas Biro had once spoken of the absolute objectivity and infallibility of fingerprint analysis, he now sounded more like a connoisseur than like a scientist. ‘I’m trying to define, for example, what is the point that something becomes a matter of interpretation,’ he said. ‘In other words, where is that line? O.K., on the one hand, fingerprint practitioners state that fingerprint identification is a science. I’m more toward the other side, where I’m convinced by my own personal experience that it is very much like connoisseurship, because of . . . things I see they don’t.’”
[27] “I asked him whether he might have been wrong in suggesting that Leonardo had ever touched ‘La Bella Principessa.’ He looked up at the sky and said, ‘It’s possible. Yes.’”
In July 2011 ADWEEK reported that Biro had sued The New Yorker and David Grann for $2 million on twenty-four charges of false and malicious defamation – Forensic Art Expert Peter Paul Biro Sues New Yorker for Deformation. The action failed on every count (see “Art Authenticator Loses Defamation Suit Against The New Yorker“).
CODA: Faking A Picasso and a Provenance
In June last year, we and Martin Kemp were asked (separately) by the Daily Mail to comment on a claimed Picasso painting that supposedly had been found by an artist among his late mother’s belongings in an old suitcase in the loft – “Is this a long-lost Picasso? Painting that bears a strong resemblance to Cubist’s work is discovered rolled up in a battered suitcase that hasn’t been touched in 50 years” – the Mail reported:
“…Last month, a 1955 Picasso painting – Les Femmes d’Alger – broke auction records when it sold at Christie’s for a staggering £115 million.
“Art expert Michael Daley told MailOnline his first instinct was that the painting was not a Picasso. ‘The colours and all of that are right but I think there is too much incidental detail and not enough decisive interest or exploration. This is
all sharp edges and brown tones and what-have-you, but it doesn’t have the driving sense of Picasso getting at something, getting at a figure trying to see something about it. This is more decorative. It can be no more than an instinctive first impression, but to me it doesn’t look like a Picasso Cubist painting from that period.’
“Martin Kemp, emeritus professor of art history at Oxford University, was also skeptical. Prof Kemp said: ‘It’s pretty close to Picasso’s portrait of Daniel-Henry Kahnweiler, the dealer whom he painted in 1910 and is in the Art Institute of Chicago. This looks to be a relatively competent but not excellent near copy of it – the signature is very dodgy. Without doing a full art historical analysis – and I’m not a Picasso expert – I would say someone has made a variant of the Picasso portrait. Also the signature with the rounded S’s doesn’t seem to correspond to Picasso’s way of signing and thirdly the canvas doesn’t look quite right for Picasso of that period.
But I hope for the sake of the owner that I’m wrong.'”

On 6 July 2015 The Scotsman disclosed that the discovered ‘Picasso’ was a fake (“Picasso painting in Fife attic ‘a hoax’”). The faker, Dominic Currie, reportedly described his purported-Picasso (which had been about to be inspected by Christie’s) as “a piece of performance art [made] in order to raise awareness of the struggling artists in Scotland.” The fake is now being offered for sale on the website of a picture restoration business.
Michael Daley. 10 December 2016.
12 December 2016. Postscript: “Bode gave an opinion on art works from many fields, on Netherlandish painting of the seventeenth century, on Italian sculpture, Persian rugs, majolica, German wood sculpture, and many other things. His writings were for him always a means to an end, and were frequently controversial and advocatory. Almost always he judged correctly, and at the time he expressed them, his communications were of significance and infinitely enriched knowledge in many fields. But the tragic fate of the ‘connoisseur’ lies in the fact that yesterday’s new, strikingly accurate definitions are today’s common properties and banalities, that only the mistakes linger in the memory under the name of the originator.”
~ Max J. Friedländer on Wilhelm Bode – Reminiscences and Reflections.
